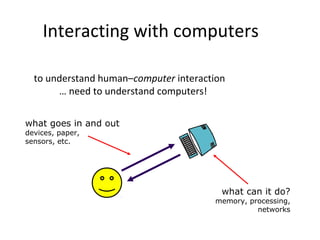
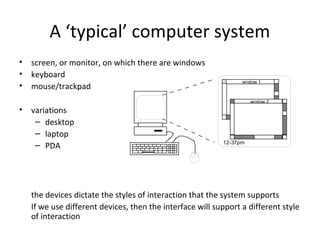
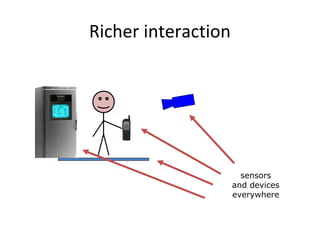
The document discusses the elements that make up a computer system and how they affect human-computer interaction. It notes that input devices like keyboards and pointing devices, as well as output screens, virtual reality devices, and physical interaction tools all shape the interaction style a system supports. The document also addresses how memory capacity and processing speed influence what a computer can do and provides examples of common computer devices found in homes and on persons.