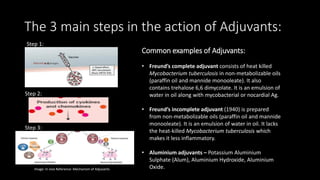
This document discusses the development of polymer-based nanoadjuvants for a hepatitis C virus (HCV) vaccine. It first provides background on vaccines and adjuvants, describing common adjuvants like Freund's complete adjuvant. It then discusses nanoparticles made from polymers like poly lactic-co-glycolic acid (PLGA), which are biodegradable and can effectively encapsulate antigens. One study showed PLGA nanoparticles encapsulating HCV proteins enhanced cellular immunity in mice. The document notes challenges to an HCV vaccine like genetic diversity between virus strains, but suggests surface-modified polymeric nanoparticles may help optimize drug release and targeting to improve vaccine delivery.