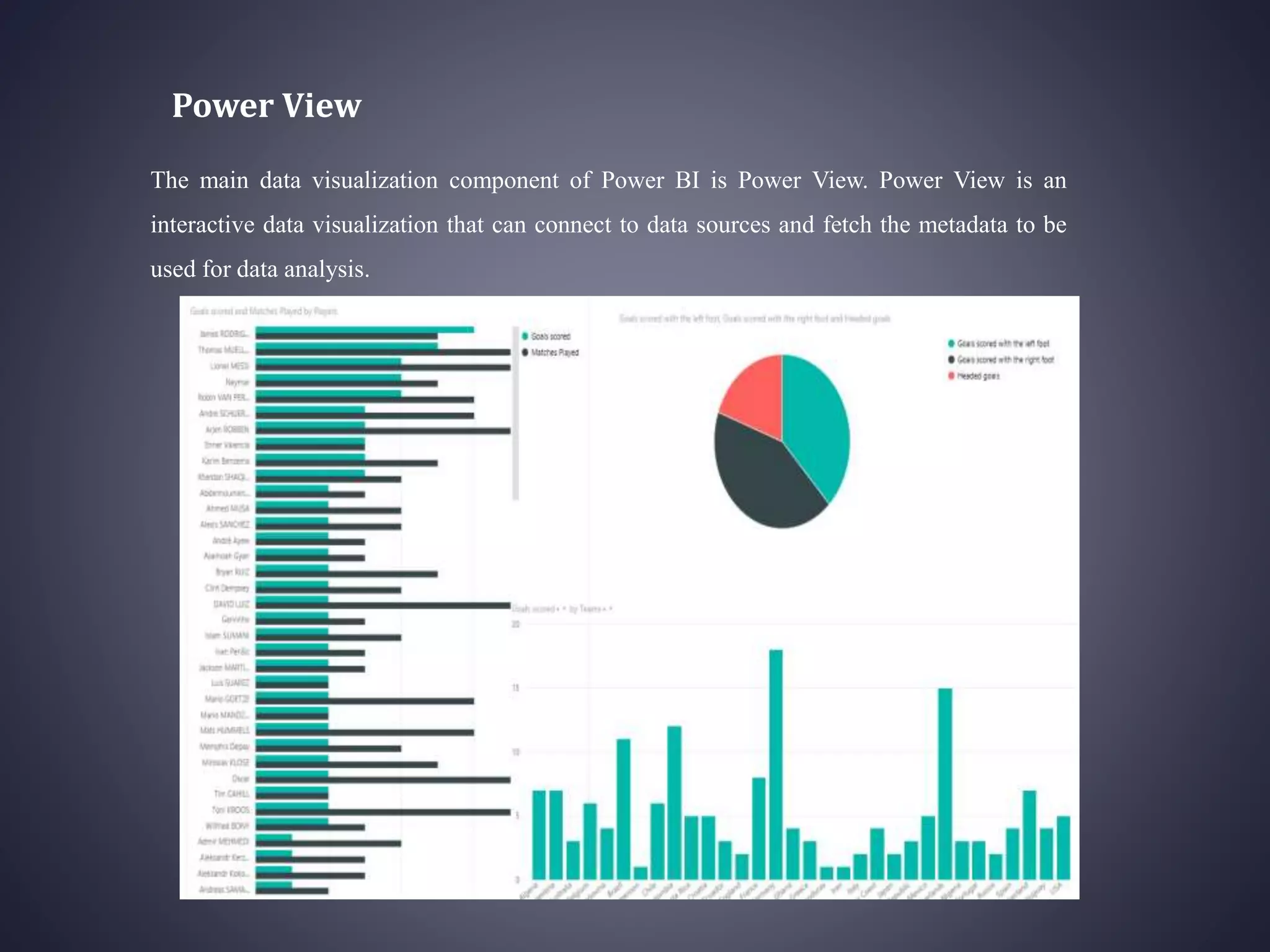
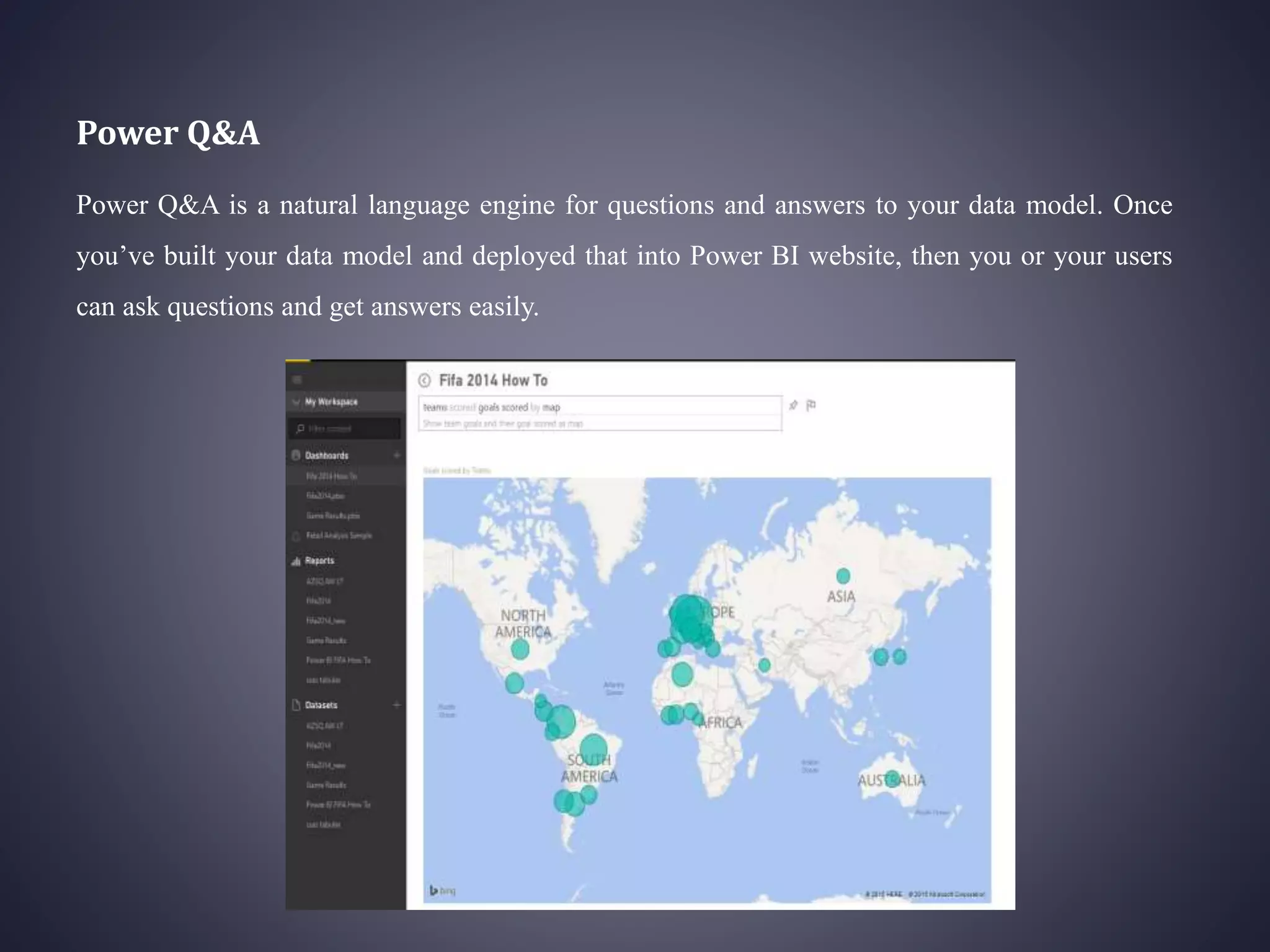
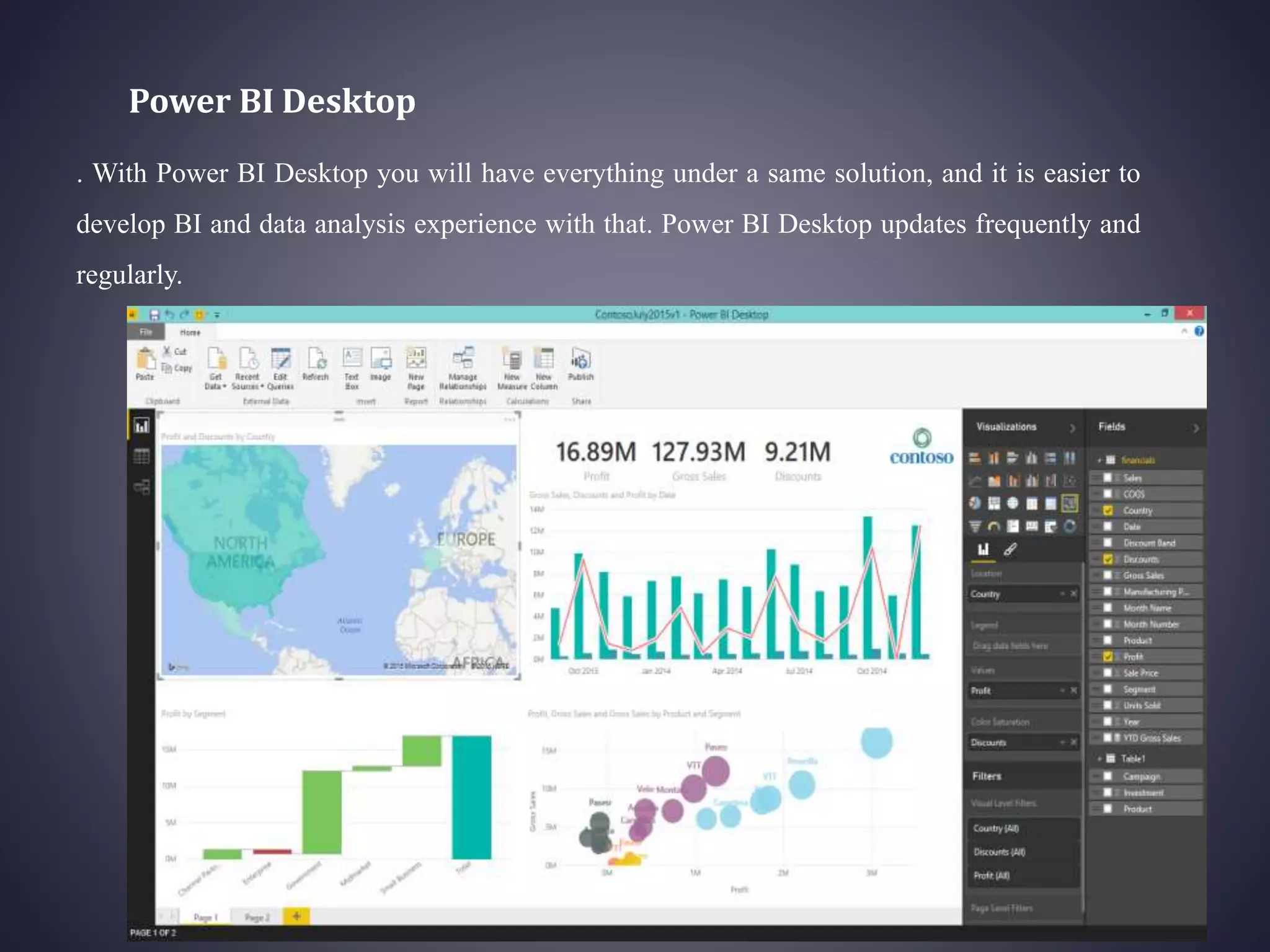
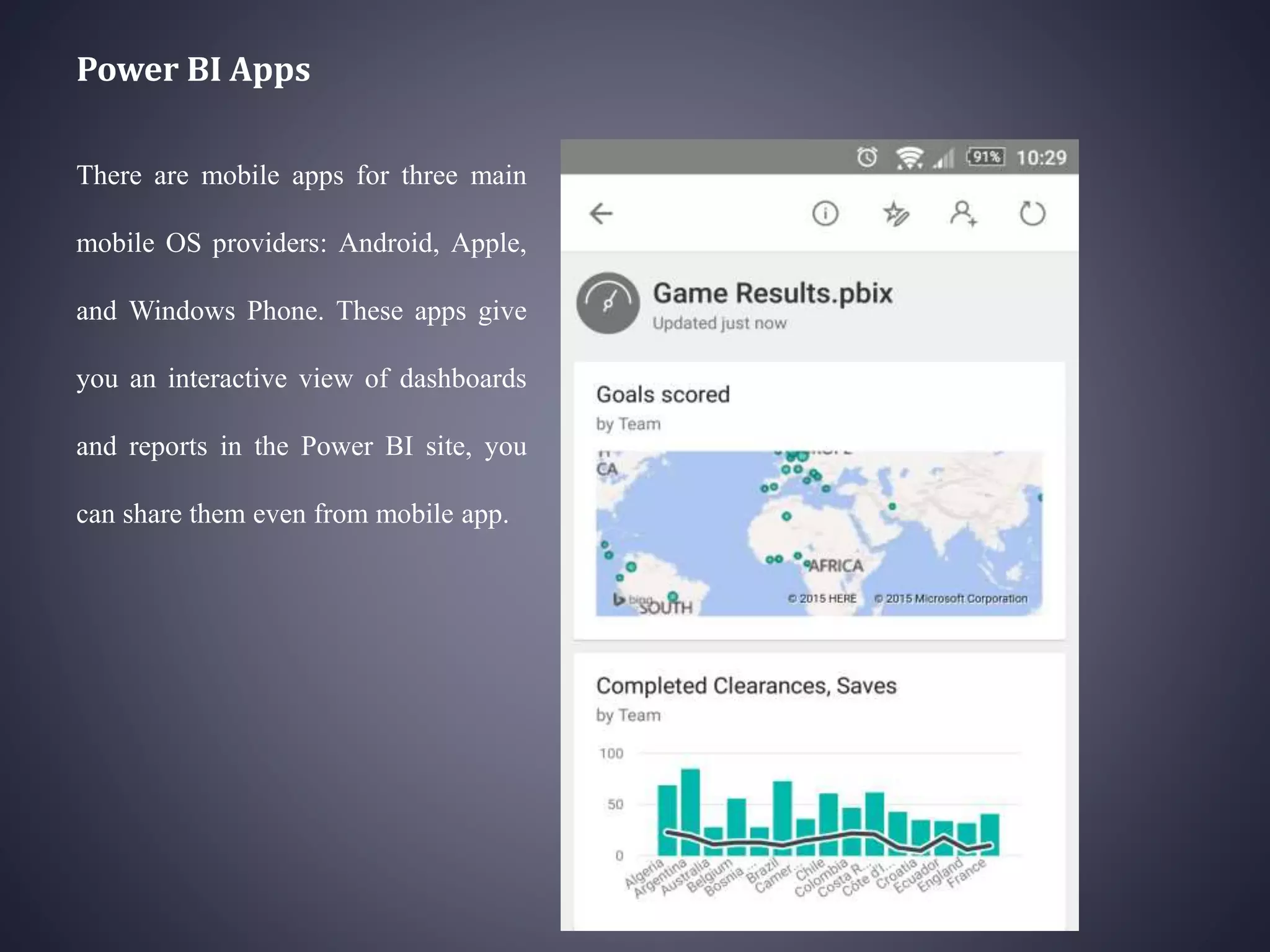
Power BI is a collection of software services, apps, and connectors that work together to transform unrelated data sources into interactive visualizations and insights. It has 6 main components: Power Query for data transformation, Power Pivot for tabular data modeling, Power View for data visualization, Power Map for 3D geospatial visualization, Power Q&A for natural language questions, and Power BI Desktop for report development. Power BI can connect to various data sources and publish reports, dashboards, and datasets to the Power BI website for sharing and accessing on mobile devices. It provides an integrated solution for self-service business intelligence but has some limitations around customization, large datasets, and cross-domain sharing.