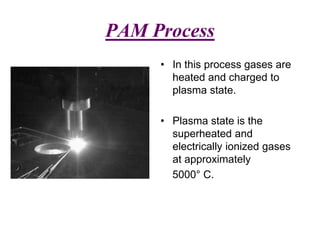
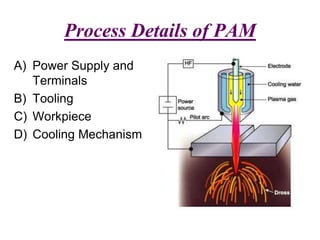
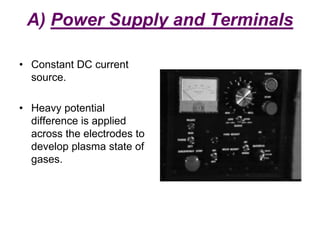
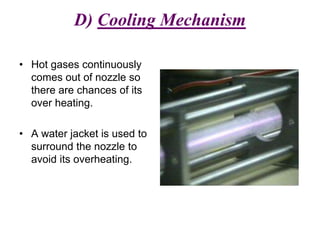
Plasma Arc Machining (PAM) utilizes a high-velocity jet of superheated gas to cut through various metals by melting and displacing material. The process uses different gases depending on the thickness and type of material, with advantages such as fast production rates and the ability to machine hard materials, though it comes with high initial costs and requires safety precautions. PAM is primarily used for profile cutting and machining small, difficult materials, necessitating operator training and safety gear.