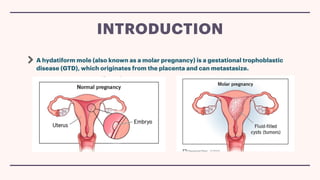
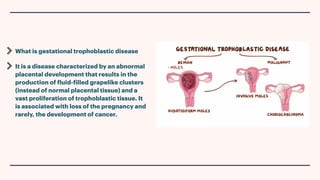
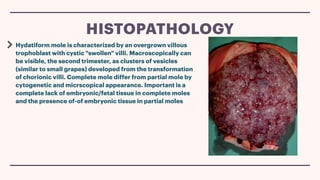
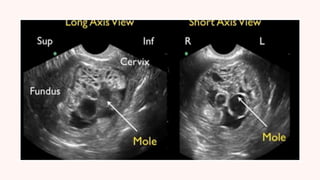
A hydatidiform mole, or molar pregnancy, is a gestational trophoblastic disease caused by abnormal placental development that results in fluid-filled cysts instead of normal placental tissue. There are two types of molar pregnancies: complete and partial. A complete molar pregnancy occurs when an empty egg is fertilized, so the embryo cannot survive, while a partial molar pregnancy involves the fertilization of one egg by two sperm, leading to an abnormal embryo. Molar pregnancies are typically diagnosed through ultrasound and blood tests measuring HCG levels, and are treated by surgically removing the molar tissue through dilation and curettage. Complications can include gestational trophoblastic neoplasia requiring