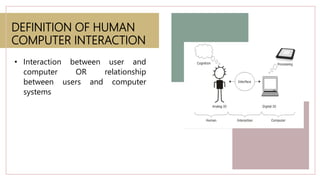
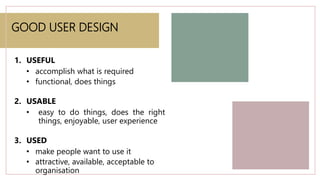
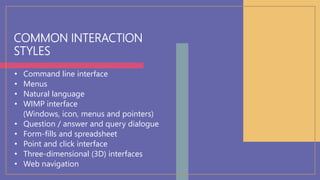
This document provides an introduction to human-computer interaction. It defines HCI as the interaction between users and computer systems. The three fundamental components of HCI are the human user, computer system, and interactive process between them. The goals of HCI are to improve usability and design systems that minimize barriers between the human and computer models of tasks. User interface design is crucial to HCI as it mediates interaction and conceptual models. Input/output devices, interaction styles, and computer technologies influence the nature of interaction.