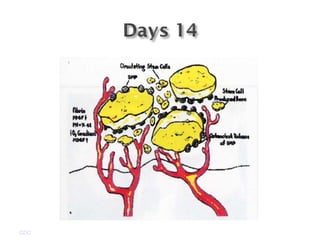
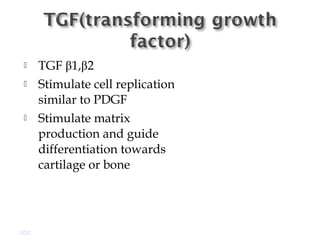
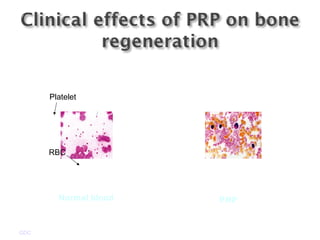
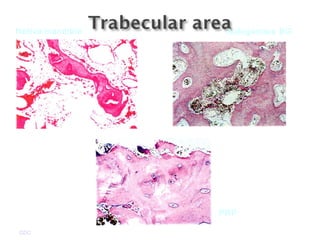
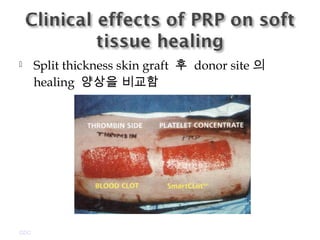
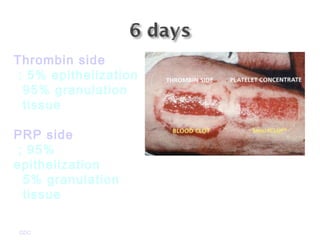
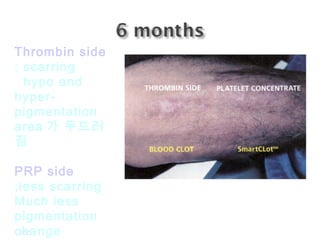
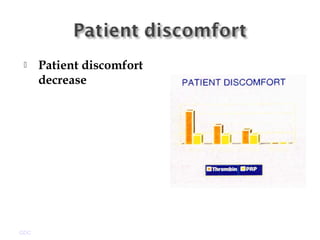
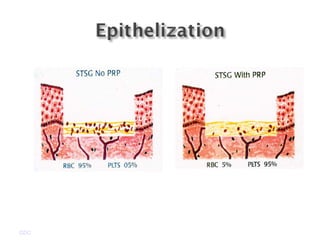
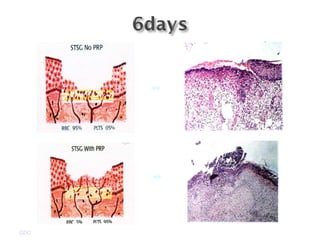
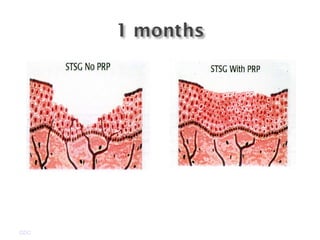
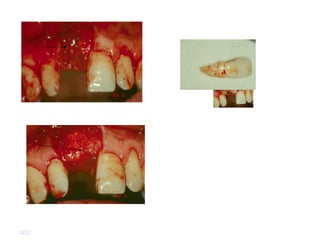
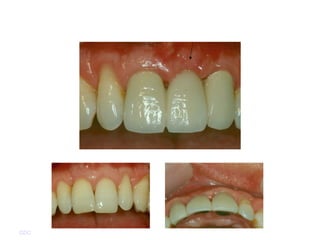
Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) is a concentrated source of autologous platelets that contain at least 7 different growth factors. When platelets are activated after injury, these growth factors are released from the alpha granules and promote processes like bone and soft tissue healing, angiogenesis, and re-epithelization. Studies have shown PRP can stimulate more rapid bone formation and earlier bone maturation compared to autogenous bone grafts. PRP has also been shown to reduce scarring and pigmentation changes at skin graft donor sites compared to the use of thrombin as the clot activator. However, PRP requires the use of bovine thrombin which carries risks like potential transmission of diseases.