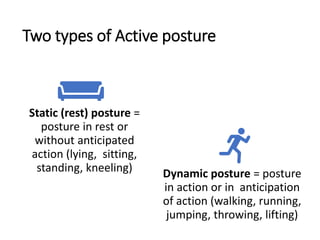
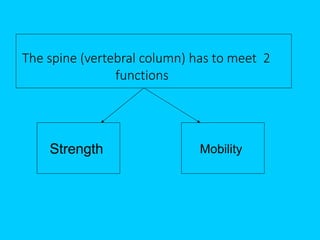
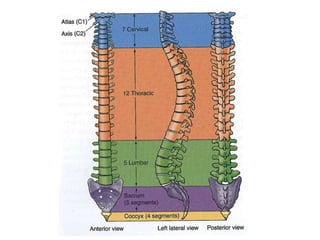
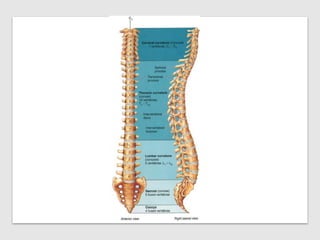
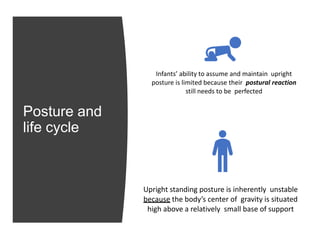
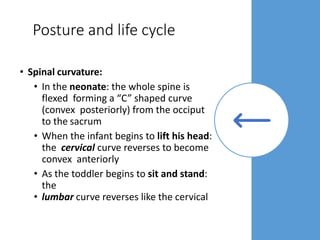
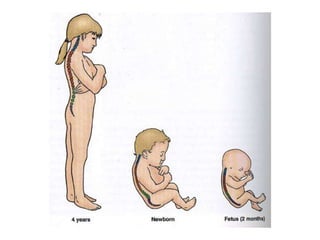
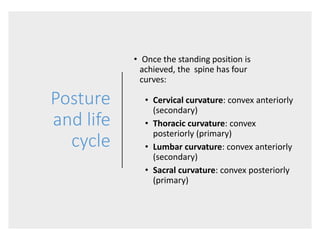
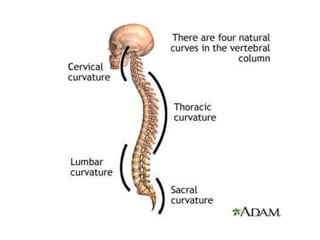
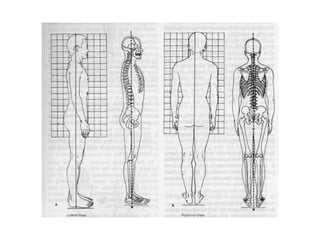
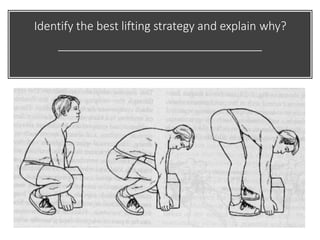
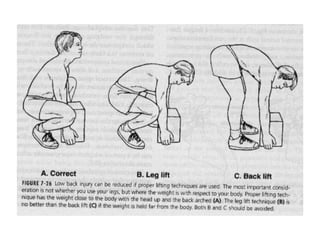
This document discusses posture and factors that affect it. It defines good posture as optimal muscular balance and efficiency. Posture changes throughout life and with activity. The spine curves allow strength and mobility. Maintaining upright standing, sitting, and lifting postures protects the back, while improper forms can strain muscles and ligaments over time. Small postural sways help prevent fatigue and aid circulation while balancing.