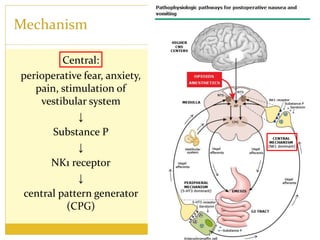
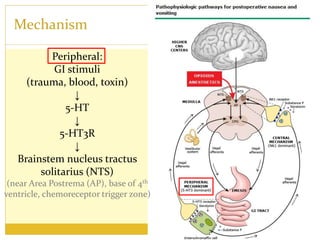
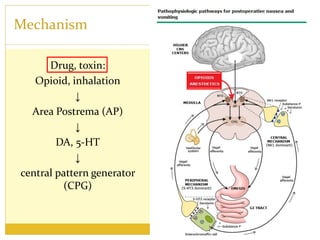
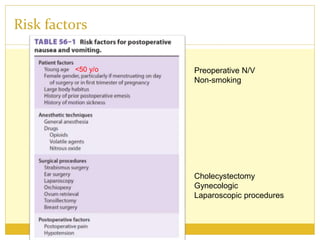
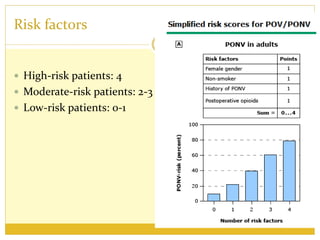
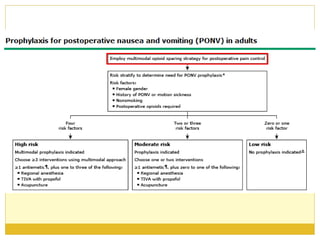
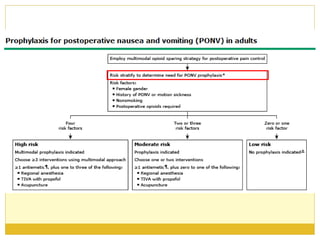
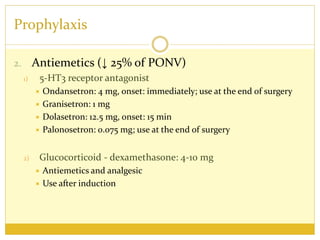
PONV, or postoperative nausea and vomiting, is the most common problem patients experience after surgery requiring anesthesia. It occurs in approximately 30% of patients and is caused by stimulation of various neurotransmitter receptors in the brain and gut. Risk factors include a history of PONV, non-smoking status, age under 50, and certain surgical procedures like cholecystectomy or gynecological surgery. Prophylaxis involves reducing baseline risk factors, administering antiemetics that target the 5-HT3, glucocorticoid, anticholinergic, and neurokinin 1 receptors, and meeting specific discharge criteria once patients have sufficiently recovered.