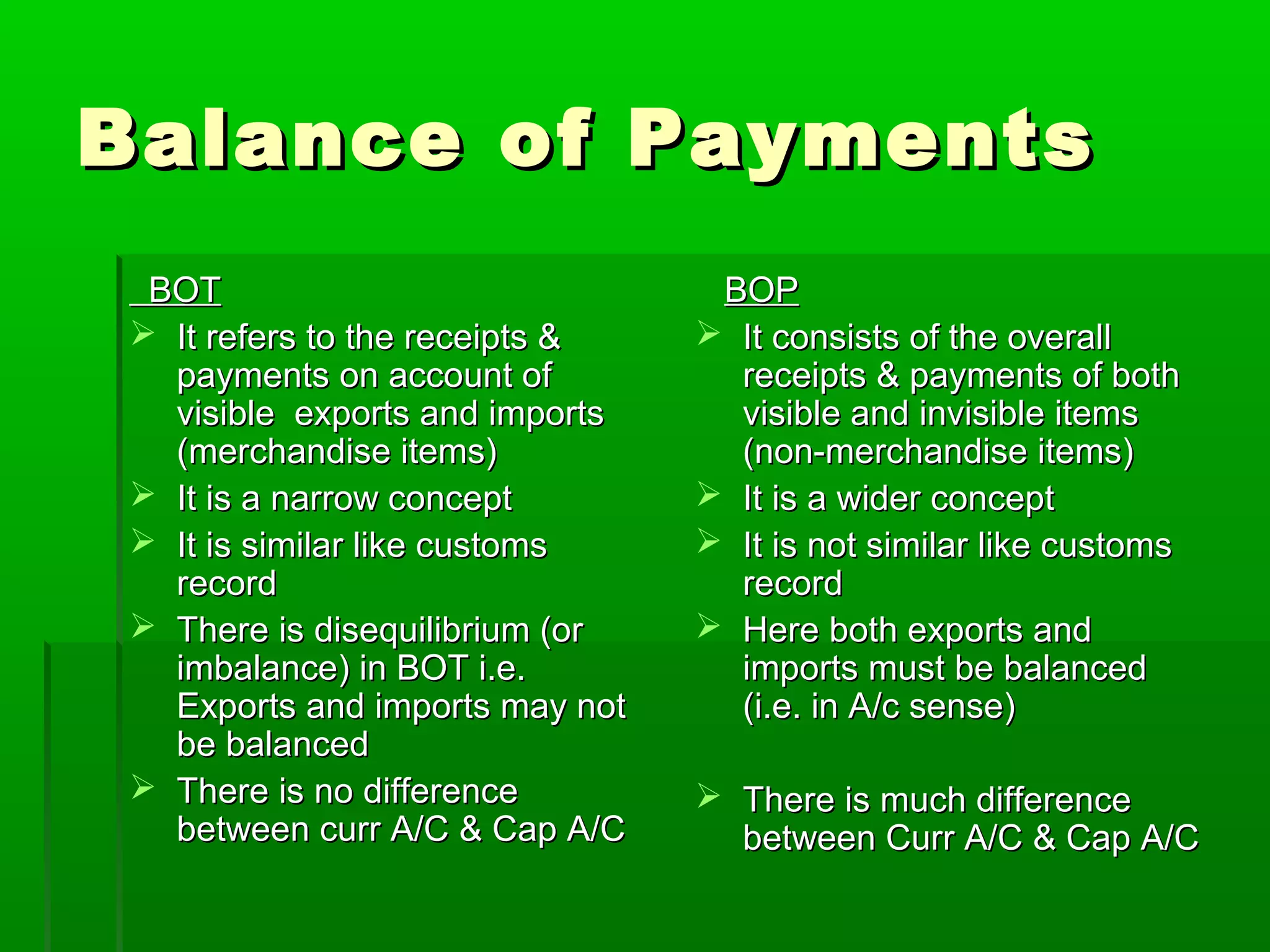
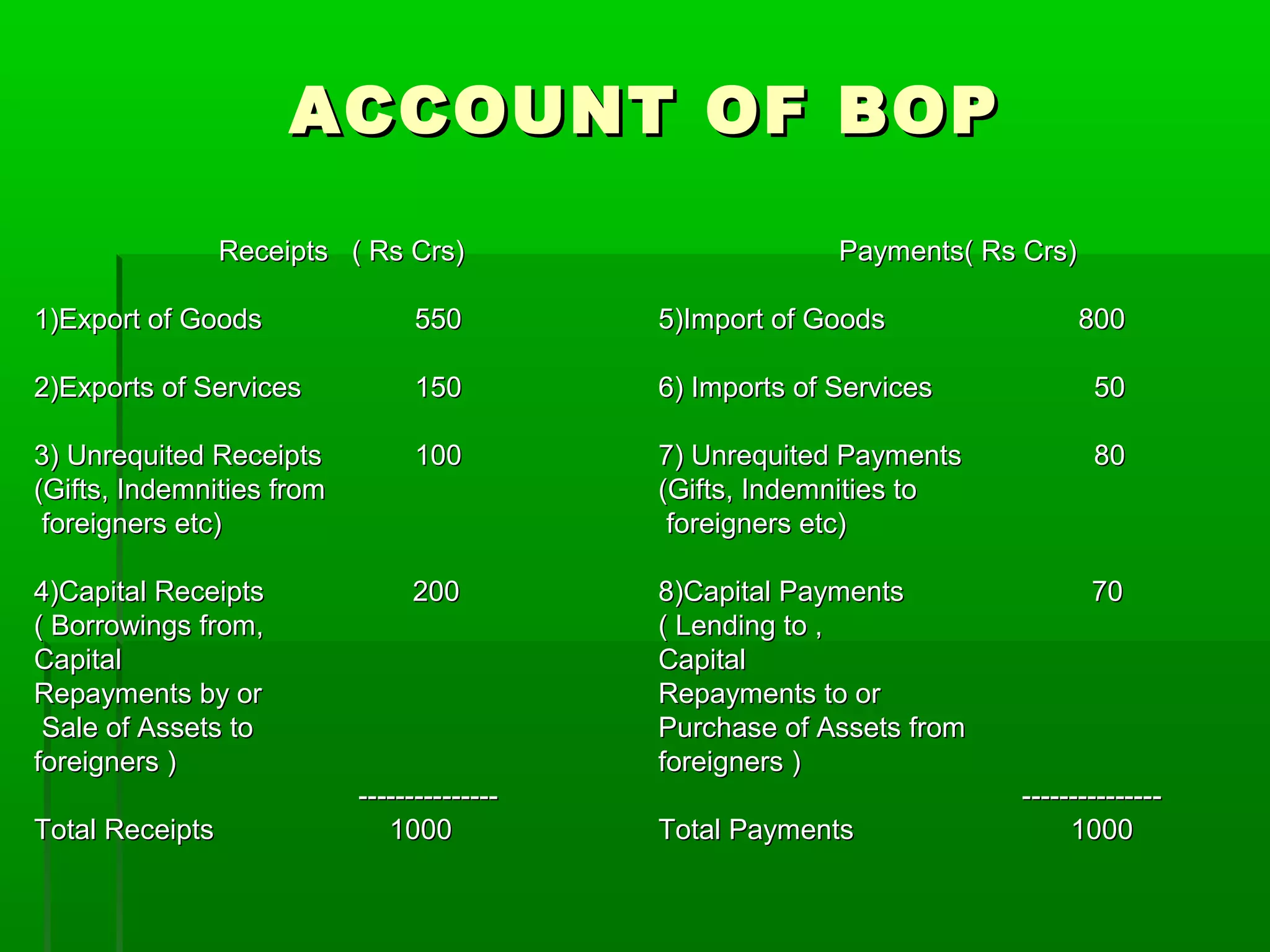
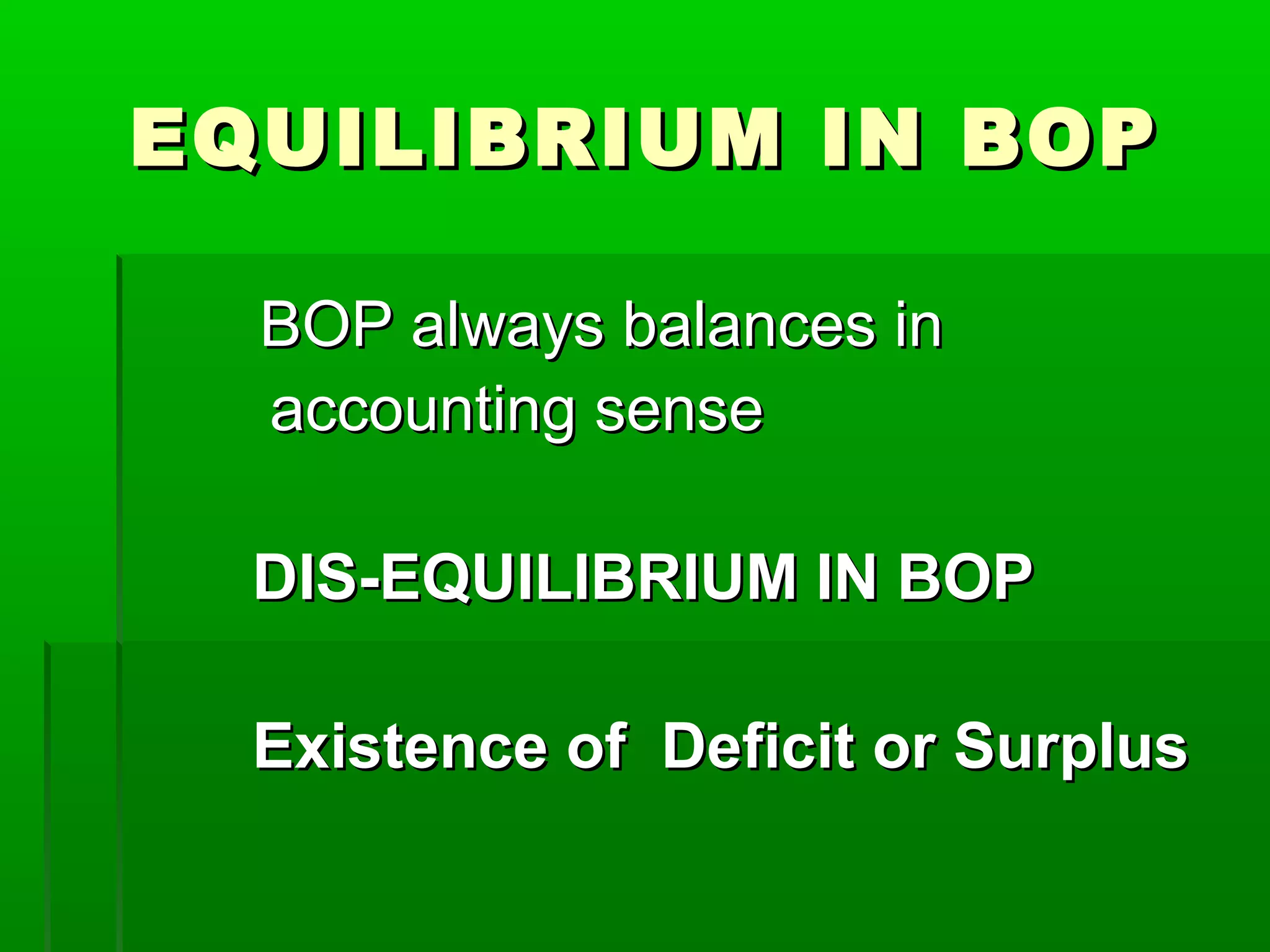
This document discusses the balance of payments and the distinction between the balance of trade and balance of payments. It notes that the balance of trade refers narrowly to visible exports and imports, while the balance of payments includes both visible and invisible items. The balance of payments accounts must always balance, while disequilibriums can exist in the balance of trade. Various types of disequilibriums in the balance of payments are also outlined, along with their causes and potential corrective measures.