Embed presentation
Download to read offline





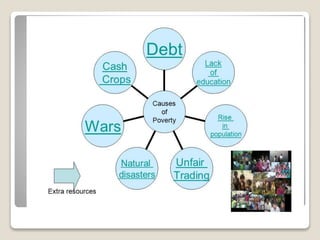


The document defines poverty as the condition of lacking the means to afford basic human needs such as clean water, nutrition, health care, clothing and shelter. It states that poverty refers to having fewer resources or less income than others within one's society or country. The document also lists several causes of poverty, including lack of education, large scale imports, division of agricultural land, issues with moral culture and government policies, corruption, privatization, overpopulation, and unemployment.







