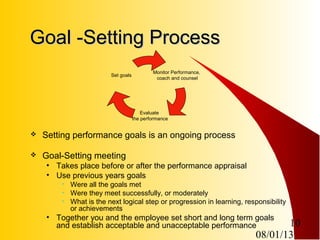
This document outlines an agenda and presentation for a performance management training for managers and supervisors. The training covers the performance management process, developing SMART goals and objectives, using a revised performance appraisal tool, conducting annual and mid-year reviews, and reinforcement strategies. It provides details on setting goals, documenting performance, evaluating performance, and completing performance appraisals. The objectives are to help managers understand and effectively implement the company's performance management system.