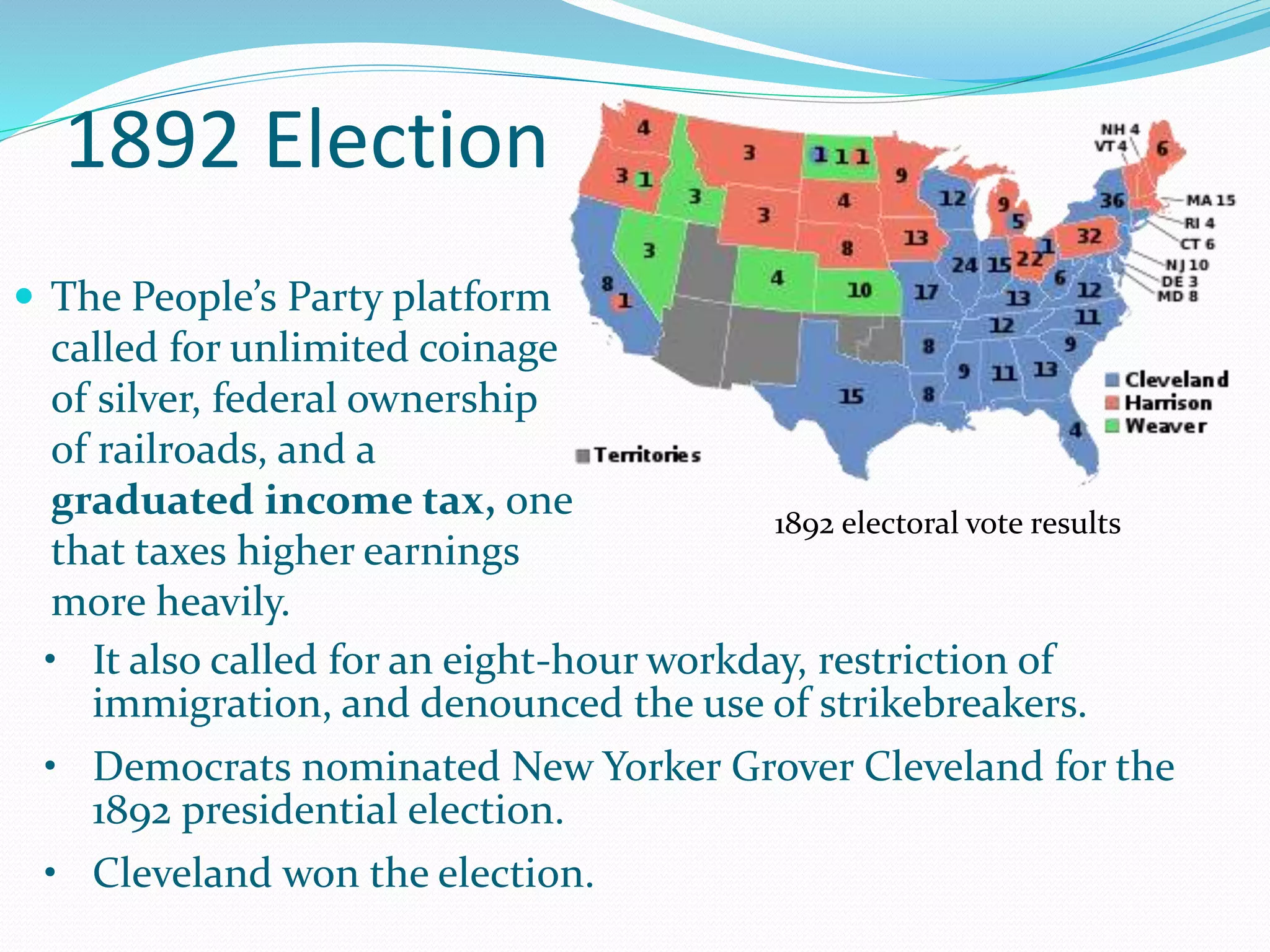
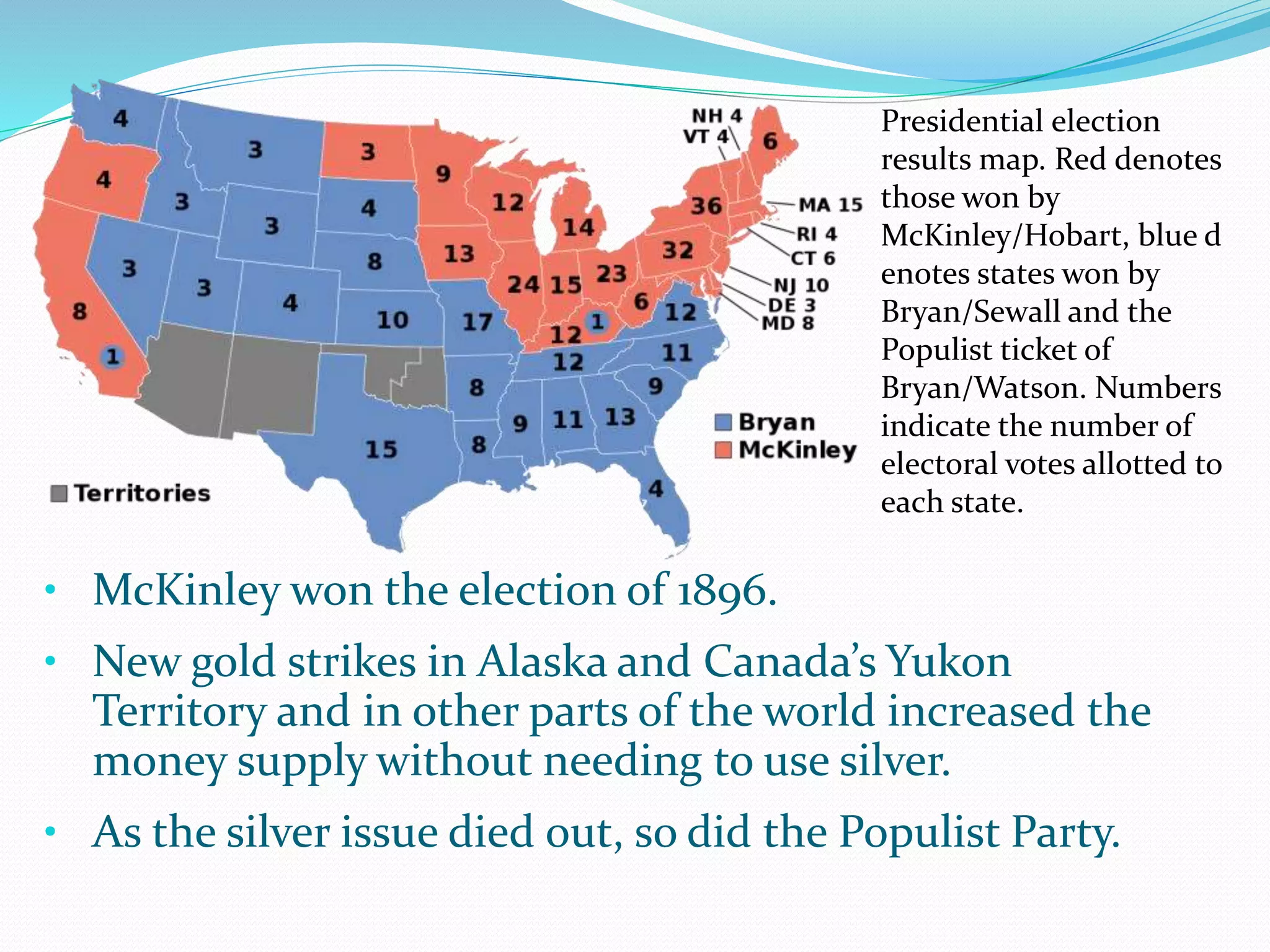
The Farmers' Alliance emerged in the 1890s to politically empower farmers and advocate for their interests. Farmers wanted more currency like greenbacks printed during the Civil War to address deflation that raised interest rates on loans. The Alliance grew but failed to achieve economic reforms. The Populist Party then formed to pursue political solutions through platforms like free silver coinage. Populism gained support but ultimately declined after William McKinley, who opposed free silver, won the 1896 presidential election.