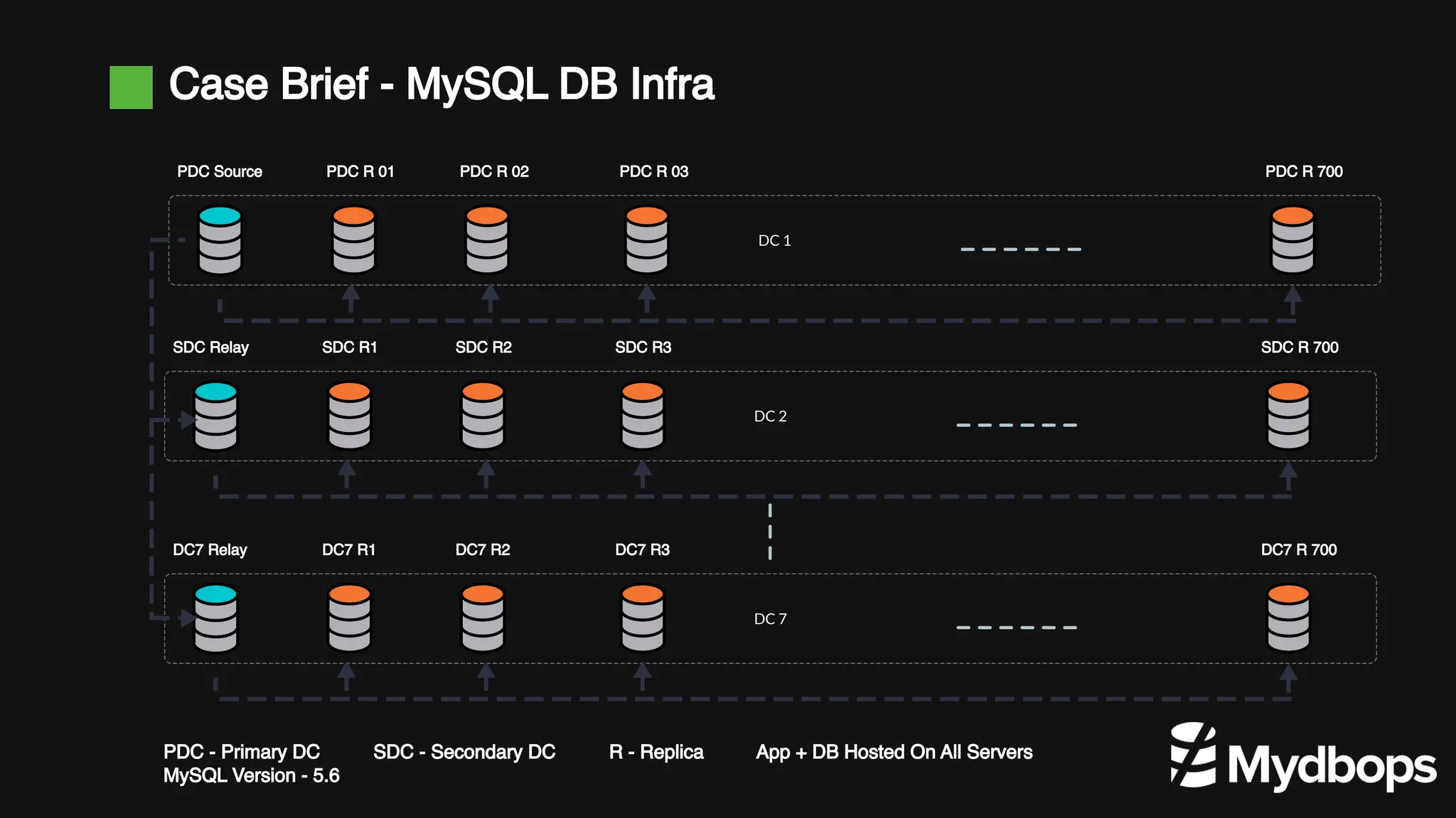
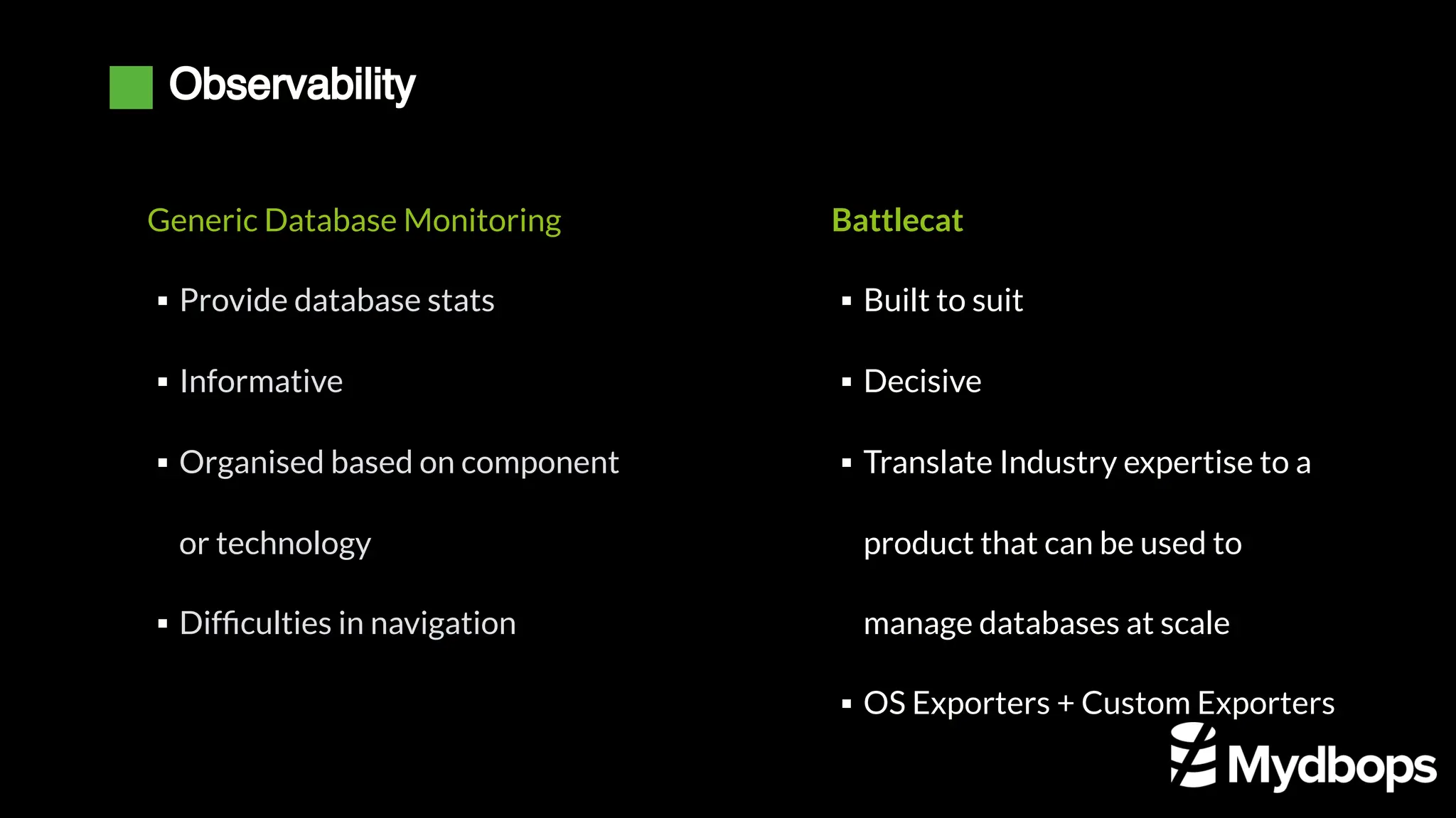
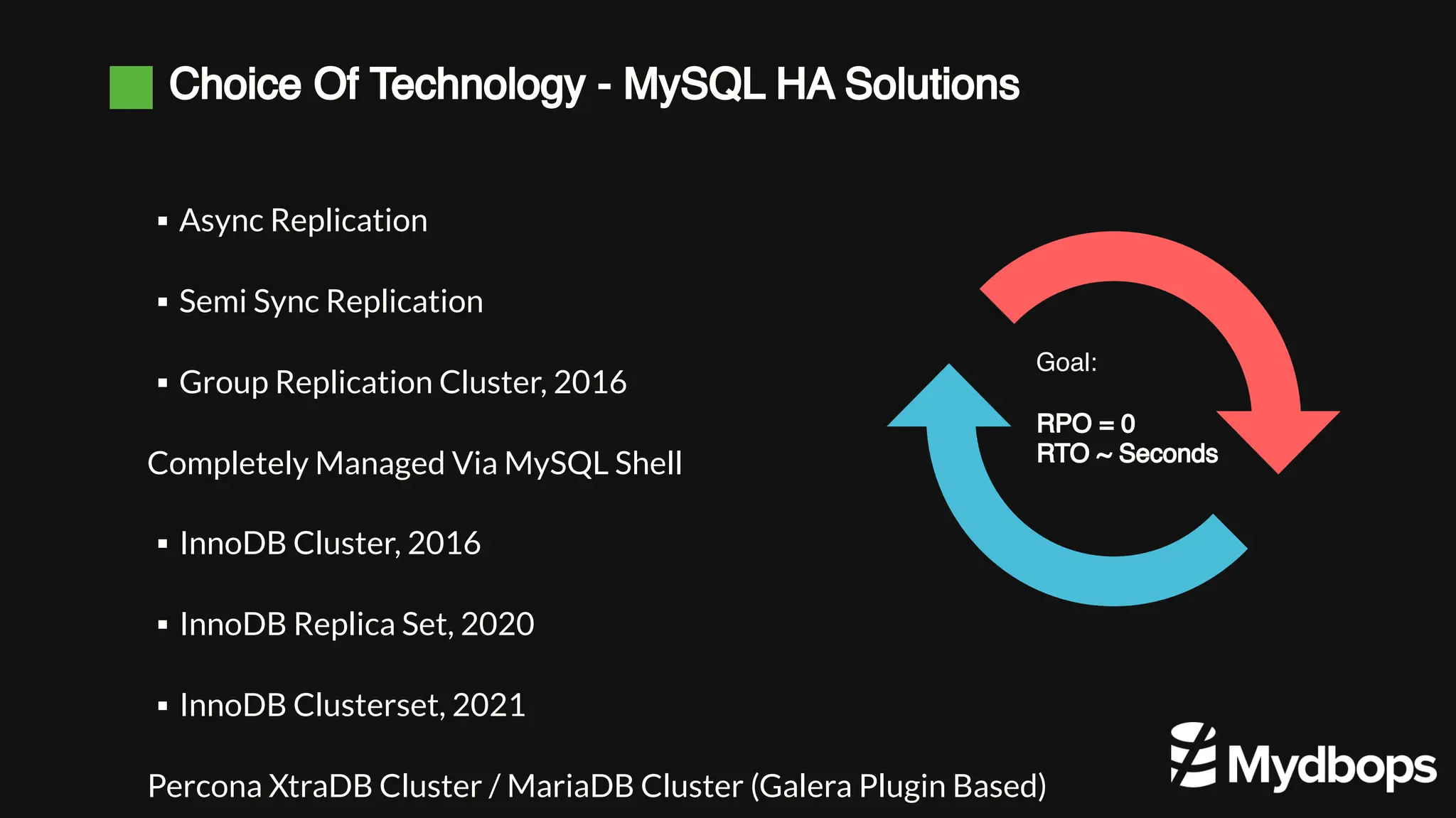
