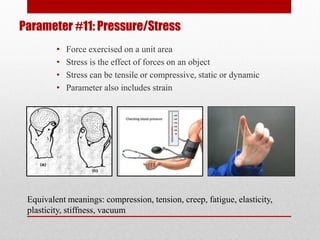
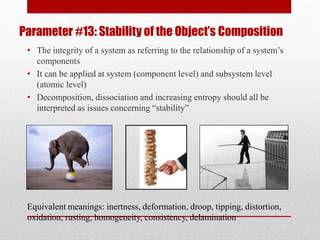
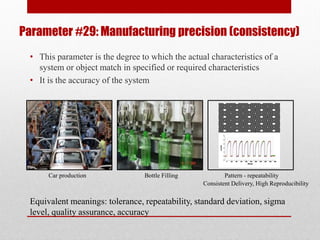
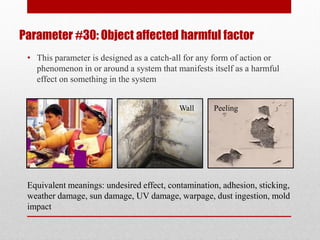
The document defines 39 system parameters that can be used to describe characteristics of a system and determine or limit its performance. The parameters include attributes like the weight, size, speed, temperature, energy use, and complexity of moving and stationary objects within a system. Each parameter is then defined in more detail, providing equivalent terms and examples.