Embed presentation
Download to read offline



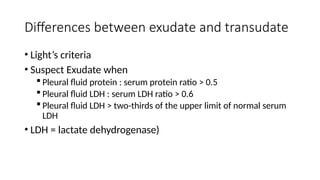


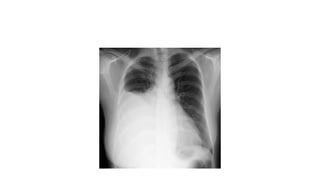

Pleural effusion, or hydrothorax, is the accumulation of serous fluid in the pleural cavity, which can be unilateral or bilateral and is clinically detectable when approximately 0.5 liters is present. It can be classified as transudate or exudate based on protein content, with transudates (<30g/l) typically resulting from systemic conditions like cardiac or liver failure, while exudates (>30g/l) arise from inflammatory or neoplastic processes. Clinical features include chest pain, cough, and difficulty in breathing, with specific physical examination signs indicating the presence of pleural effusion.







