Embed presentation
Download to read offline


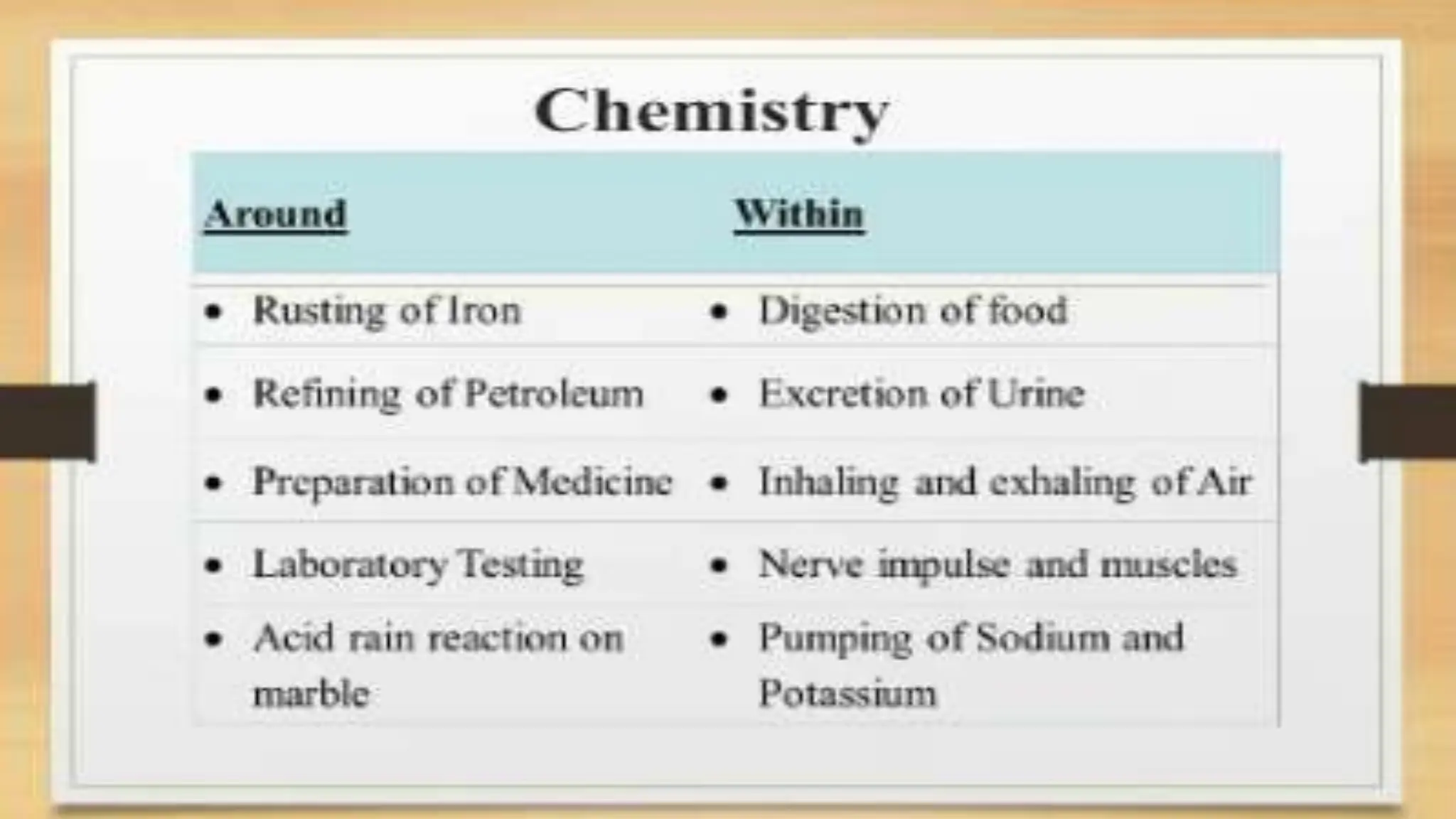











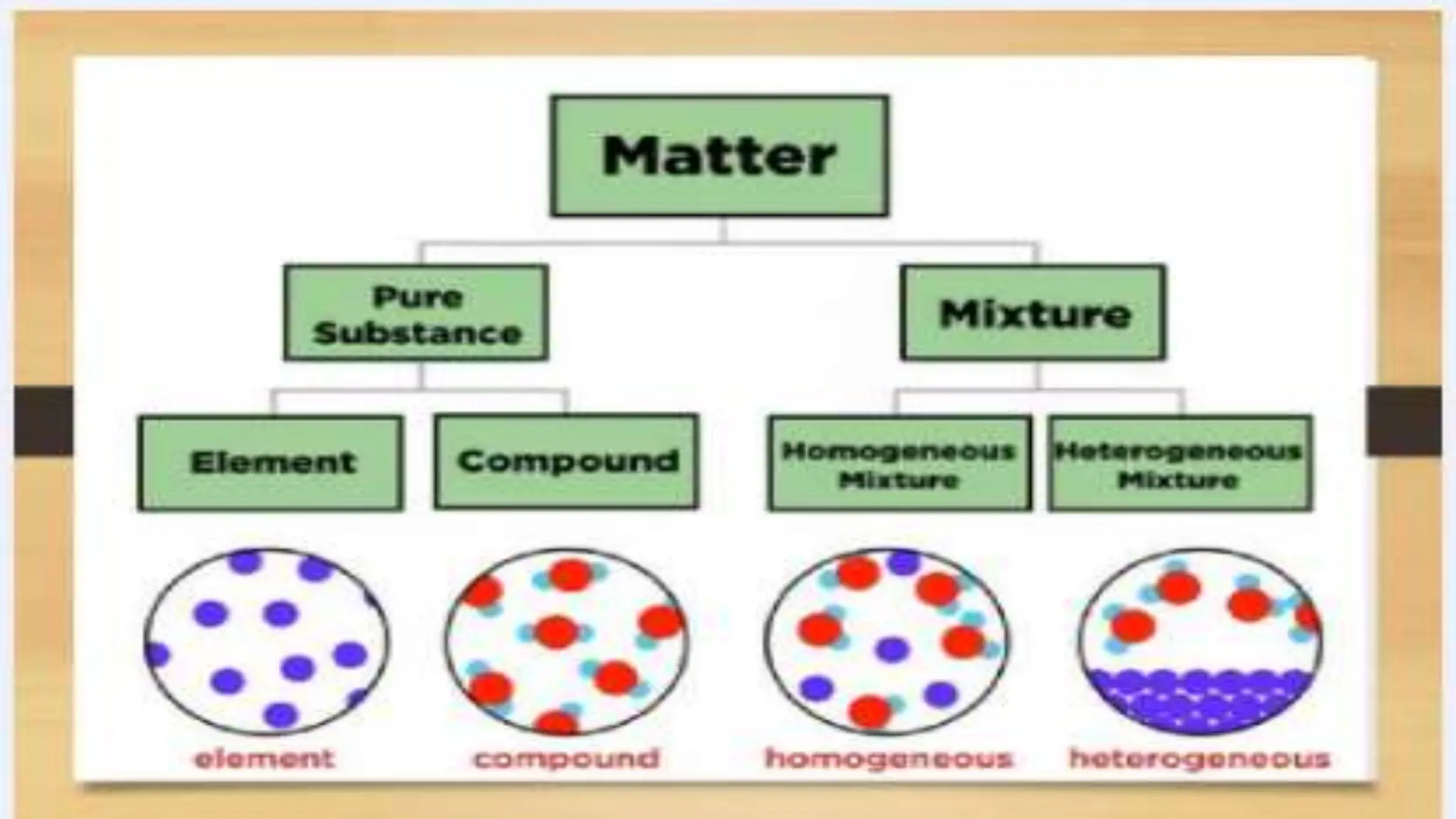












