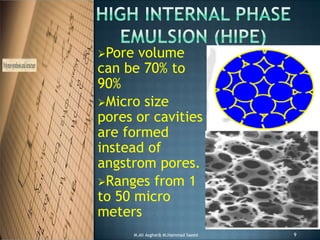
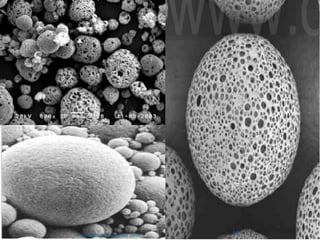
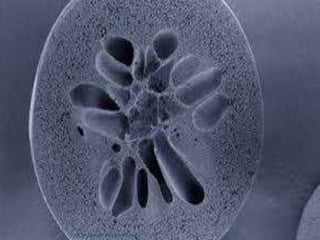
The document discusses porous polymers, covering their morphology, types, properties, and synthesis methods. It highlights micro porous, macro porous, and high internal phase emulsion (HIPE) structures, their pore sizes, and applications in fields like chromatography and vaccine preparation. Additionally, it emphasizes the role of porous polymers in environmental applications, such as oil spill control.