The document discusses various positions for positioning patients in bed, including:
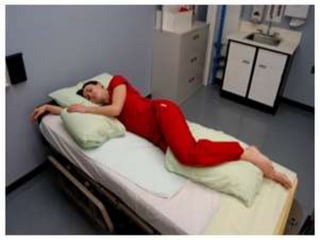
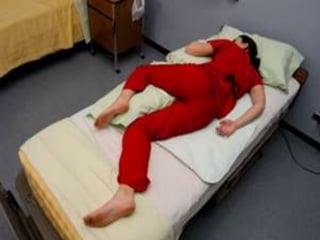
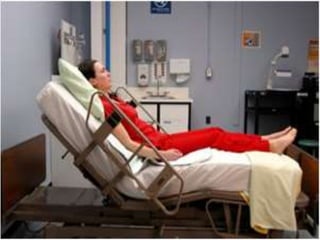
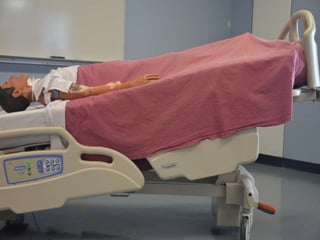
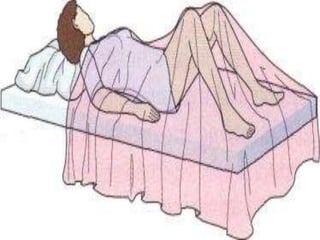
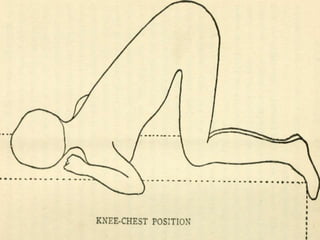
- Supine, prone, lateral, Sims, Fowler's, semi-Fowler's, Trendelenburg, lithotomy, dorsal recumbent, and knee-chest positions.
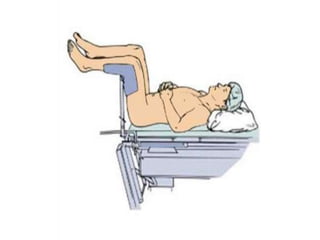
It describes the purposes and principles of positioning patients, and provides details on each position, such as how the patient is placed and when each position is used, like Fowler's position being used to relieve dyspnea and improve circulation.
The document also includes multiple choice questions to test knowledge of positioning, such as semi-Fowler's being the best position for cardiac patients and lithotomy position being used for baby delivery.