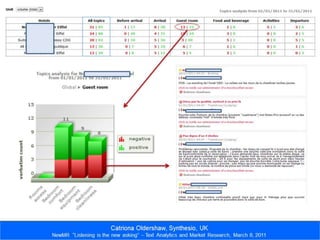
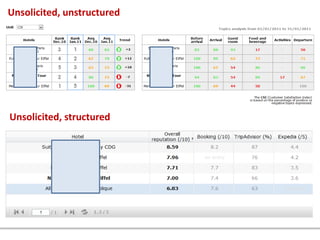
This document outlines a lesson plan on customer satisfaction research. It discusses why brands conduct customer satisfaction research, provides examples of typical customer satisfaction studies, and covers various related topics. A hypothetical customer satisfaction study for McDonald's is presented in detail across multiple slides as an example. The study would include screener questions, quotas, measures of overall satisfaction, evaluations of specific services used, demographics, and open comments. [/SUMMARY]










![A satisfaction study for McDonald’s
Screener Questions
– Do you work in any of the following areas?
• Health services
• Financial services
• Market research [Close]
• Restaurants or fast food outlets [Close]
• Sports and entertainment
• None of these
Ray Poynter, Marketing Research & Social Communication, 2015 11](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/poynterlesson9-150609151702-lva1-app6891/85/Poynter-Lesson-9-11-320.jpg)
![A satisfaction study for McDonald’s
Quota/Screener Questions
– How old are you?
• Under 18 years [Close]
• 18 to 25 years [Check Quota]
• 26 to 35 years [Check Quota]
• 36 to 45 years [Check Quota]
• 46 to 55 years [Check Quota]
• 56 to 65 years [Check Quota]
• Over 65 years [Close]
Ray Poynter, Marketing Research & Social Communication, 2015 12](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/poynterlesson9-150609151702-lva1-app6891/85/Poynter-Lesson-9-12-320.jpg)
![A satisfaction study for McDonald’s
Quota/Screener Questions
– How often do you visit a McDonald’s?
• More than once a week [Check Quota]
• About once a week [Check Quota]
• At least once a month [Check Quota]
• Less than once a month [Close]
• Never [Close]
Ray Poynter, Marketing Research & Social Communication, 2015 13](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/poynterlesson9-150609151702-lva1-app6891/85/Poynter-Lesson-9-13-320.jpg)

![A satisfaction study for McDonald’s
Overall Satisfaction
– You said you were [PIPED TEXT] with
McDonald’s. In you own words can you tell us
why, typing in the box below?
Ray Poynter, Marketing Research & Social Communication, 2015 15
PIPED TEXT is the option they picked in the previous question, e.g. “Very Satisfied”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/poynterlesson9-150609151702-lva1-app6891/85/Poynter-Lesson-9-15-320.jpg)