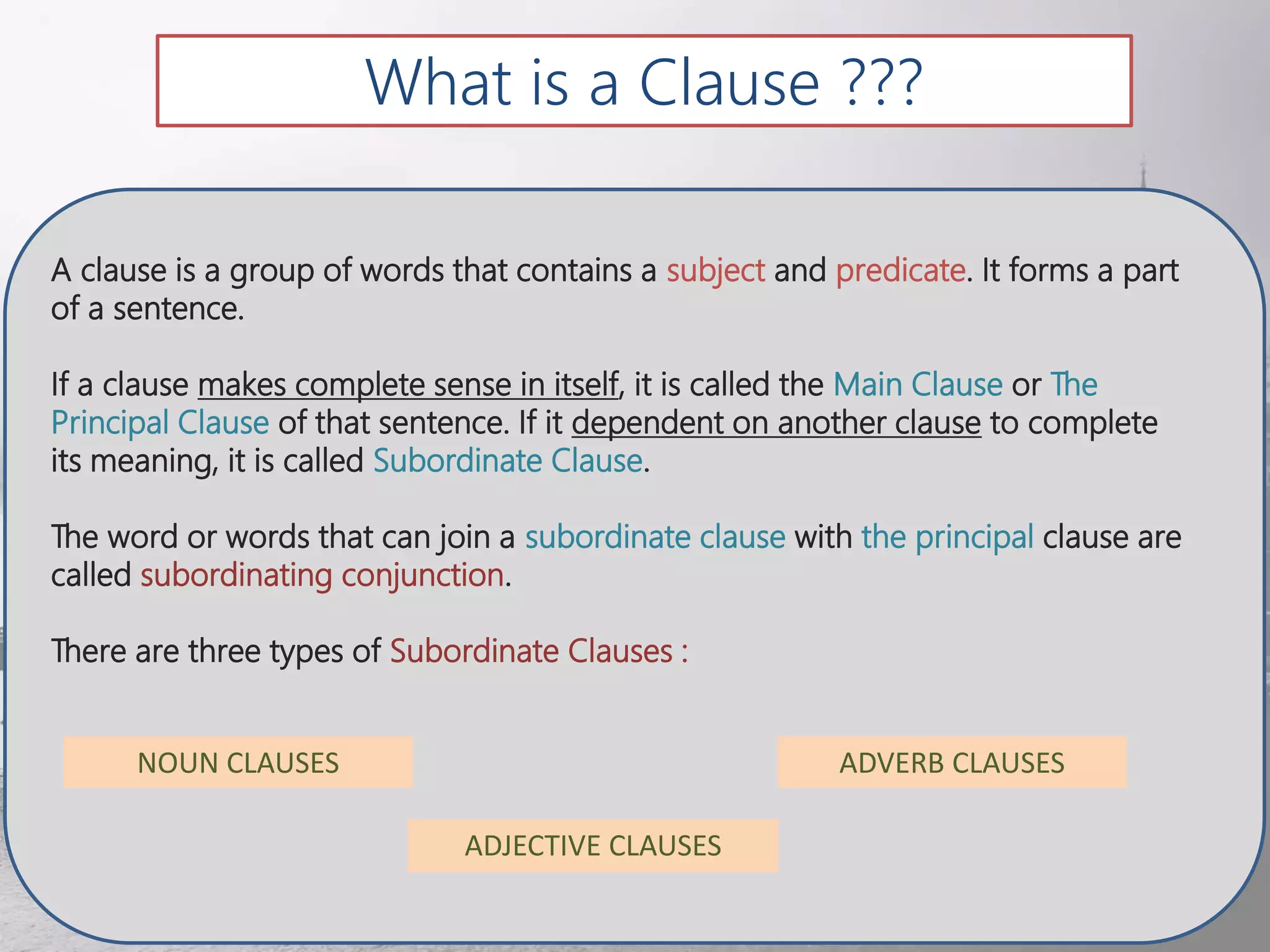
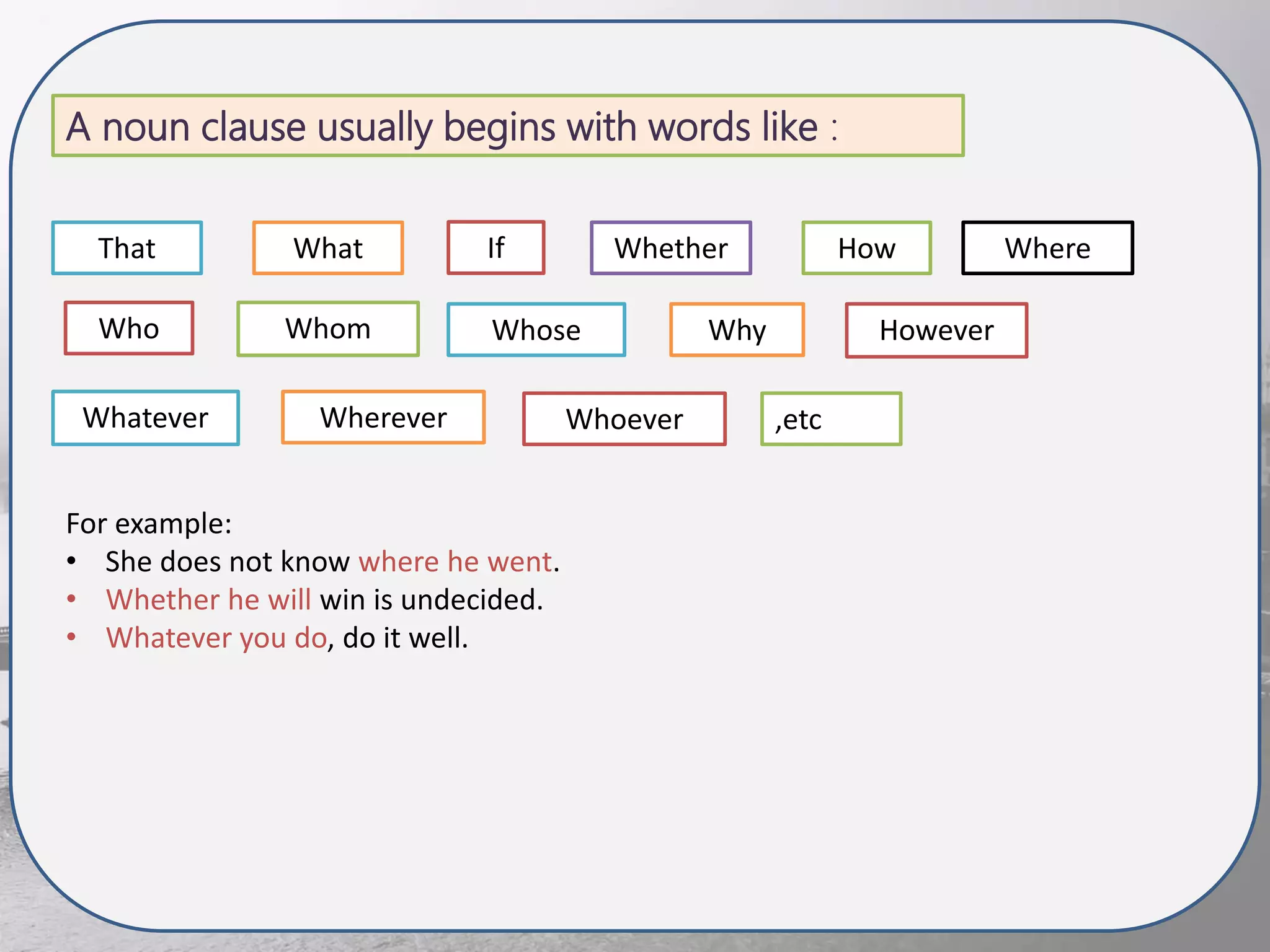
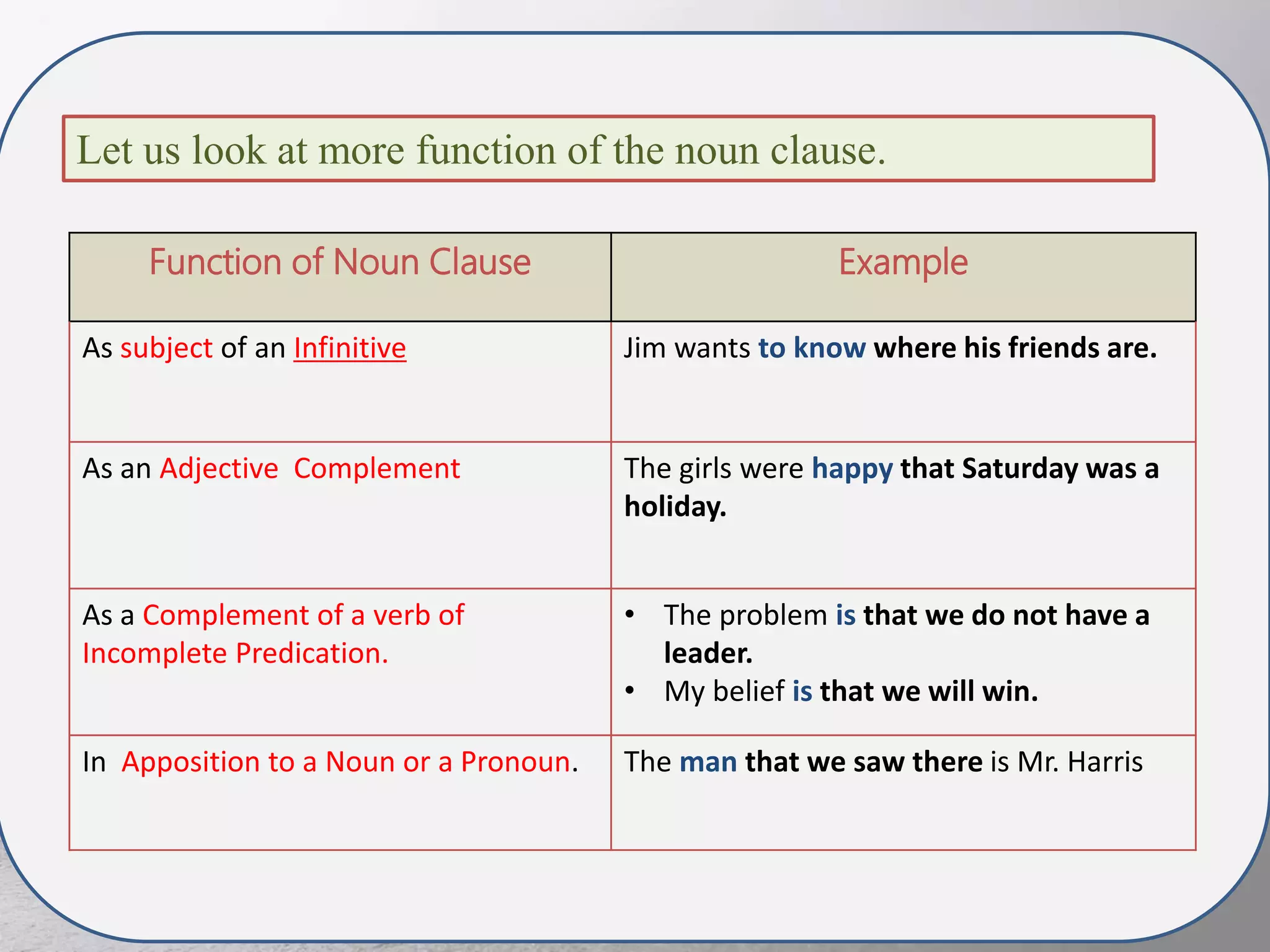
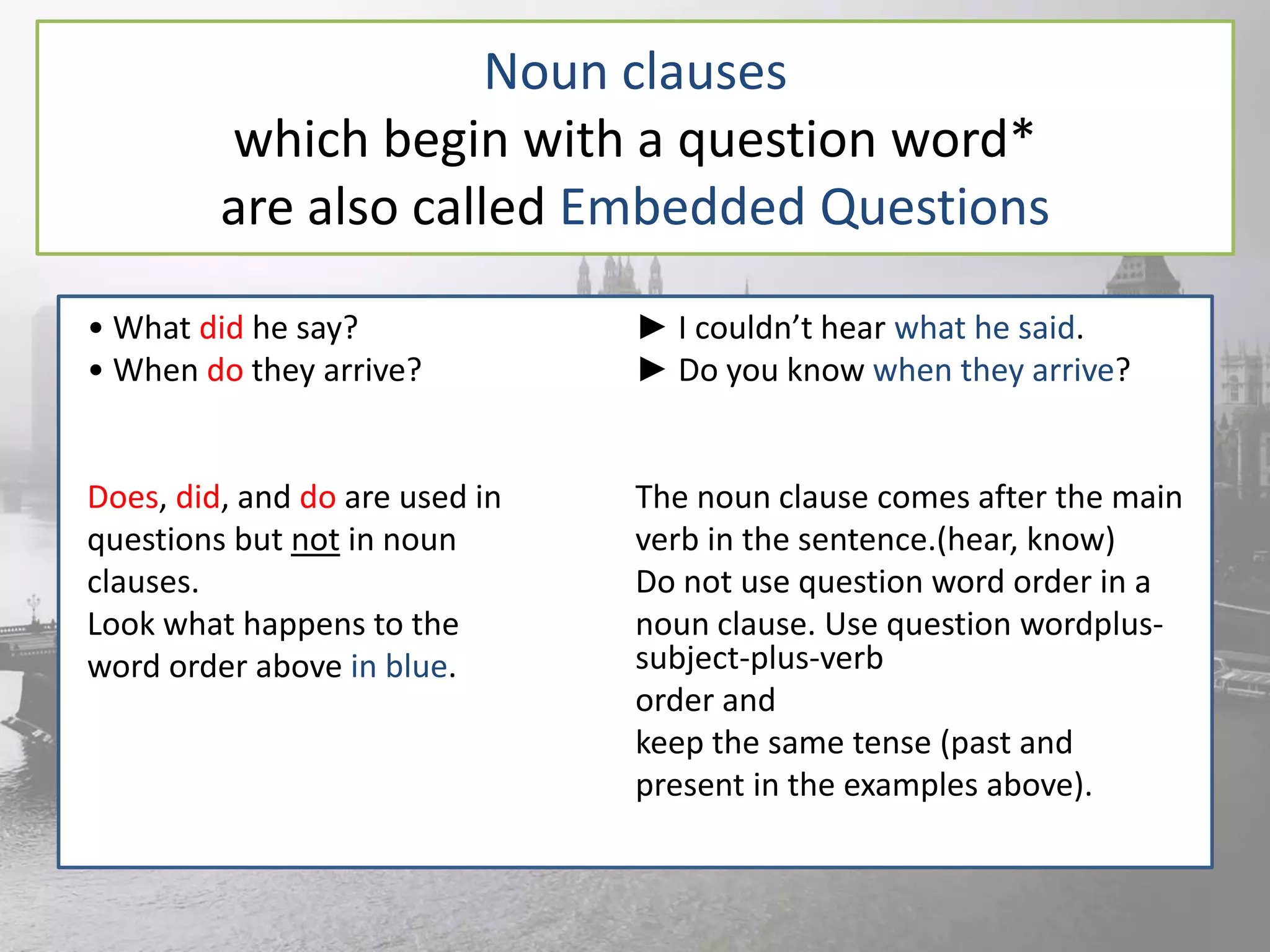
This document discusses noun clauses. It begins by defining a noun clause as a subordinate clause that does the work of a noun in a sentence. It provides examples of noun clauses and how to identify them by asking "who" or "what" questions. It then discusses the different types of words that can introduce a noun clause like "that", "what", "if", etc. It explains the different functions a noun clause can serve in a sentence like subject, object, complement. Finally, it briefly discusses that clauses, if clauses, question word clauses, and sequence of tenses as they relate to noun clauses.