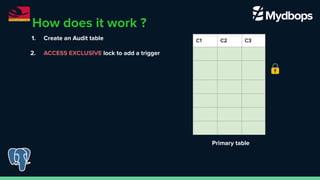
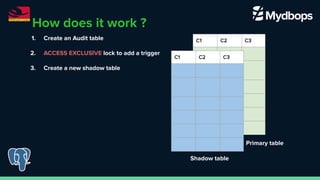
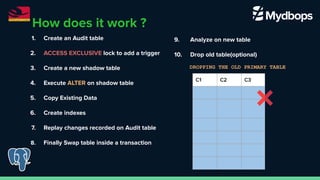
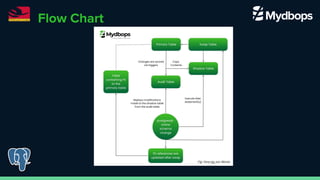
The document discusses pg_osc, a tool for making PostgreSQL schema changes with minimal locking and zero downtime, similar to MySQL's pt_osc. It outlines the step-by-step process for implementing schema changes, including creating audit tables, shadow tables, and handling data changes, while highlighting key features and considerations. The presentation was part of PGConf India on February 29, 2024.