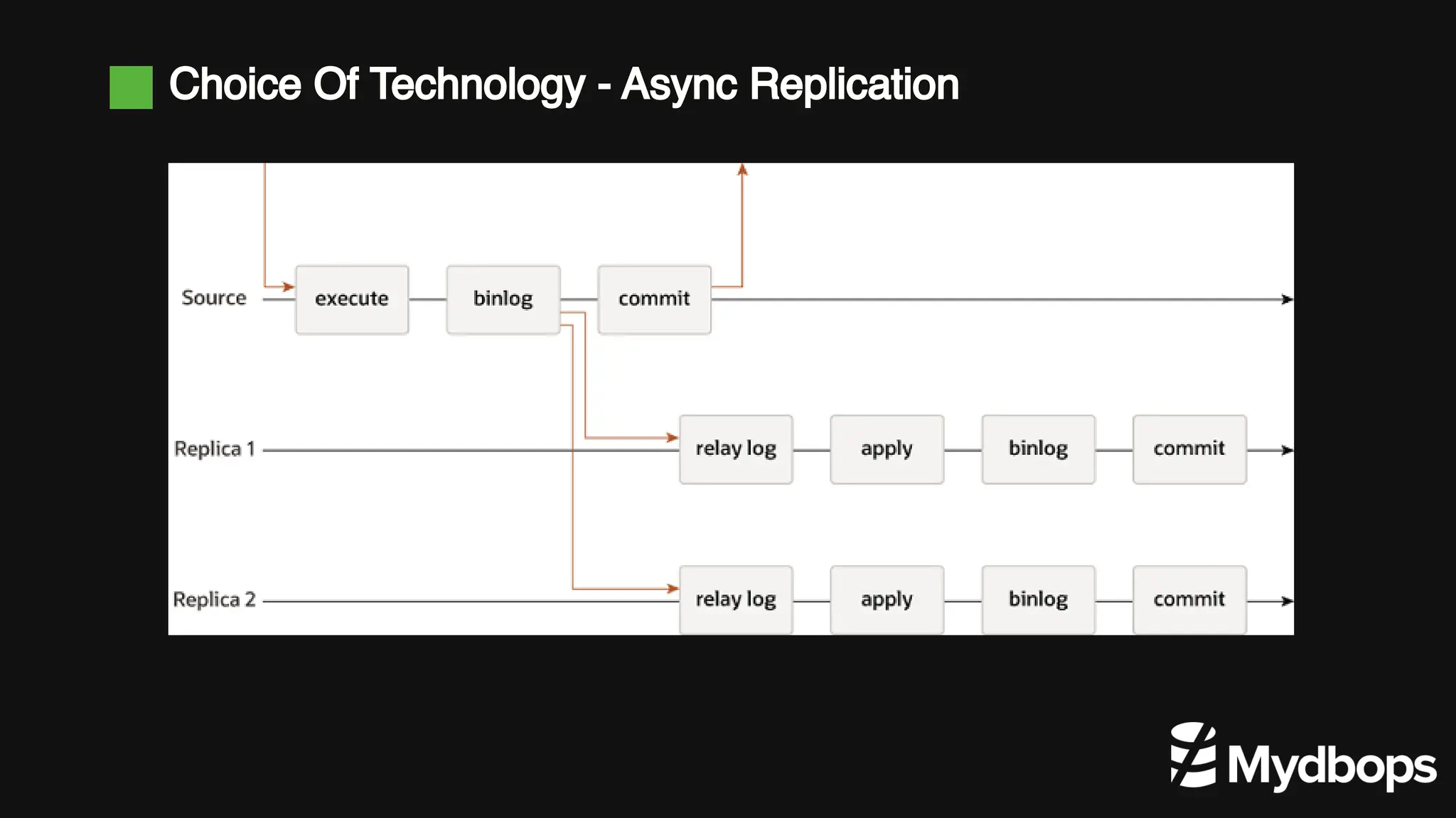
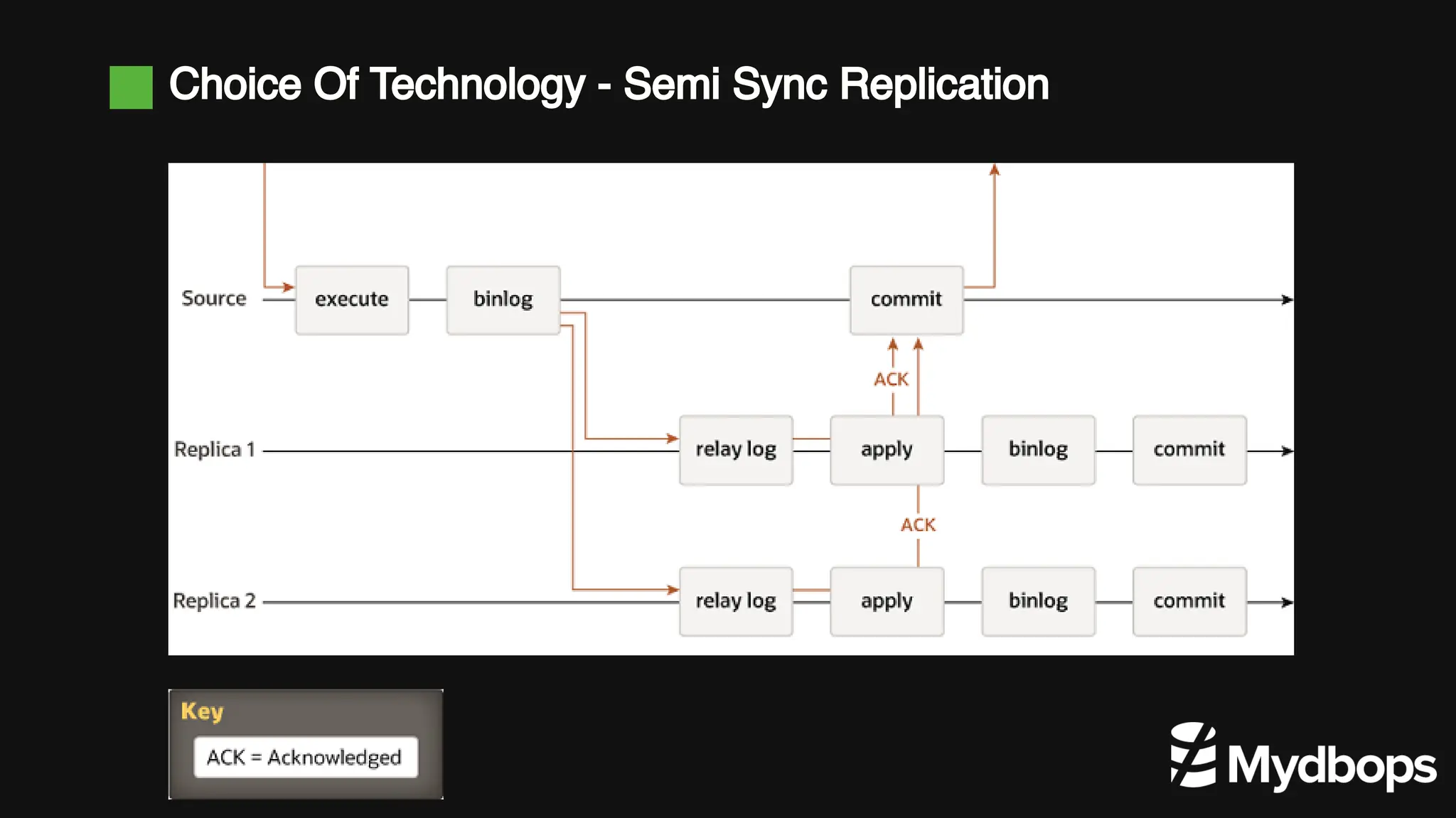
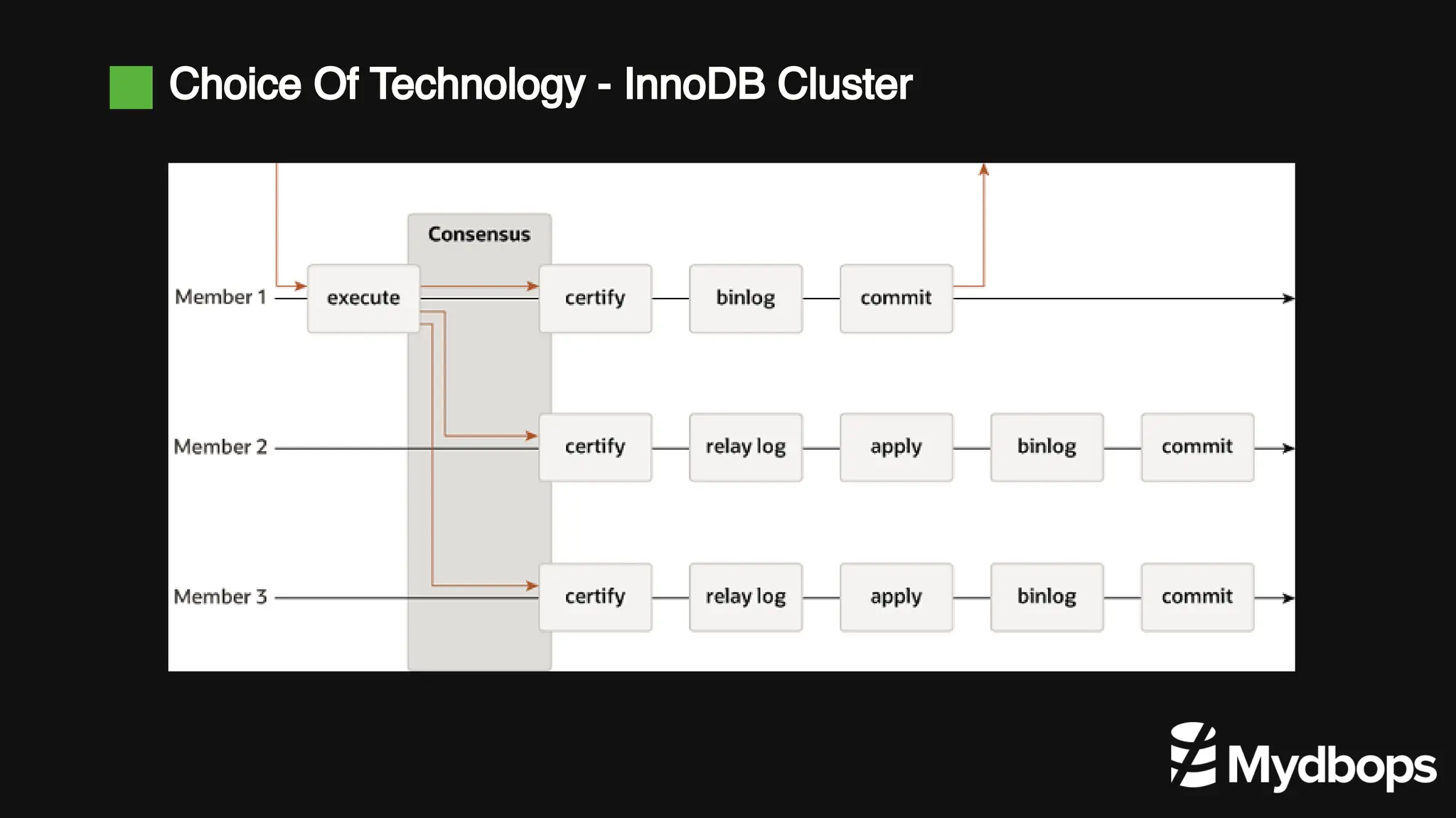
