The document discusses various topics related to political ideologies including:
1. It defines ideology as a "science of ideas" coined during the French Revolution to describe a set of beliefs and commitments to change political systems.
2. It identifies several characteristics of ideologies such as having names that end in "-ism", providing explanations for problems while presenting futuristic visions, and mobilizing large groups of people.
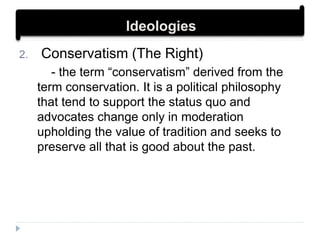
3. Several major ideologies are described briefly - liberalism, conservatism, socialism, feminism, environmentalism, and others. Key values and beliefs that define each ideology are outlined.