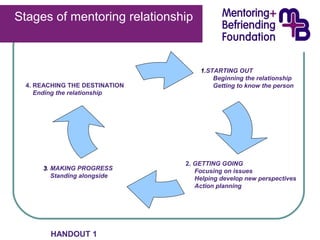
The document outlines a workshop aimed at enhancing mentors' interpersonal and communication skills in the context of mentoring relationships. It includes definitions, stages of mentoring, and essential skills such as rapport building, empathetic listening, and effective questioning. The Mentoring and Befriending Foundation also emphasizes its role in providing training, quality assurance, and resources to support mentoring initiatives.