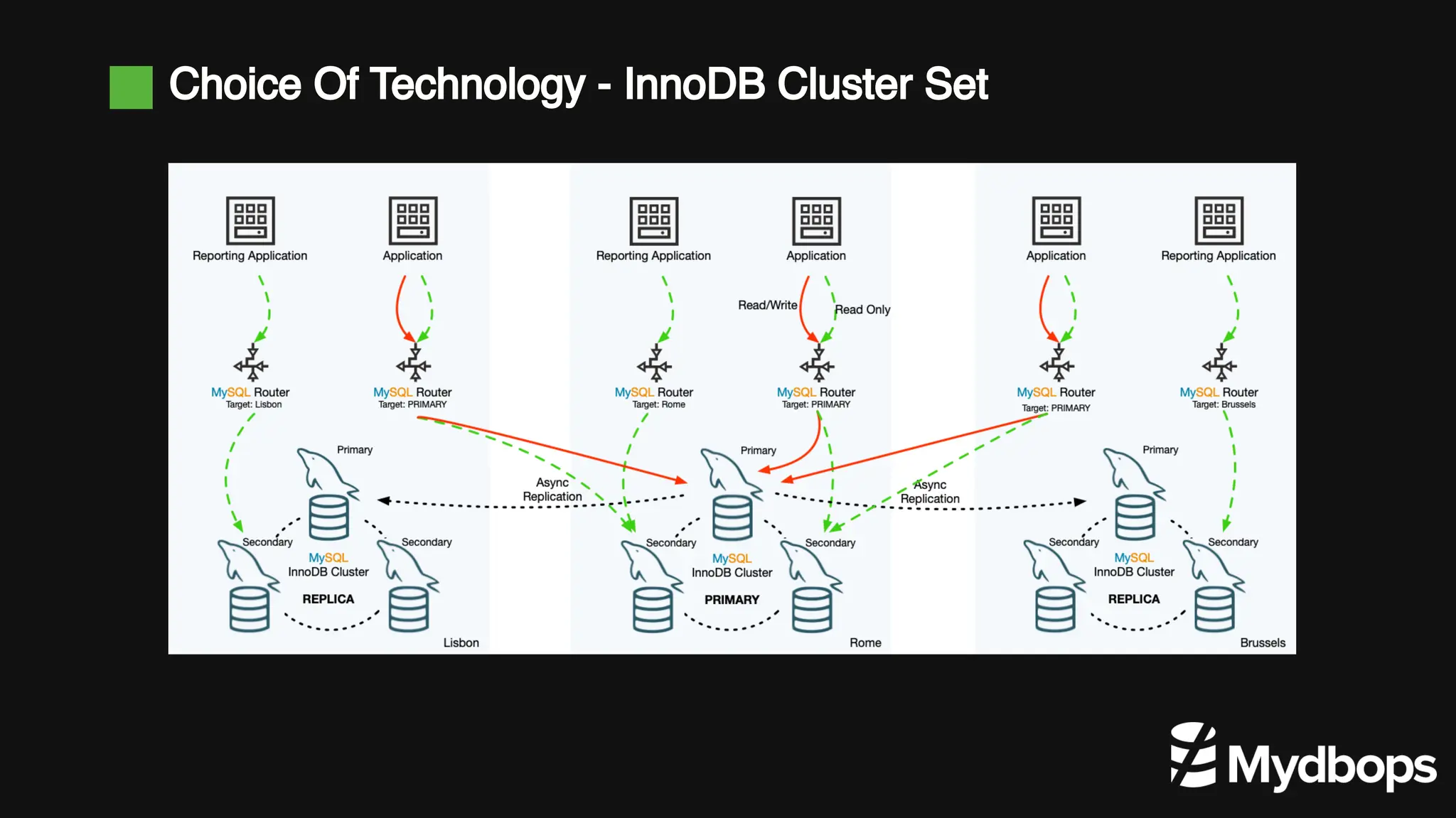
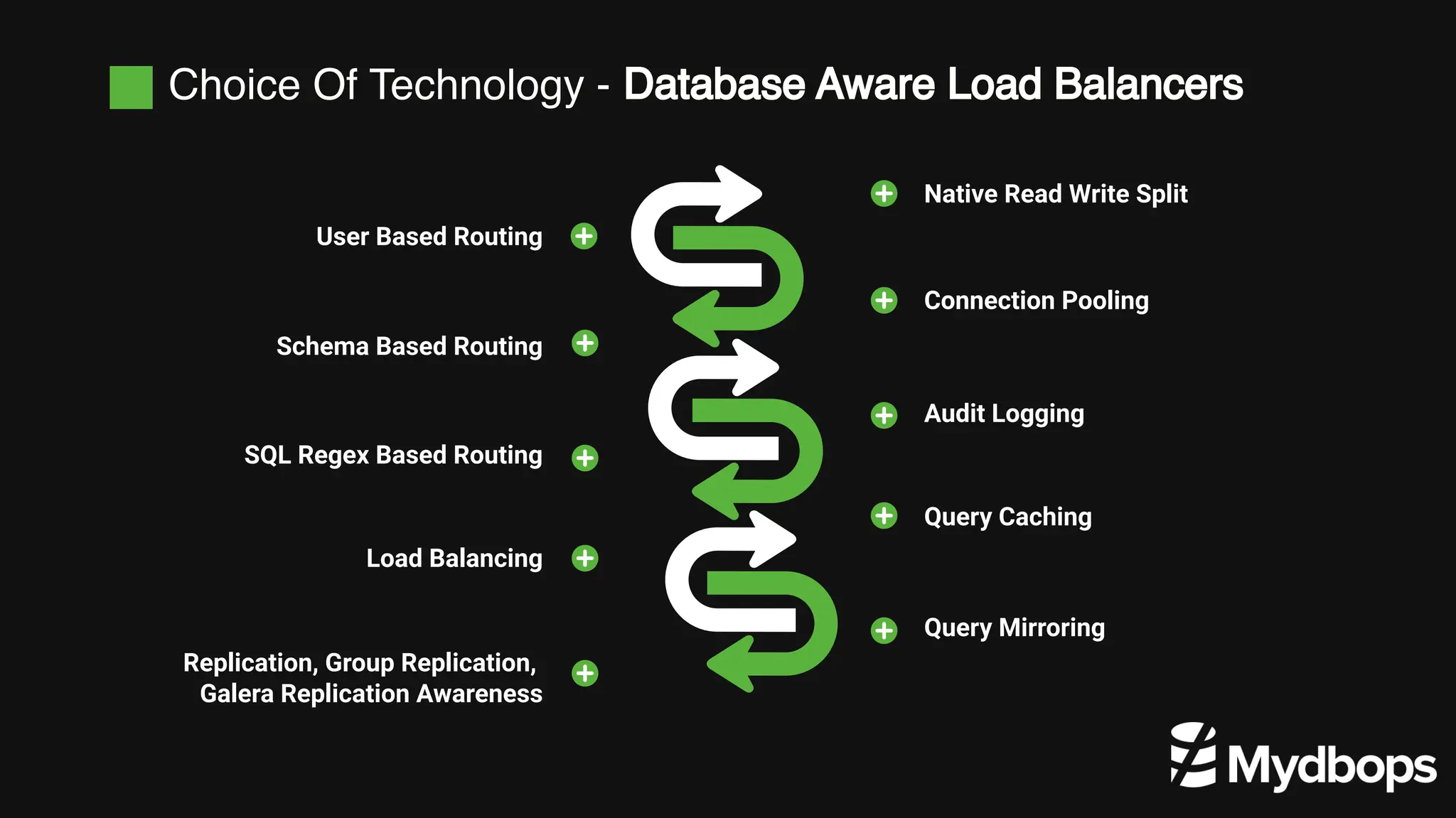
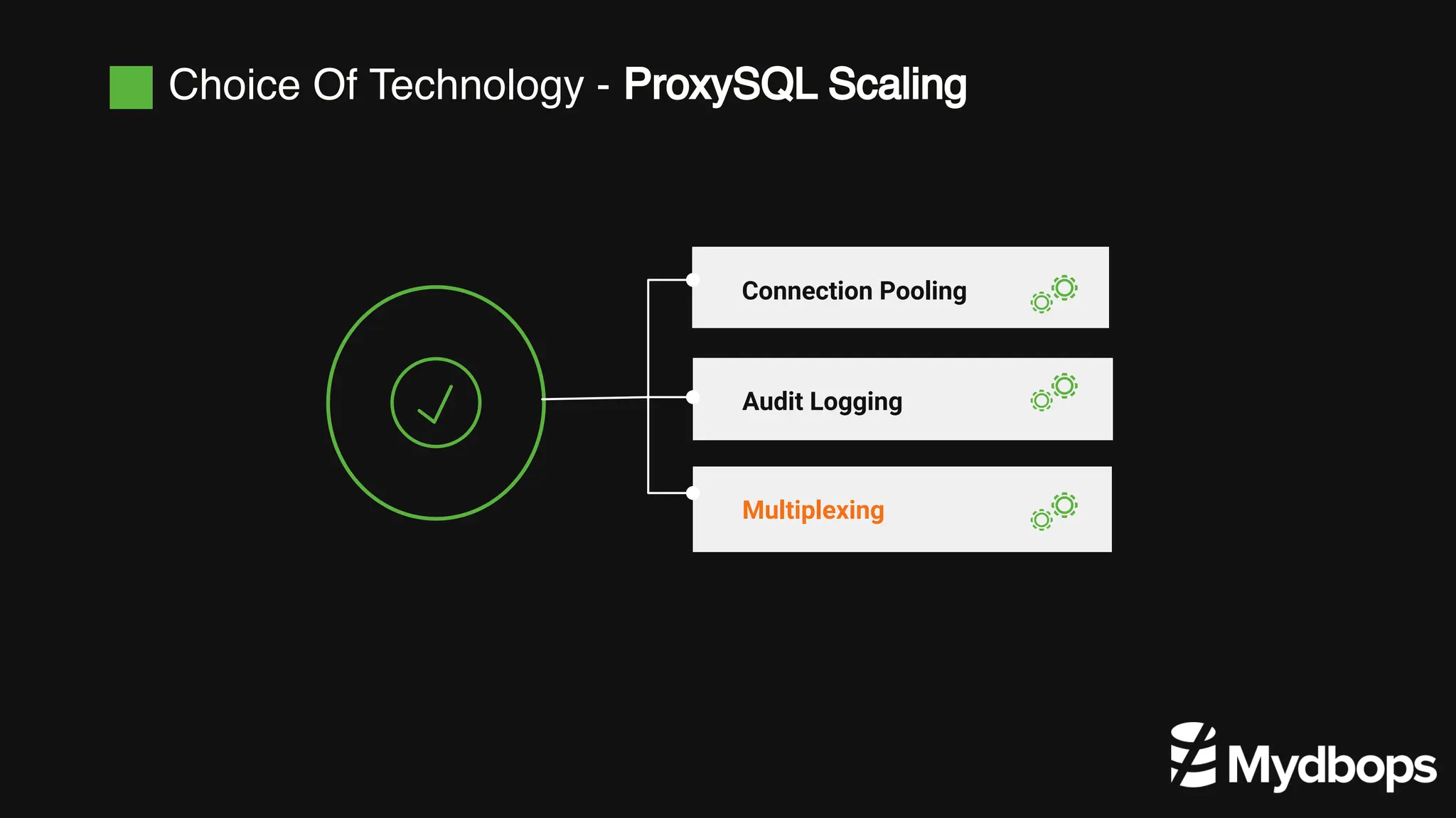
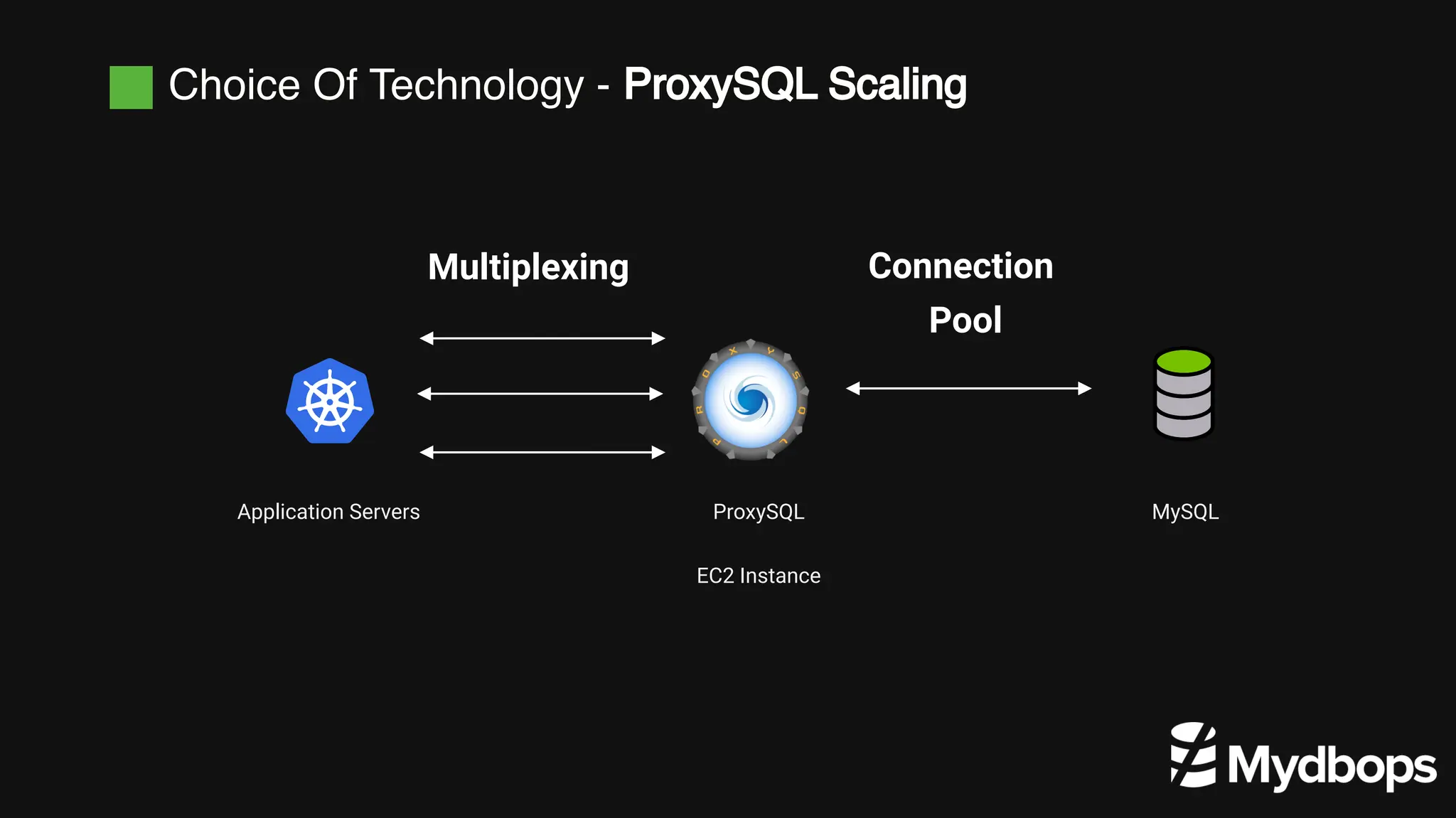
