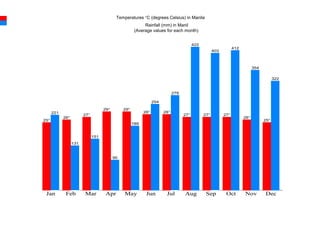
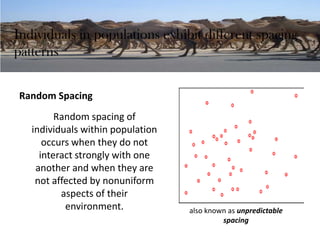
Population ecology is the study of how population sizes change over time and space due to interactions with the environment. A population is a group of the same species living in the same area that can interbreed. Population ranges and the spacing patterns of individuals within those ranges can change due to environmental factors. A metapopulation consists of distinct populations that interact by exchanging individuals, allowing species to persist even when suitable habitat is fragmented.