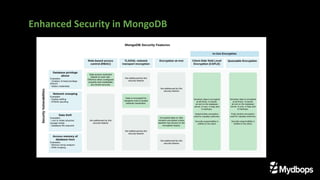
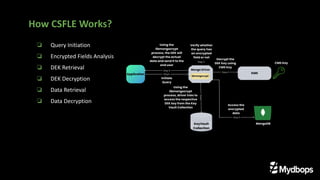
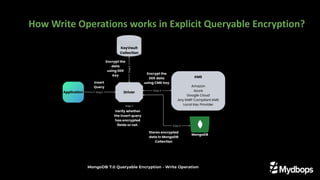
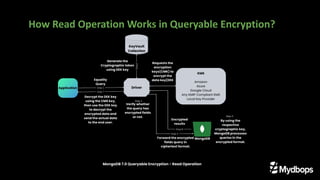
The document presents an overview of queryable encryption in MongoDB, highlighting its significance for data security and confidentiality. It distinguishes between various encryption mechanisms, including client-side field-level encryption (CSFLE) and queryable encryption, detailing their processes and applications. The framework also emphasizes key management systems and limitations associated with queryable encryption in MongoDB.