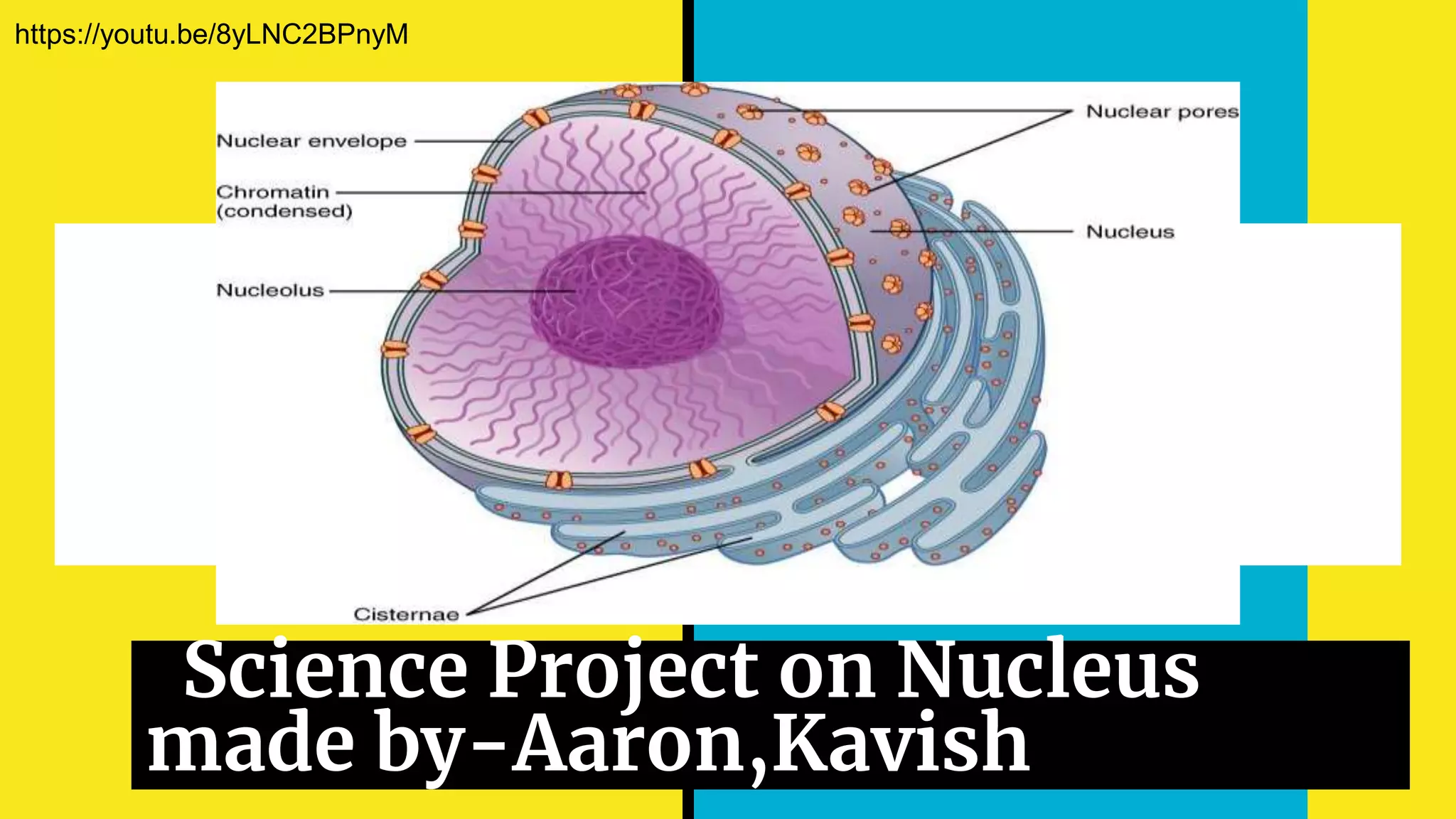
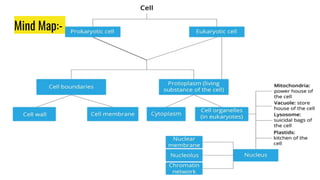
1) The nucleus is an organelle found in eukaryotic cells that contains genetic material in the form of DNA and controls cellular functions and division.
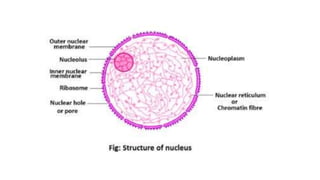
2) The nucleus has a well-defined nuclear membrane and contains chromatin made up of DNA, RNA, and proteins organized into structures called chromosomes.
3) The nucleus plays crucial roles in regulating gene expression, controlling cell division to ensure each daughter cell receives the correct number of chromosomes, and regulating cellular activities and functions.