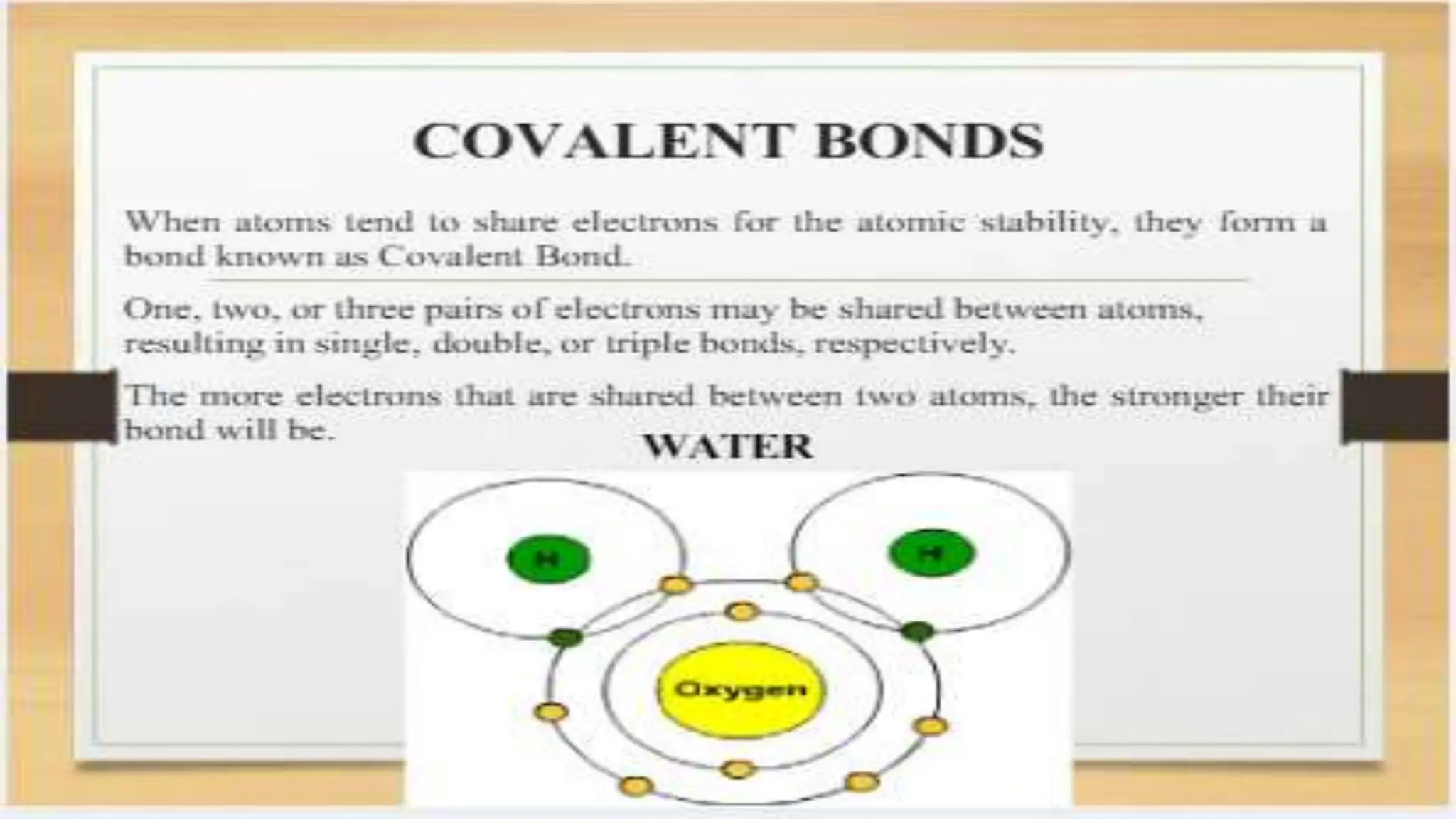
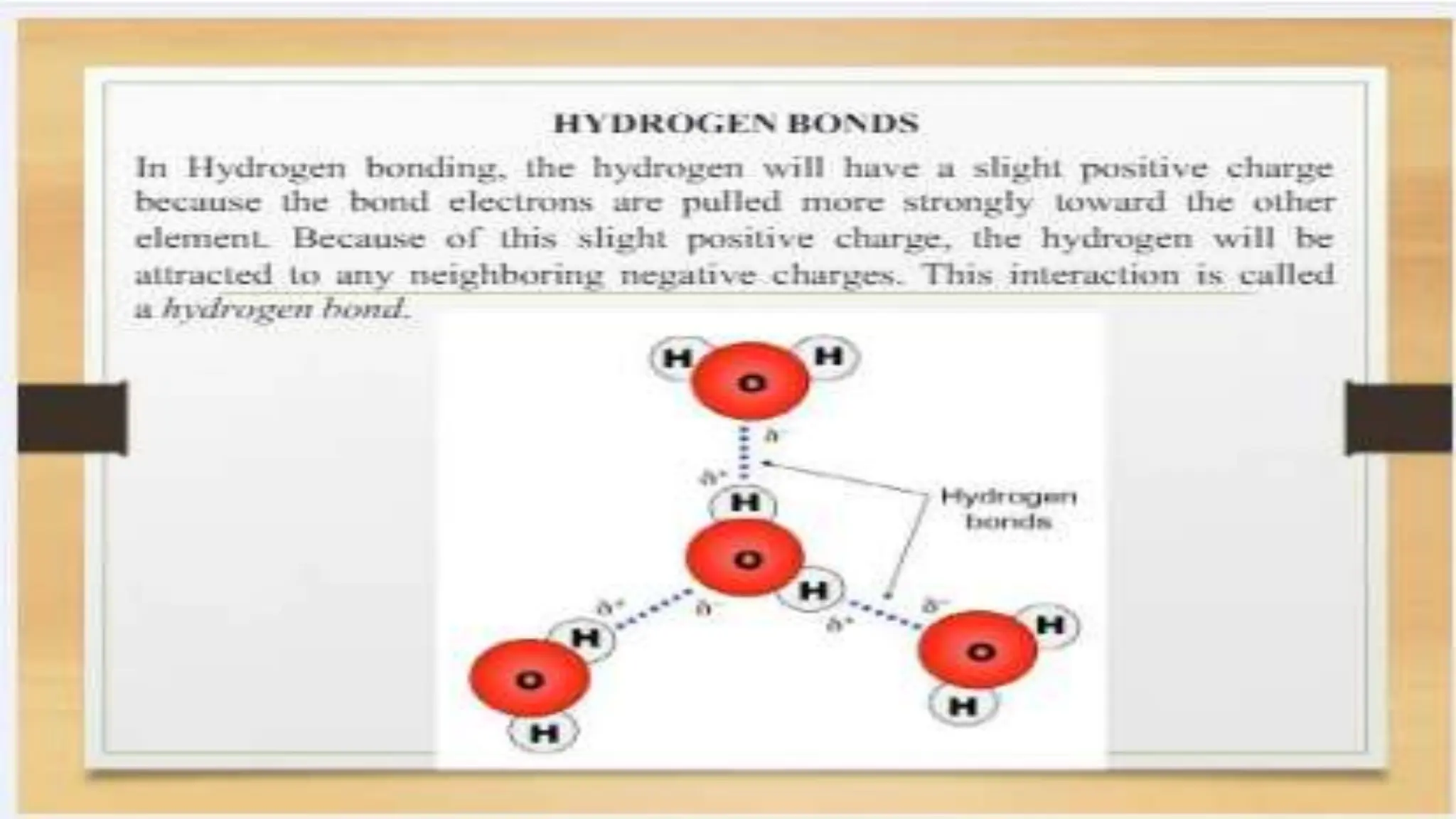




