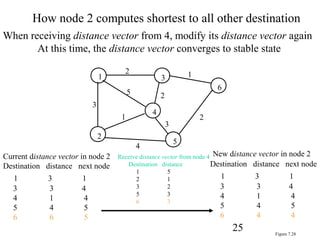
Routing in packet switching networks determines the best path for packets to travel from source to destination. There are multiple potential paths and the best path depends on objectives like minimizing hops, delay, or maximizing bandwidth. Routing algorithms must have global network knowledge and be correct, robust, clever, and efficient. Algorithms can be static or dynamic, centralized or distributed. Distance vector routing uses Bellman-Ford algorithm where each node shares its distance vector with neighbors periodically. Link state routing uses flooding to share link state packets and Dijkstra's algorithm to compute shortest paths from the network map.