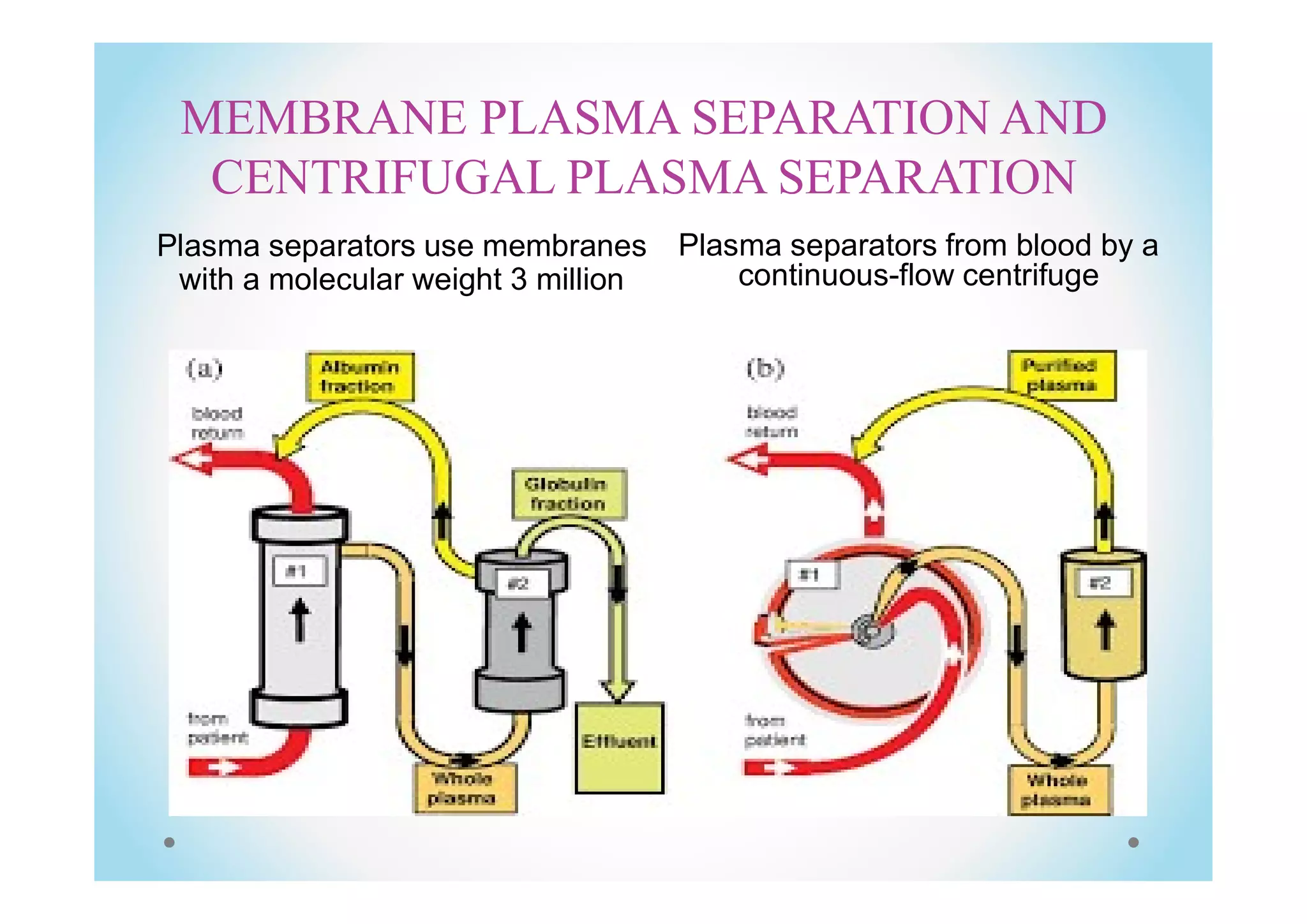
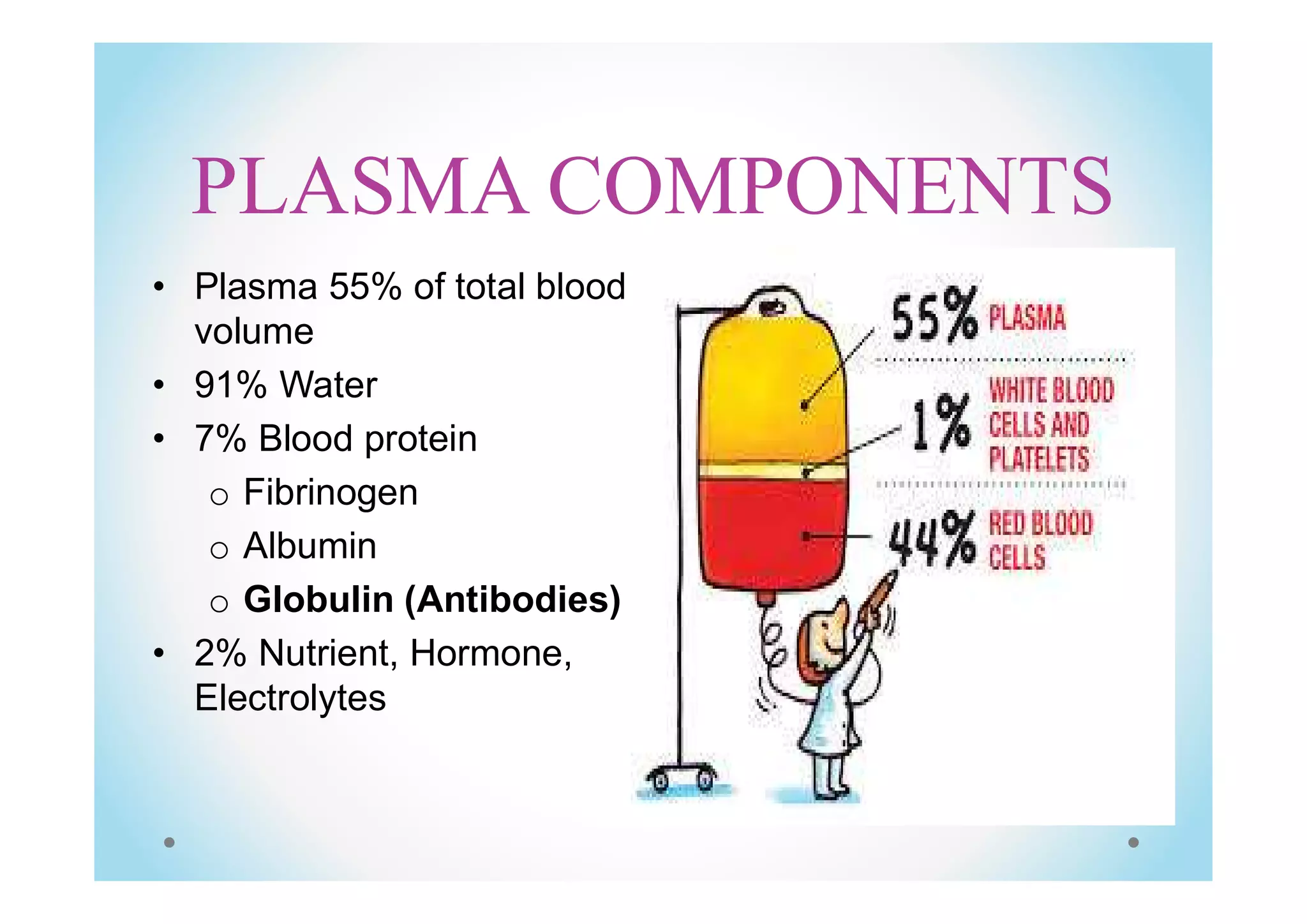
Plasma exchange, or plasmapheresis, is a treatment used for neurological autoimmune disorders by separating and replacing blood plasma to remove harmful antibodies. The document details the procedure, including the use of centrifugal and membrane plasma separation, potential adverse reactions, and the essential role of nursing in administering the treatment. A case report illustrates its effectiveness in a patient with acute relapse multiple sclerosis, highlighting the need for ongoing management and patient support.