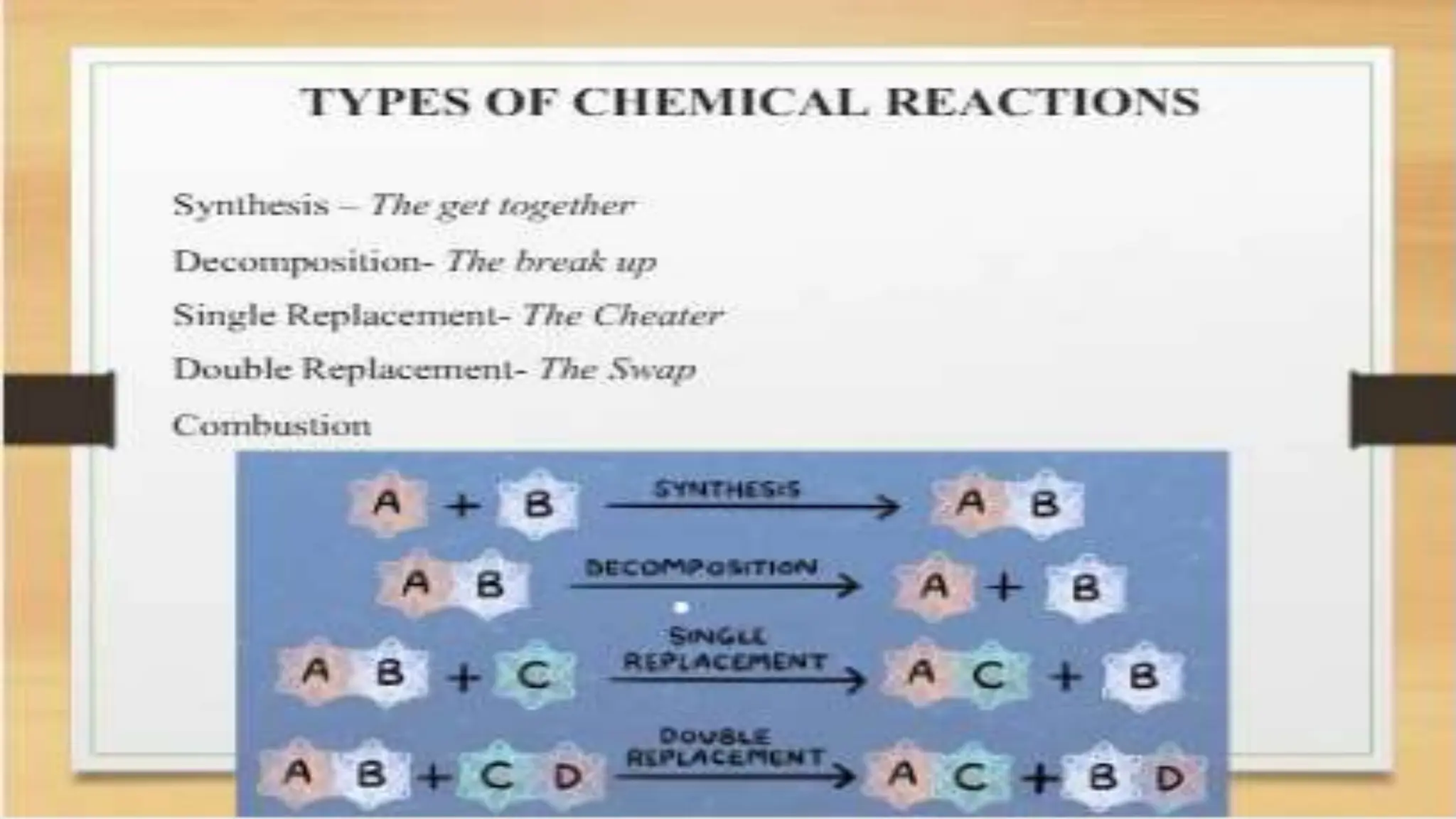

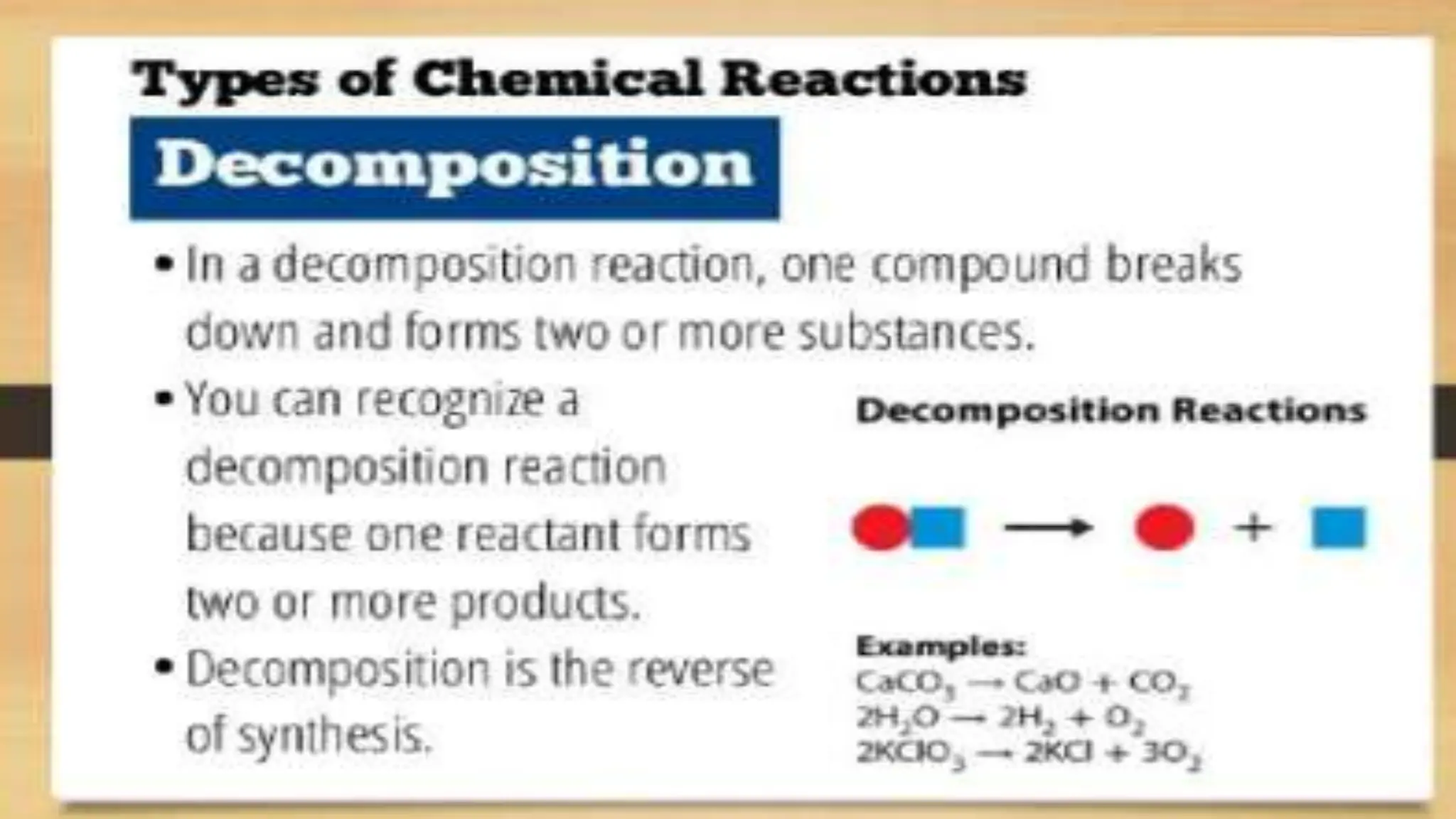

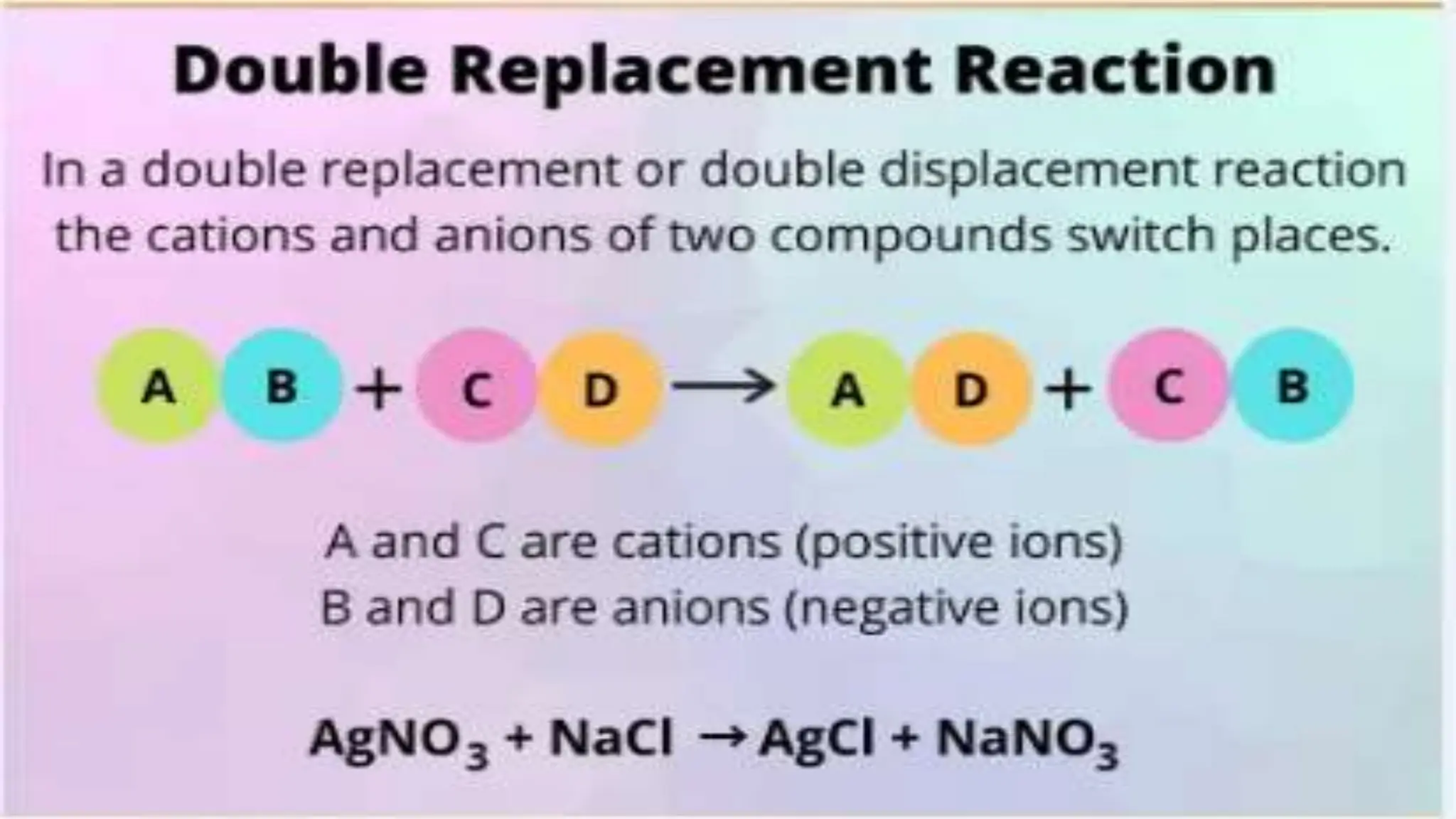
