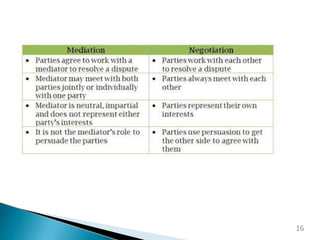
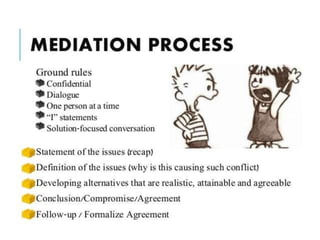
Contract administration involves managing the agreement between an employer/client and contractor to ensure objectives are met on time and within budget. It also requires monitoring performance for deficiencies and resolving conflicts. Key stakeholders in a construction project include design teams, clients, contractors, and project managers. Managing contract risk involves identifying, analyzing, evaluating, and treating risks, as well as monitoring risks over time. Disputes can be resolved through negotiation between parties or mediation with a neutral third party to reach an agreed settlement.