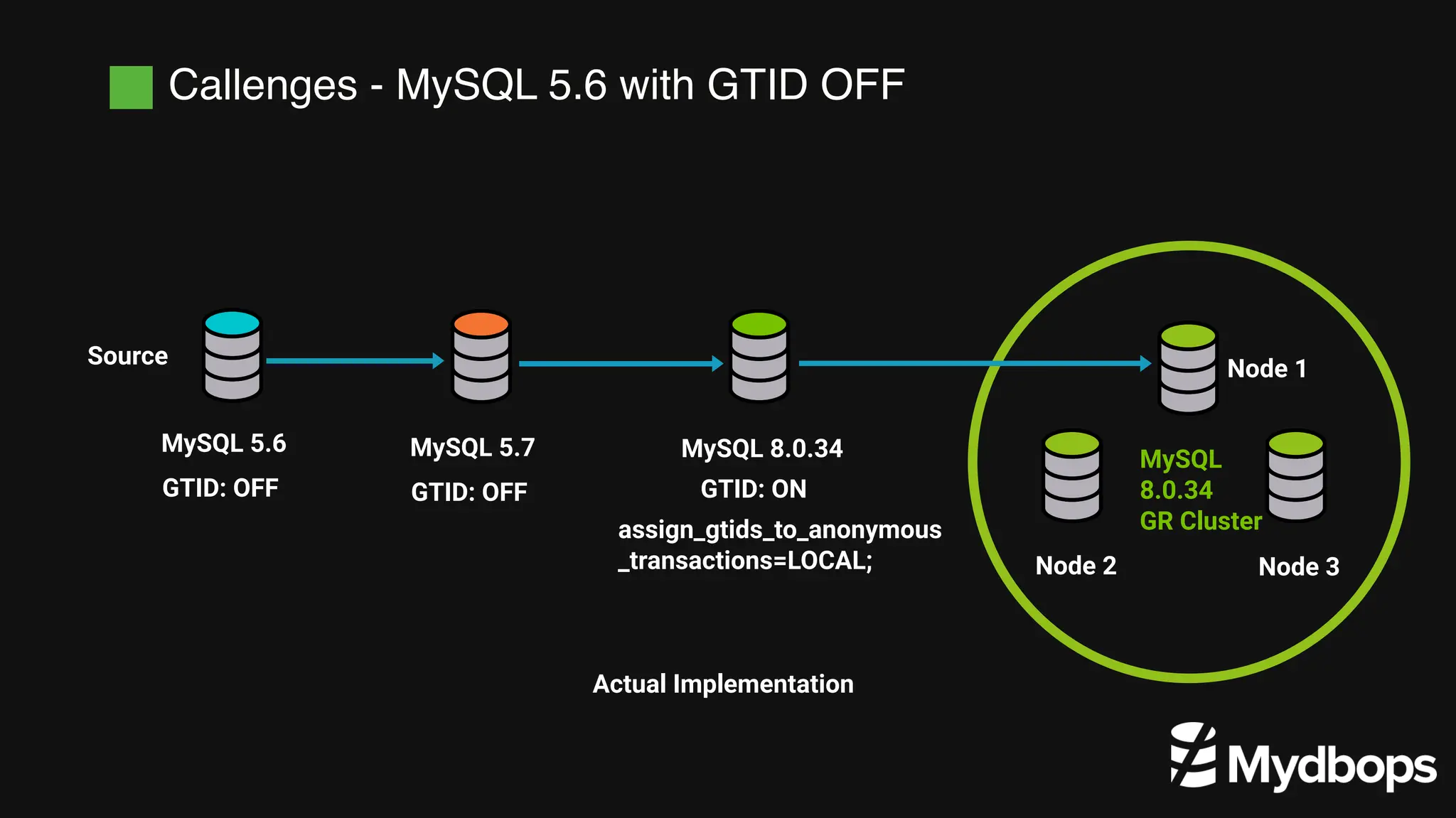
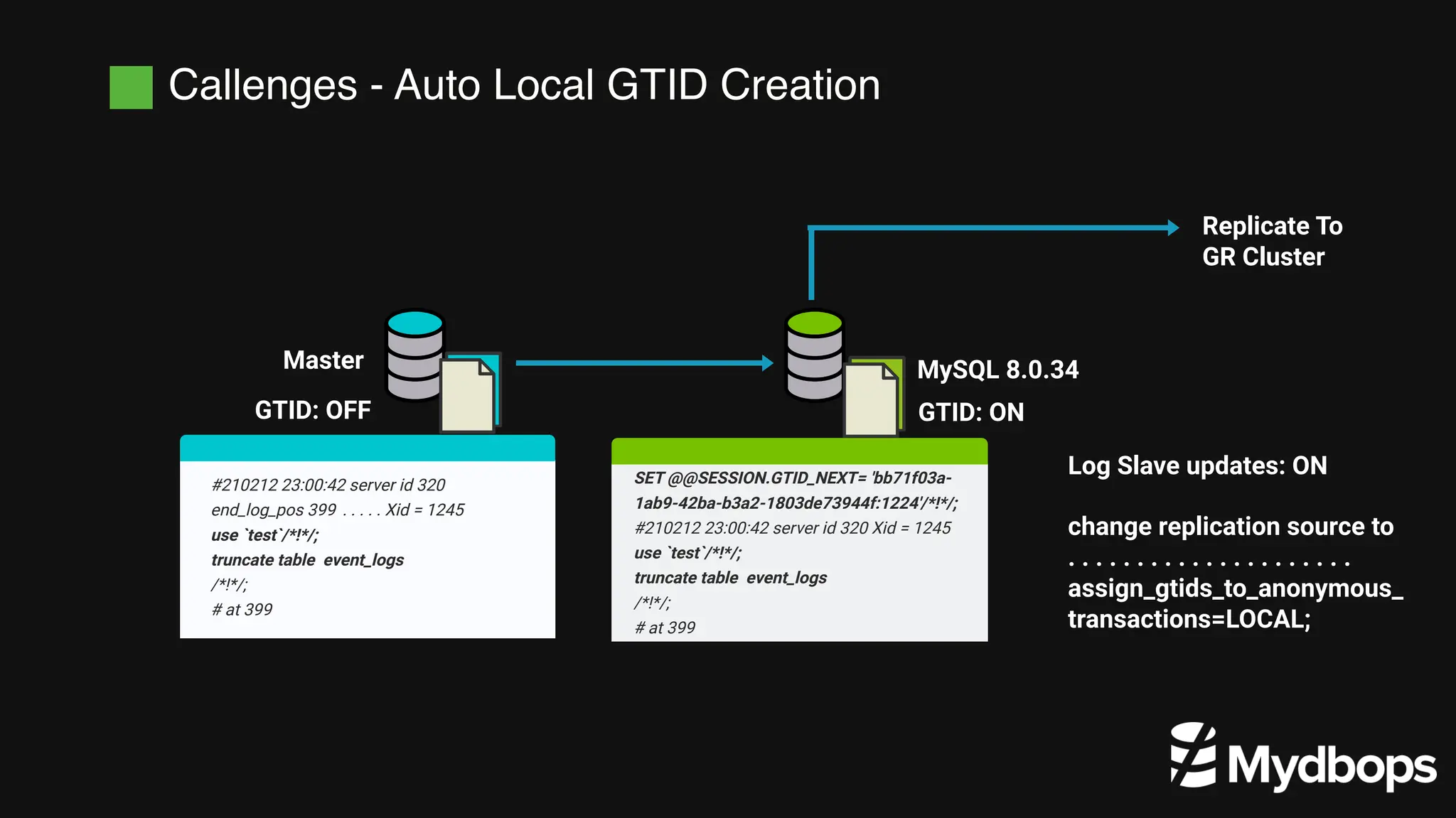
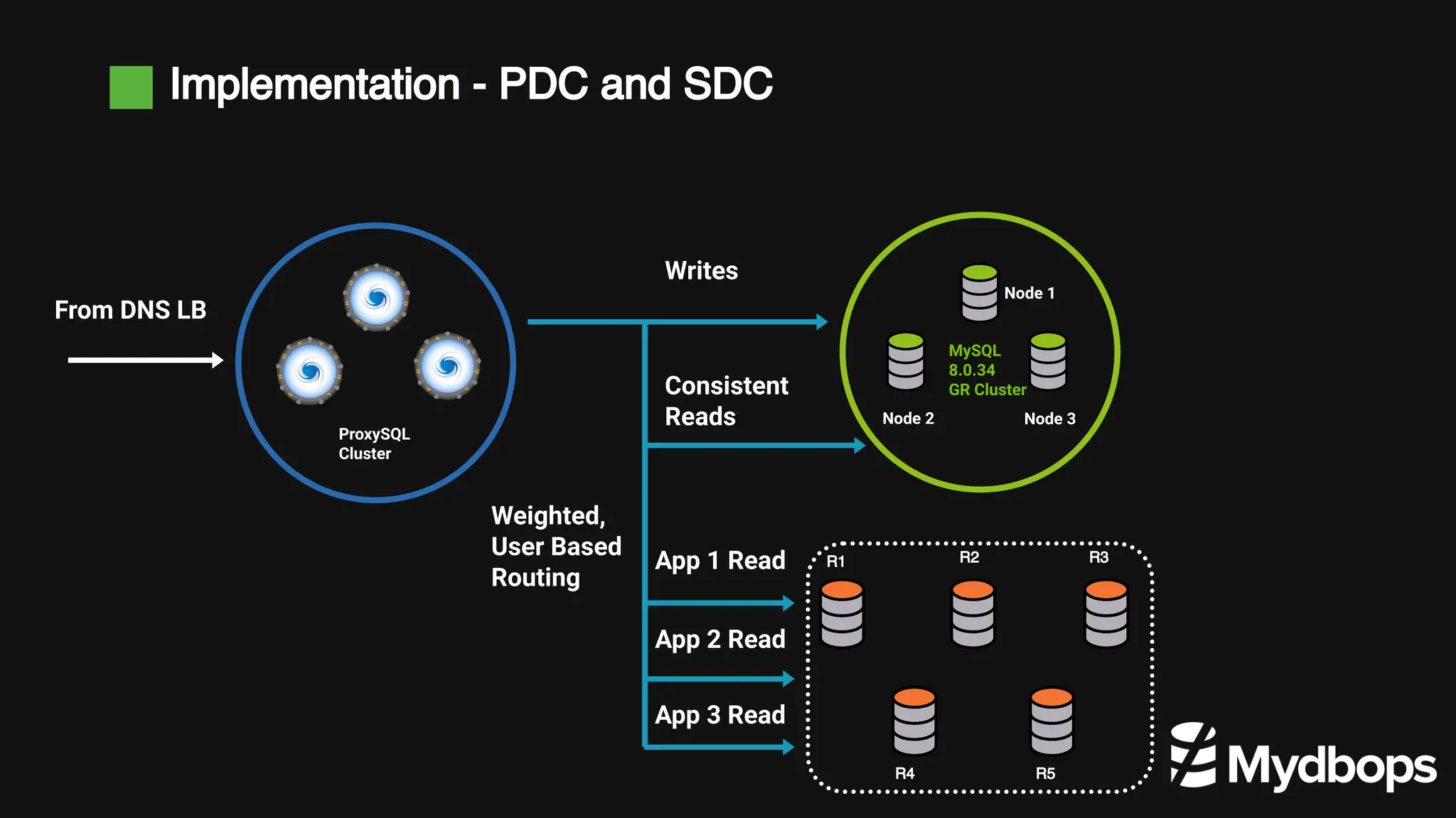
The document details a case study presented by Vinoth Kanna RS at a MyDBOps open-source database meetup, focusing on MySQL database transformation. Key highlights include the discussion of database observability challenges, high availability solutions, replication strategies, and significant operational savings achieved by optimizing infrastructure. The presentation emphasizes the importance of regular audits and defining recovery objectives (RPO and RTO) as part of database management best practices.