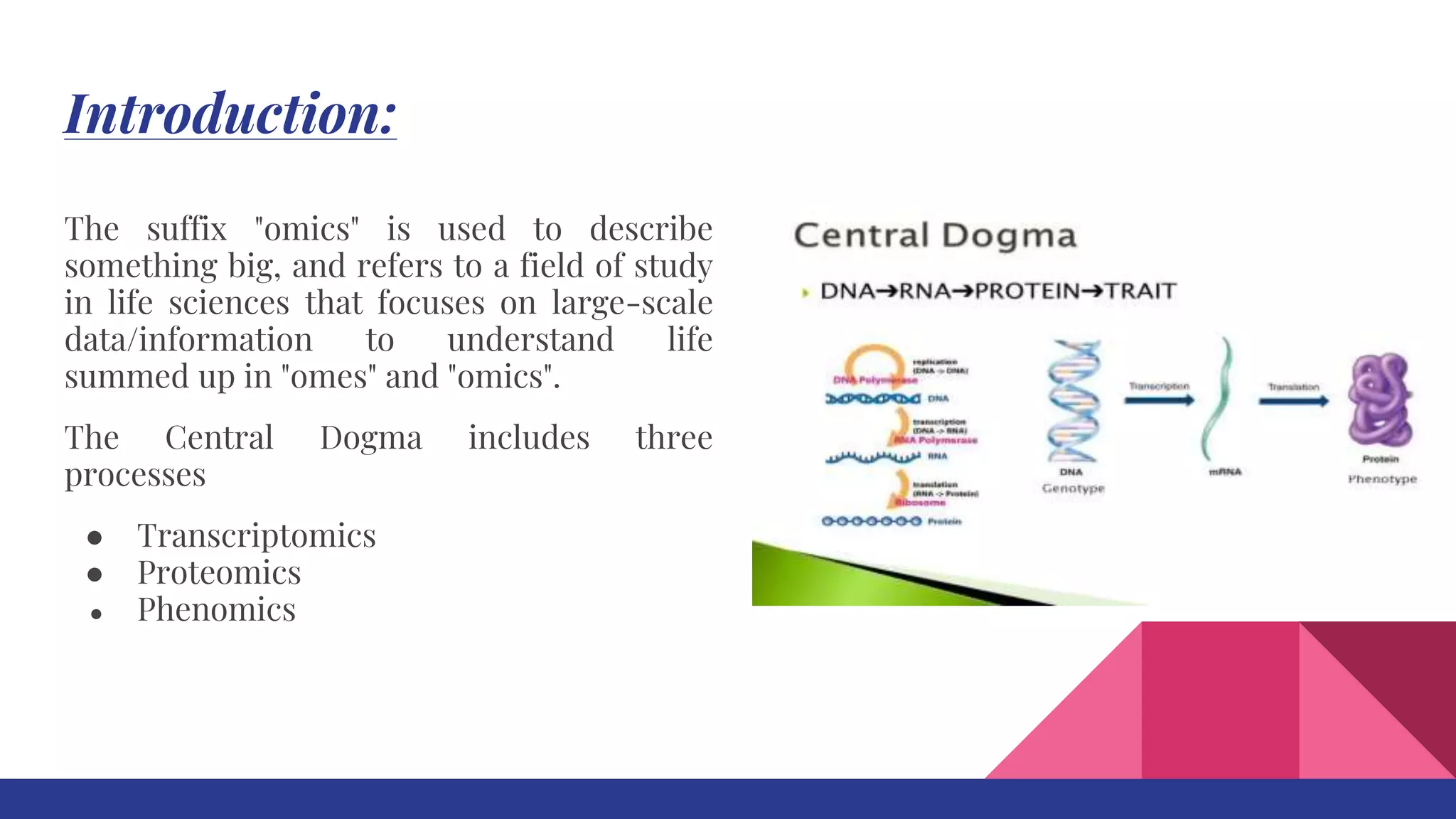
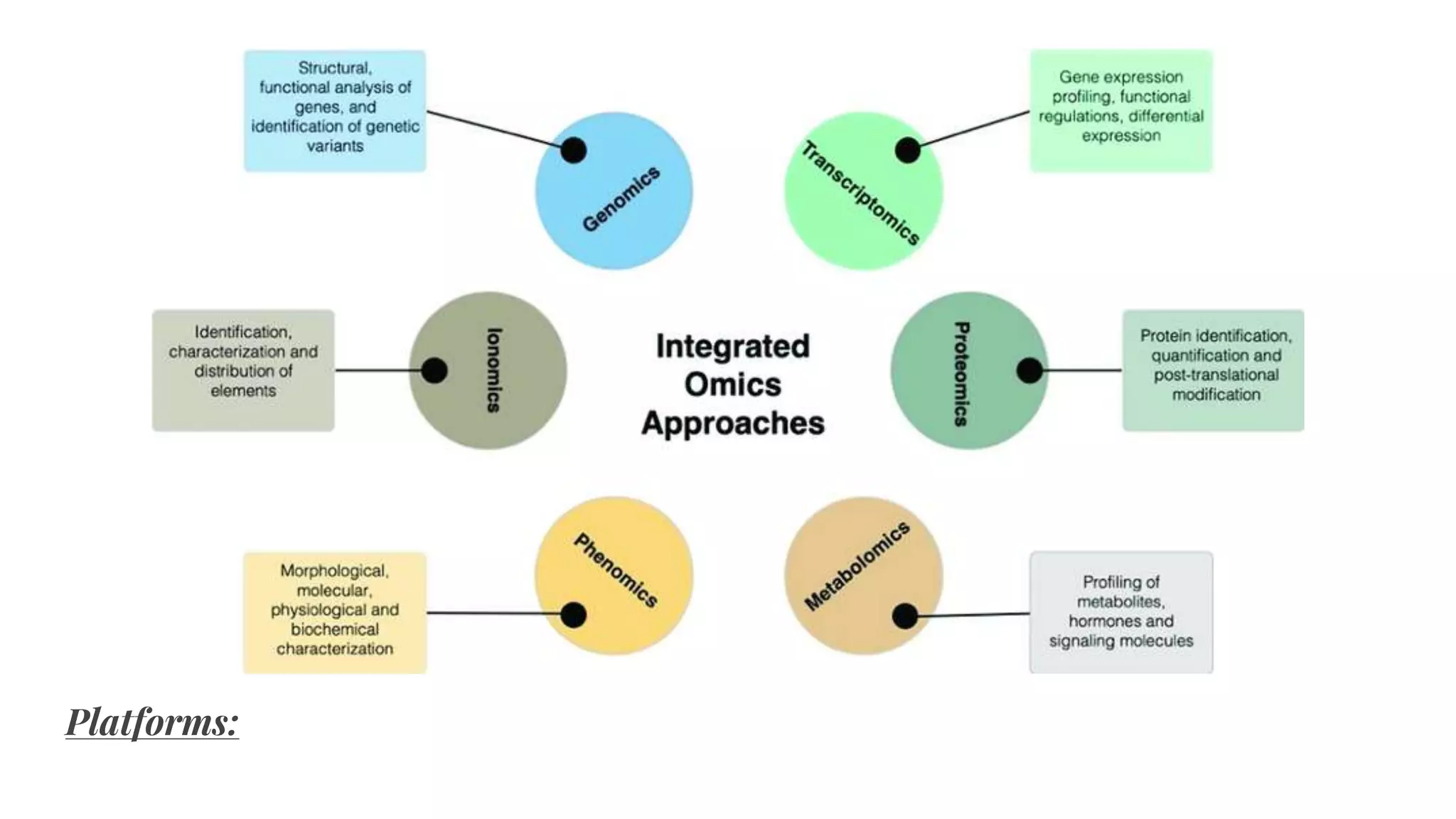
This document discusses various 'omics' fields that focus on large-scale data to understand life at a molecular level. It describes genomics, transcriptomics, proteomics, metabolomics, and phenomics. Transcriptomics studies the complete set of RNA transcripts produced by the genome, proteomics examines the complete set of proteins in a cell, and phenomics analyzes observable traits. The document explores how these omics fields can provide insights into plant development, crop breeding, gene expression, and protein interactions and modifications.