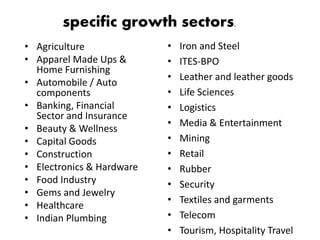
The document provides information on Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana (PMKVY) scheme in India. It discusses the objective of the scheme which is to provide skills training and monetary rewards to Indian youth. It details the eligible sectors for training, role of National Skill Development Corporation as implementing agency, monetary rewards provided under the scheme and strategy of implementing the scheme through public-private partnerships.























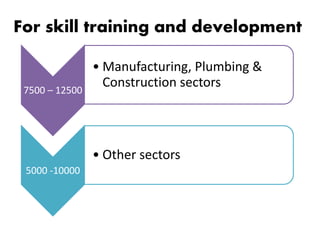
![For Recognition of Prior Learning [RPL]
2500
• Manufacturing, Plumbing &
Construction sectors
2000
• Other sectors](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pmky-22ndbatchbleader-deepu-161222143334/85/Pmky-by-prime-minister-25-320.jpg)