Embed presentation
Downloaded 14 times







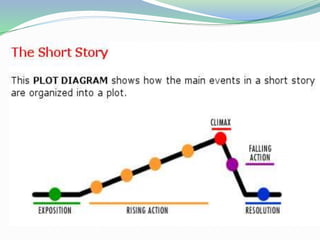

The document outlines the five basic elements that structure a plot: 1) Exposition establishes the characters, setting, and main conflict. 2) Rising action introduces problems that create tension. 3) The climax is the main event where the character faces their greatest challenge. 4) Falling action shows the results of actions from the climax. 5) Resolution concludes the story by resolving conflicts and tying up loose ends.







