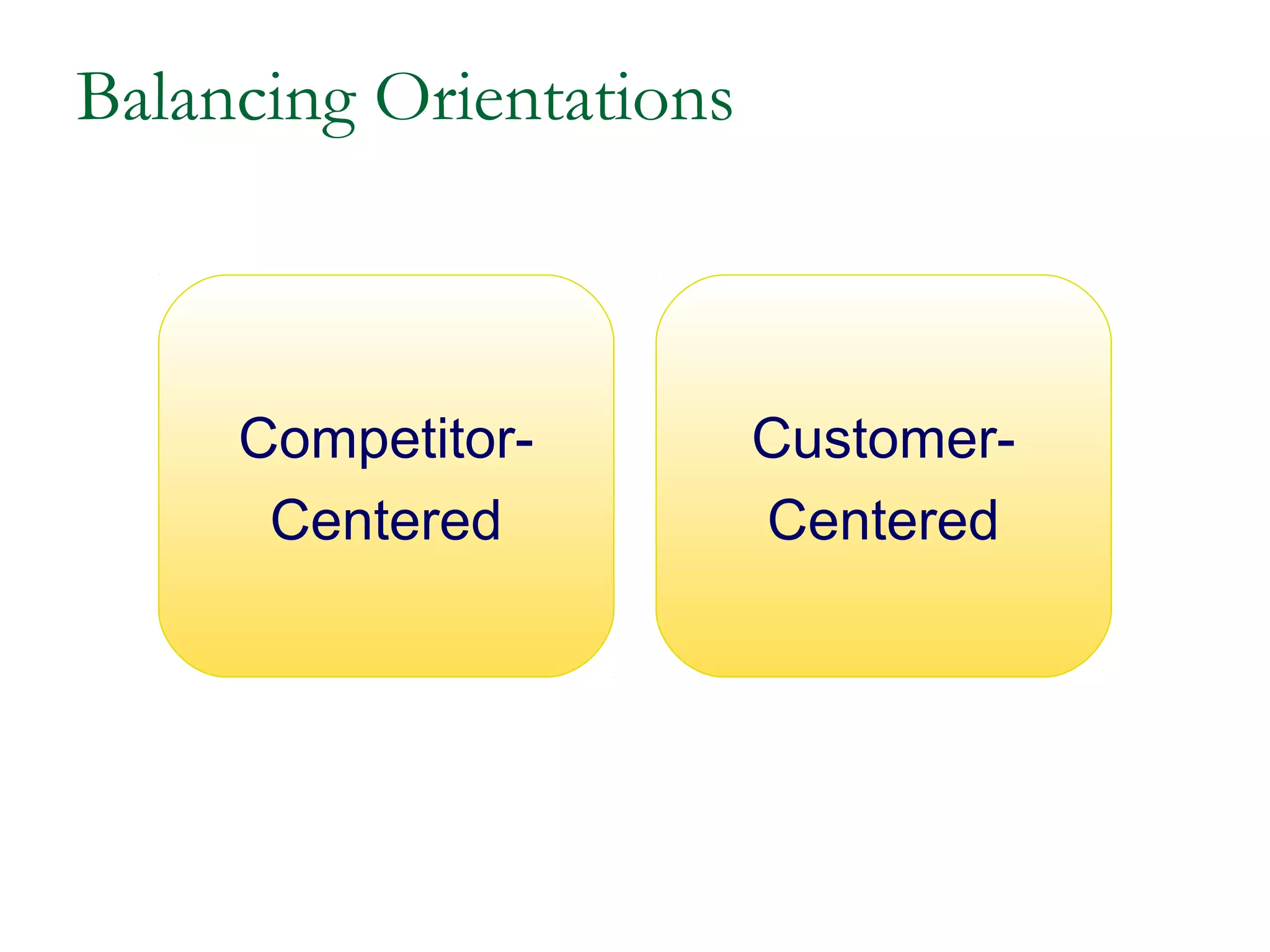
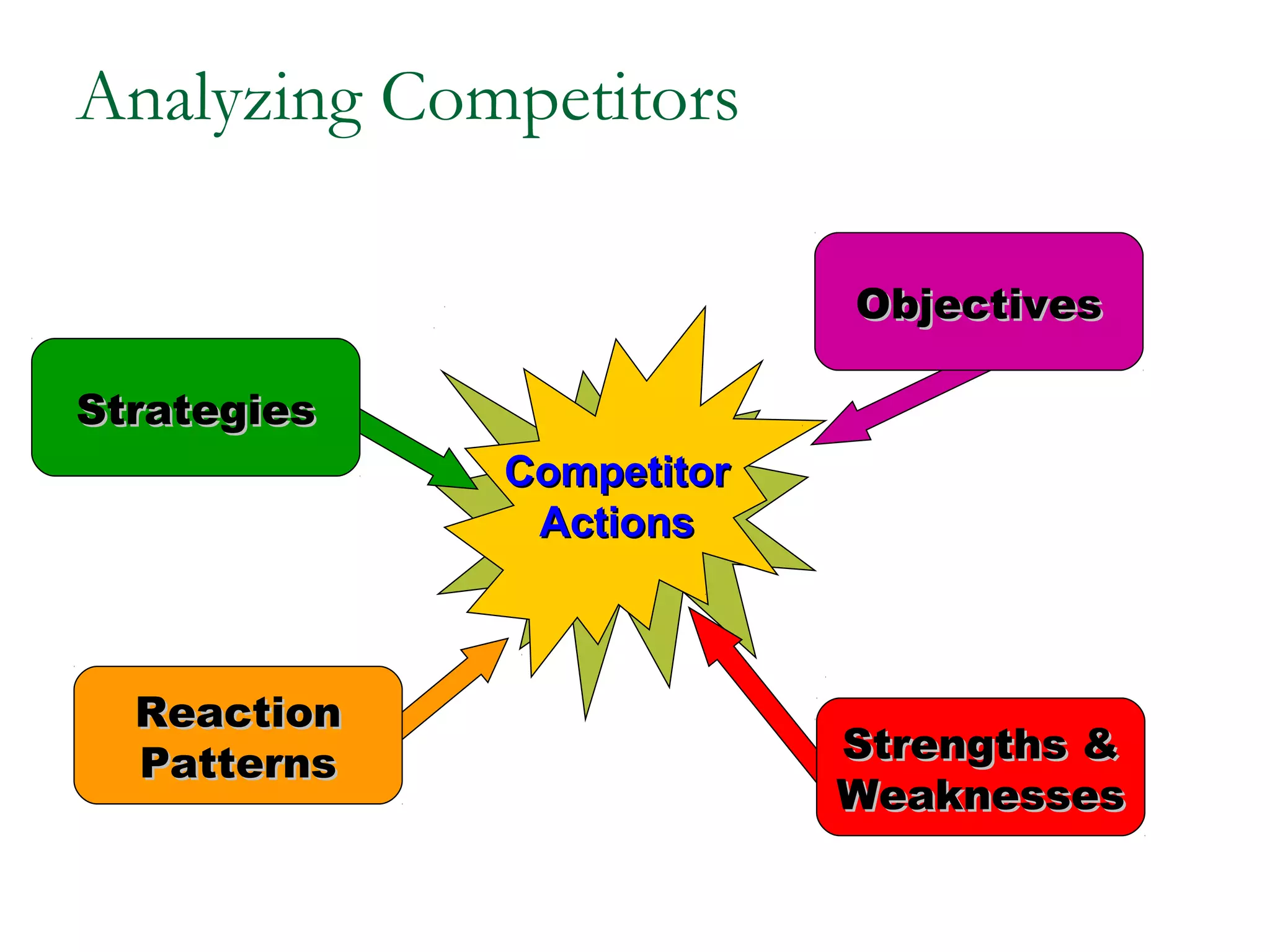
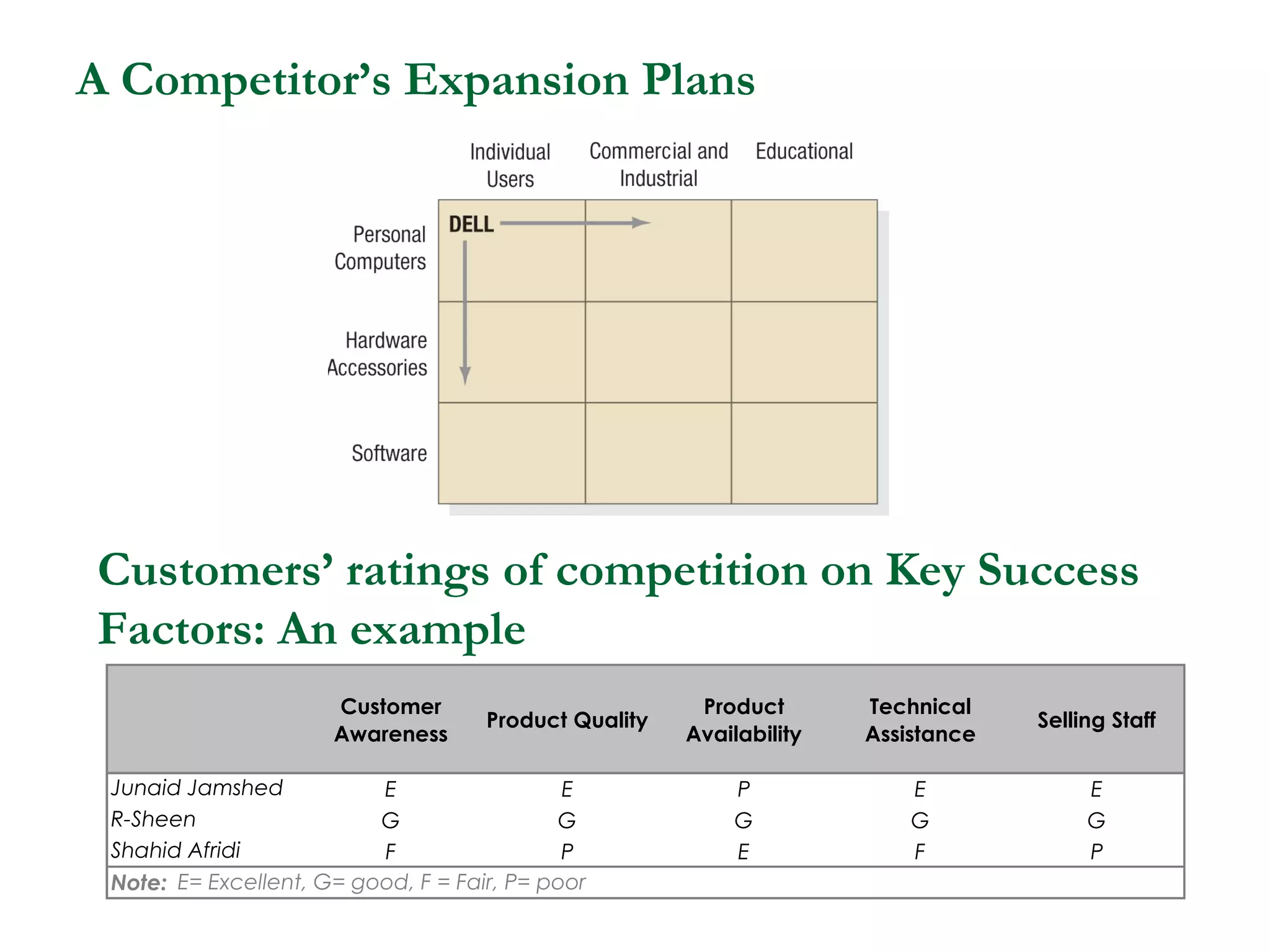
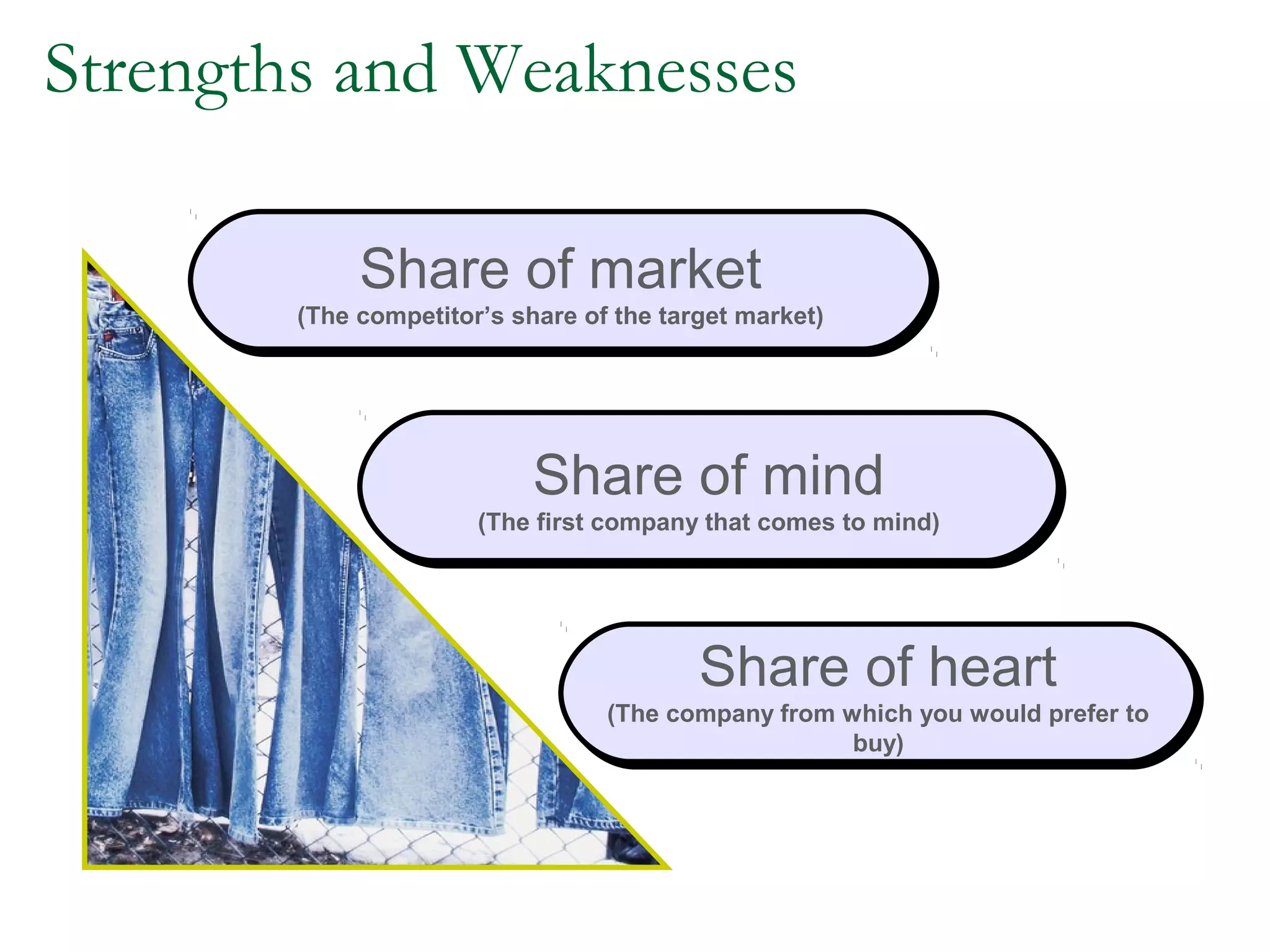
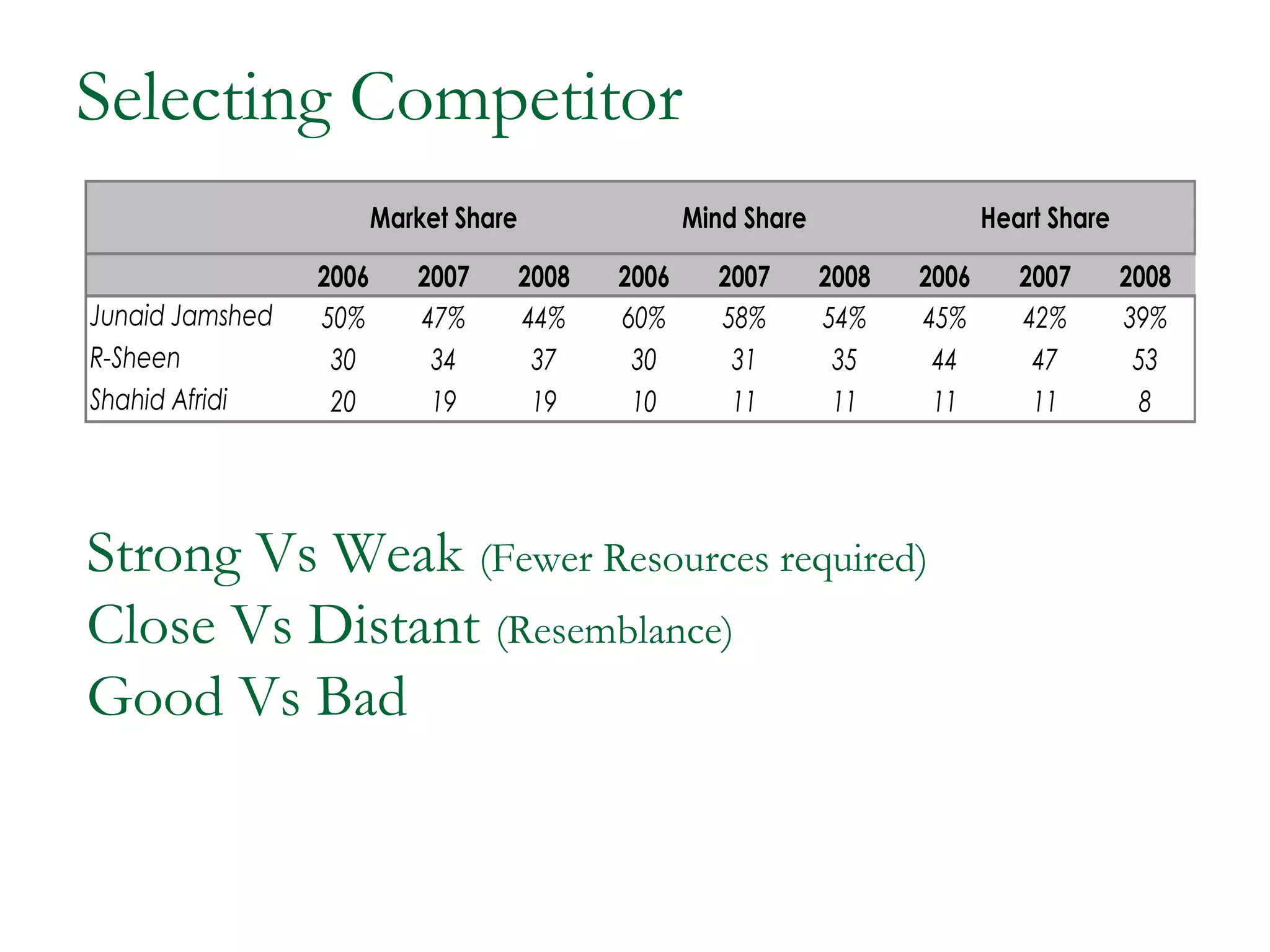
