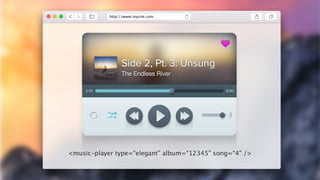
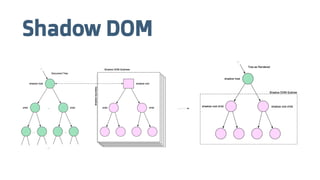
The document provides an introduction to web components and the Polymer library, highlighting their modularity and ease of use for developers. It explains key concepts such as templates, decorators, shadow DOM, and custom elements, as well as Polymer's support for material design and data binding. Additionally, it discusses the need for polyfills for browser compatibility and compares Polymer with Angular, emphasizing the benefits of open standards.