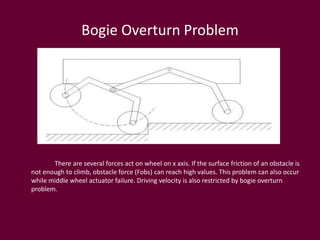
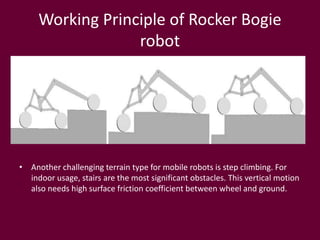
The document describes a rocker-bogie suspension mechanism for a rover robot. It discusses how mobile robots can be classified based on their locomotion, suspension, steering, and other properties. The rocker-bogie suspension allows a rover to traverse rough terrain by providing independent wheel movement and high ground clearance. Examples of past rover robots discussed include Lunakhod, NASA's Sample Return Rover, and the Mars Exploration Rovers. Applications mentioned include planetary exploration, operations in dangerous areas like nuclear plants, and potential future uses like indoor service robots.