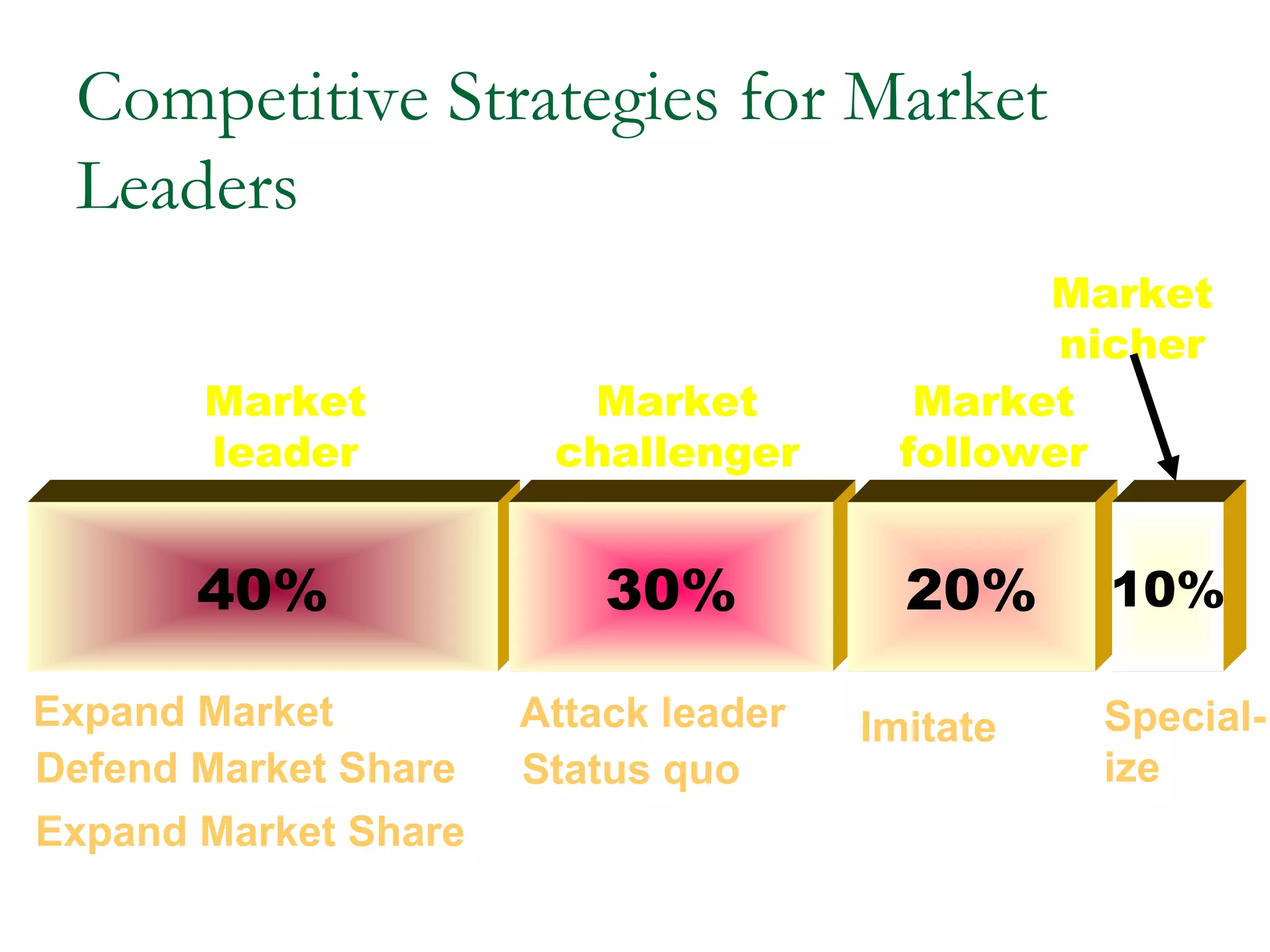
The document discusses different competitive strategies that firms can adopt based on their position in the market. Market leaders aim to expand the total market and defend their market share through creative defense strategies or by attacking competitors. Market challengers seek to gain market share by attacking the market leader through frontal, flank, encirclement, bypass or guerrilla attacks. Market followers imitate the market leader through cloning or adapting. Smaller firms can target market niches not addressed by larger competitors. Firms must balance competitor-centered and customer-centered orientations when developing competitive strategies.
















![Multiple Niching
“[A] firm should `stick to its niching’ but not
necessarily to its niche. That is why multiple
niching is preferable to single niching. By
developing strength in two or more niches the
company increases its chances for survival.”
Philip Kotler](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch9-dealingwithcompetition1-130227071433-phpapp01/75/Ch-9-dealing-with-competition-1-26-2048.jpg)