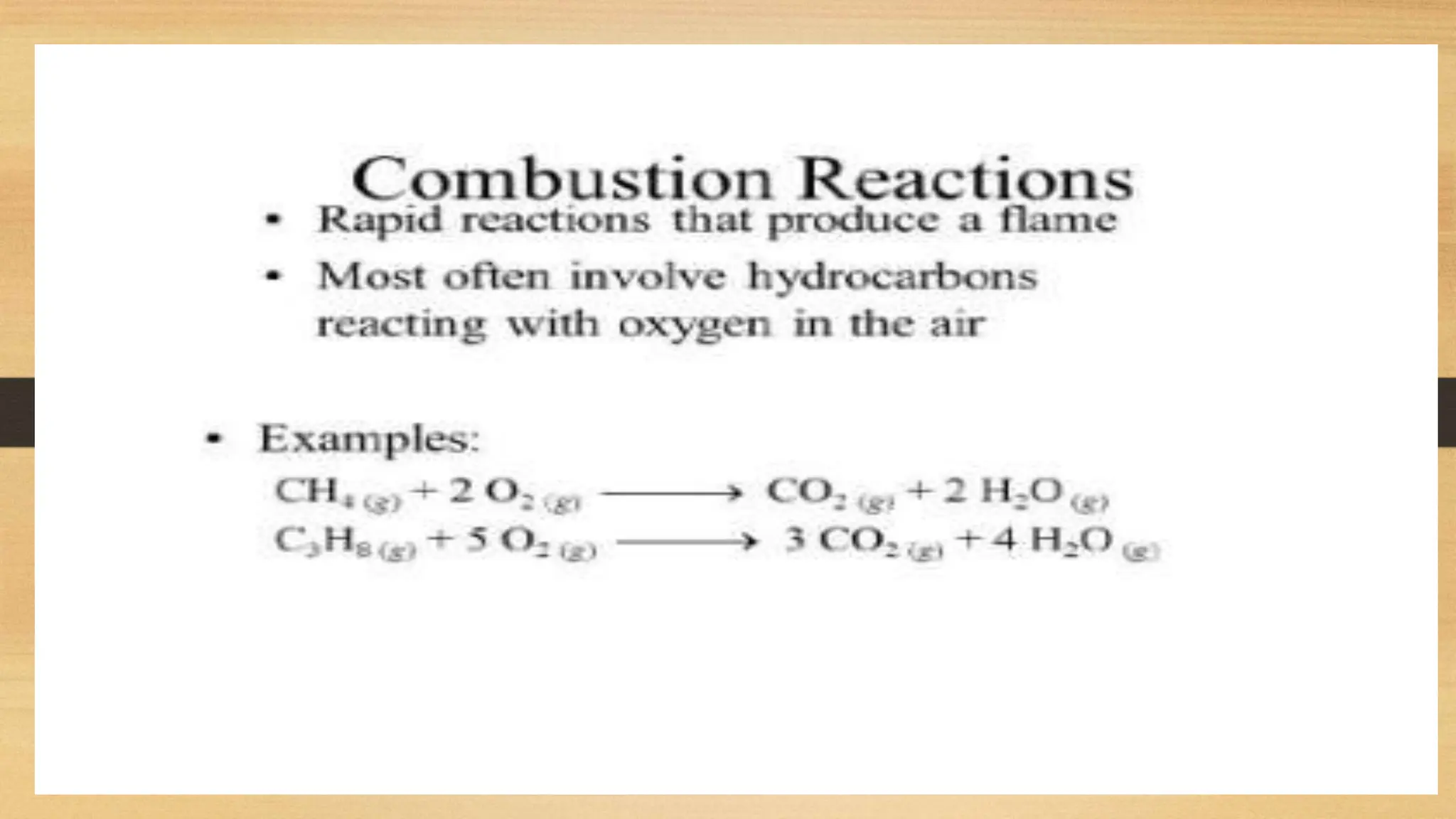







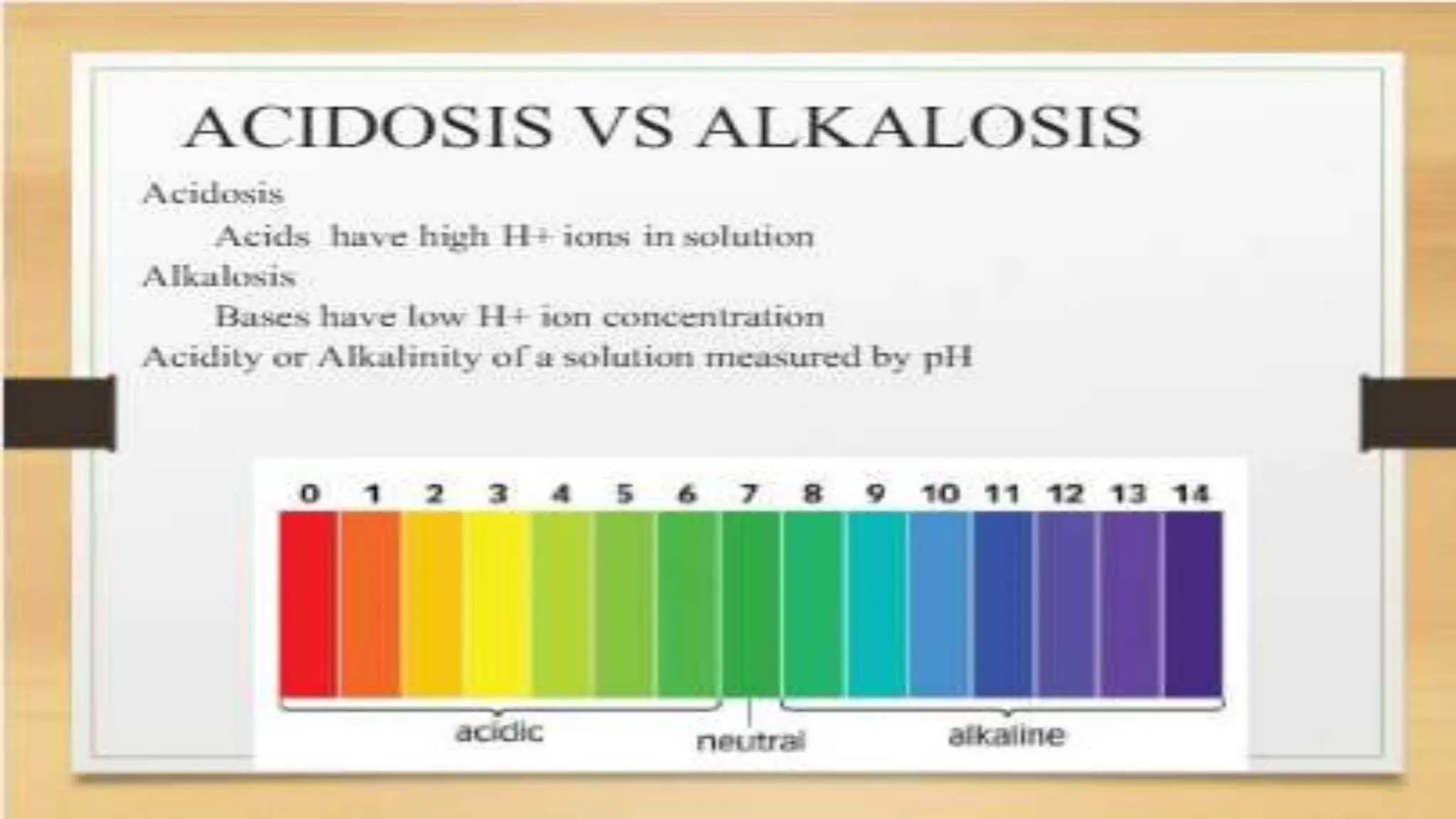
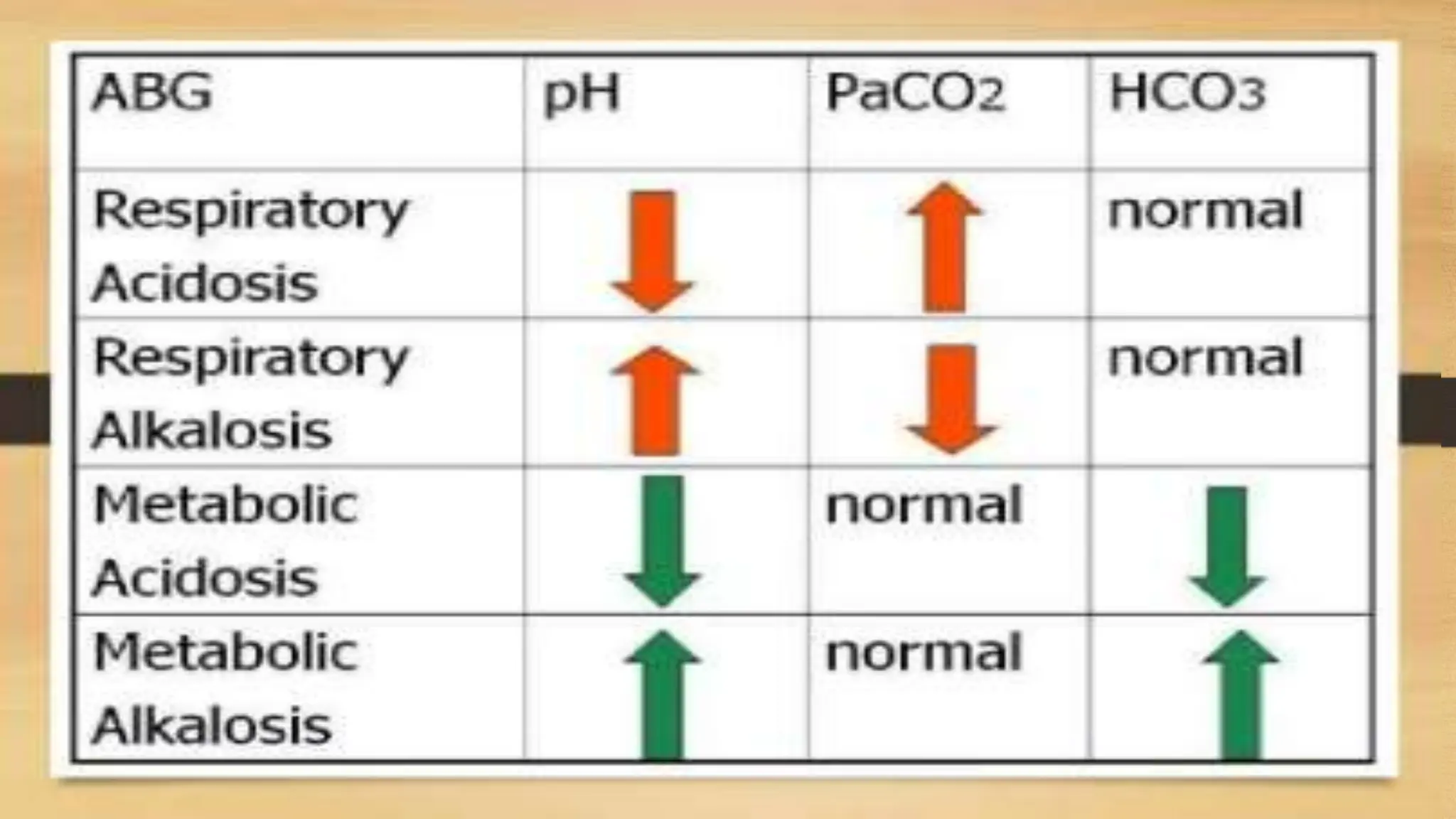


The document covers fundamental concepts of chemistry relevant to biochemistry, including the structure of matter, types of chemical bonds, and various chemical reactions, particularly redox reactions. It also explains the significance of acids, bases, and pH in biological systems, detailing the pH scale and its implications for acidity and basicity. Overall, it emphasizes the importance of chemical principles in understanding biological processes.

















































