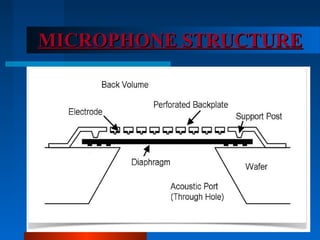
This document provides an outline and overview of MEMS microphones. It begins with an introduction to MEMS technology and how it can be used to implement microphones. It then describes the typical structure of a MEMS microphone, including a fixed backplate and movable membrane, and how sound waves cause the membrane to flex and create changes in capacitance to convert sound to electrical signals. Key performance parameters like sensitivity, noise floor, dynamic range, and applications are discussed. Advantages of MEMS microphones are their small size, ability to withstand vibrations, ease of integration with CMOS processes, and good noise cancellation and signal-to-noise ratio.