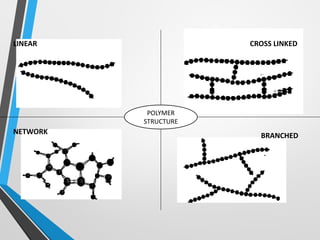
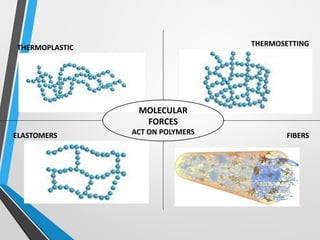
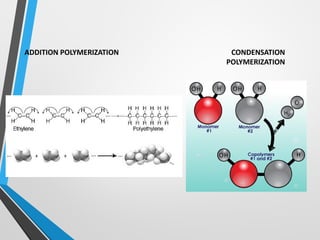
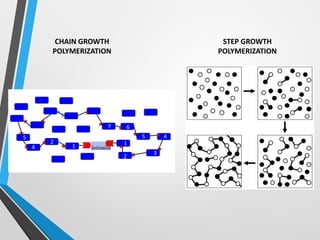
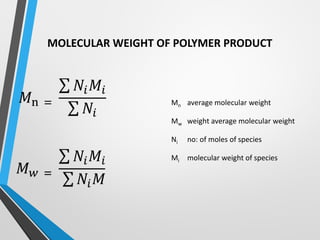
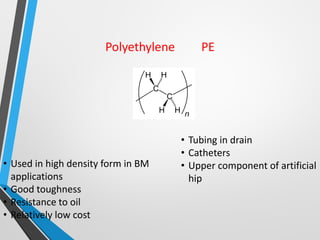
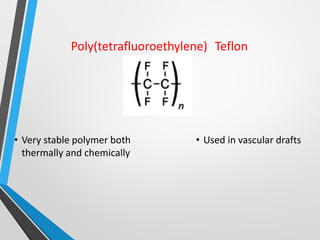
Polymers are long chain molecules composed of repeating structural units. They can be classified based on their structure, molecular forces, and source. Polymers have different structures including linear, branched, cross-linked, and network structures. They are also classified as thermoplastics, elastomers, or thermosettings based on the molecular forces. Polymers can be natural, semi-synthetic, or synthetic and are produced through addition, condensation, step-growth, or chain-growth polymerization. Common medical polymers include polyethylene, polytetrafluoroethylene, polyvinyl chloride, nylon, and implantable polymers like polyethylene and bioresorbable polymers.

![POLYMER
S
LONG CHAIN
MOLECULES COMPLEX
[CH2 ]n](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/polymers-180721115008/85/Polymers-2-320.jpg)