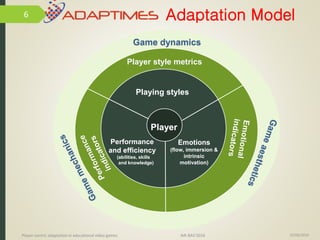
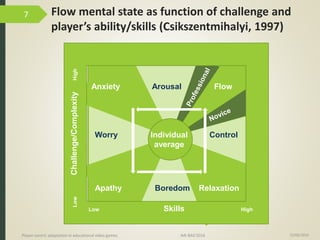
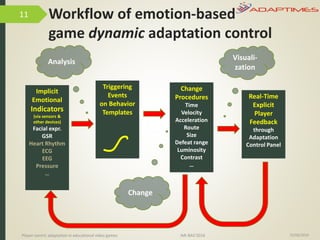
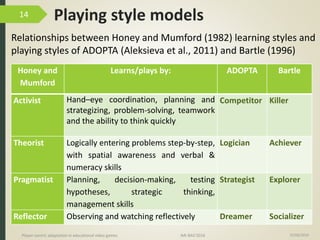
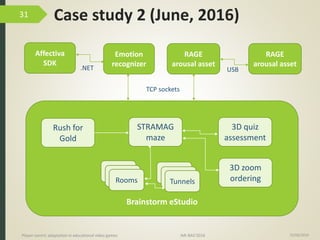
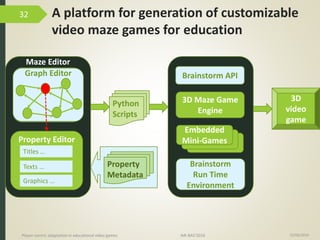
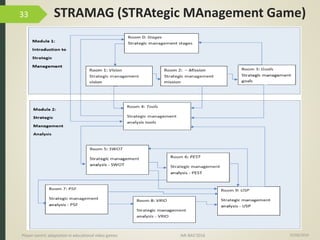
1) The document discusses player-centric adaptation in educational video games. It focuses on player modeling and using a player's performance, emotions, and playing style to dynamically adapt game features.
2) An experiment was conducted with 34 participants playing an action game called "Rush for Gold" that adapted based on the player's emotions. Players who experienced emotion-based adaptation reported higher preference and performance.
3) Analysis found correlations between a player's implicit and explicit playing styles. It also found that adapting brightness/contrast impacted puzzle versus discovery performance differently. Adaptation improved the game experience overall.