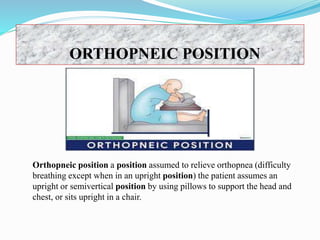
The document discusses various patient positioning techniques used in nursing. It defines positioning as placing a patient in proper body alignment for health purposes. Several positions are described including prone, lateral, supine, lithotomy, Fowler's, Sims, Trendelenburg, and others. The purposes, indications, contraindications and positioning procedures for each are outlined. Positioning aims to promote comfort, circulation and prevent pressure injuries while nurses must follow safety principles and ensure patient comfort.