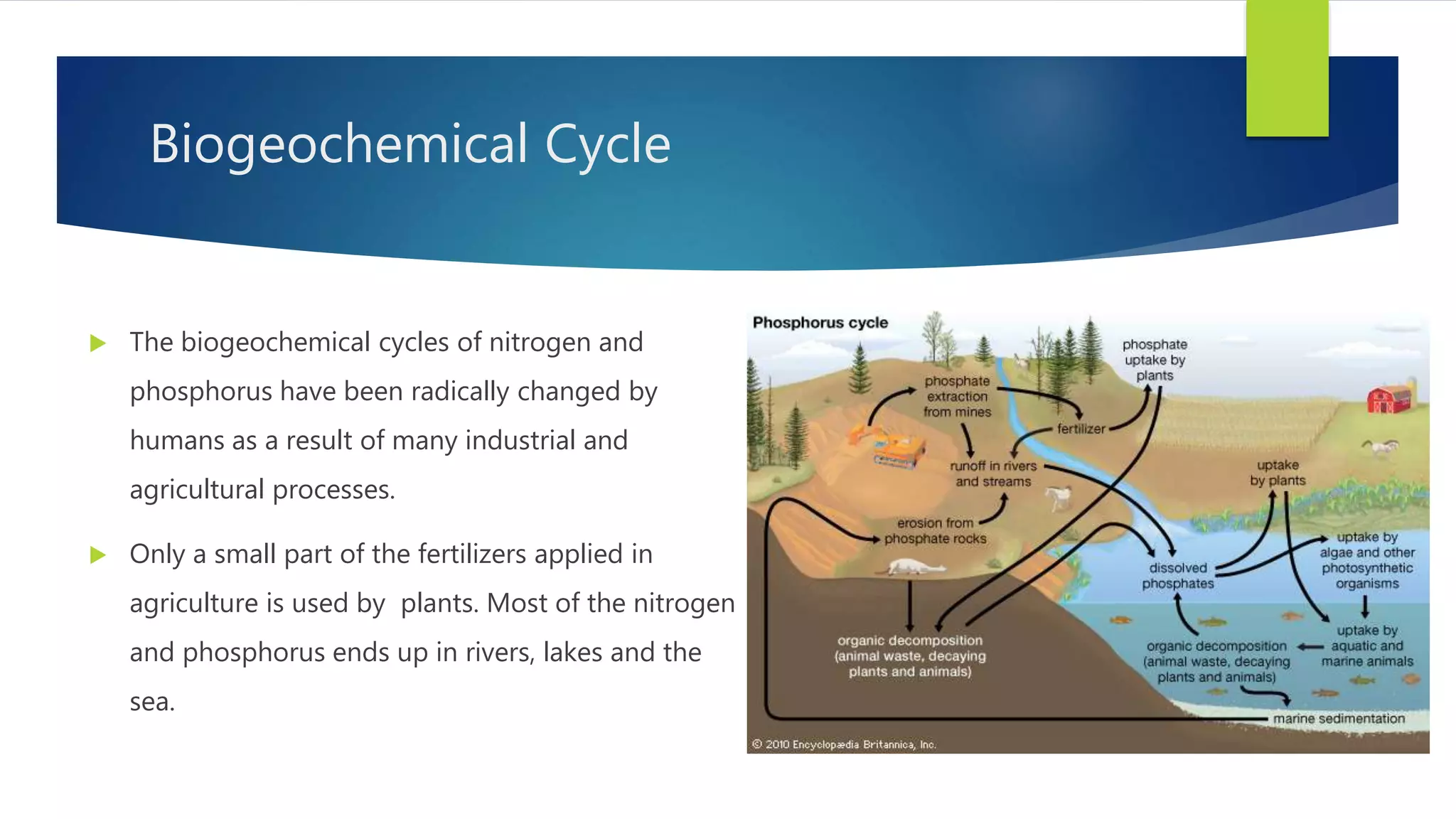
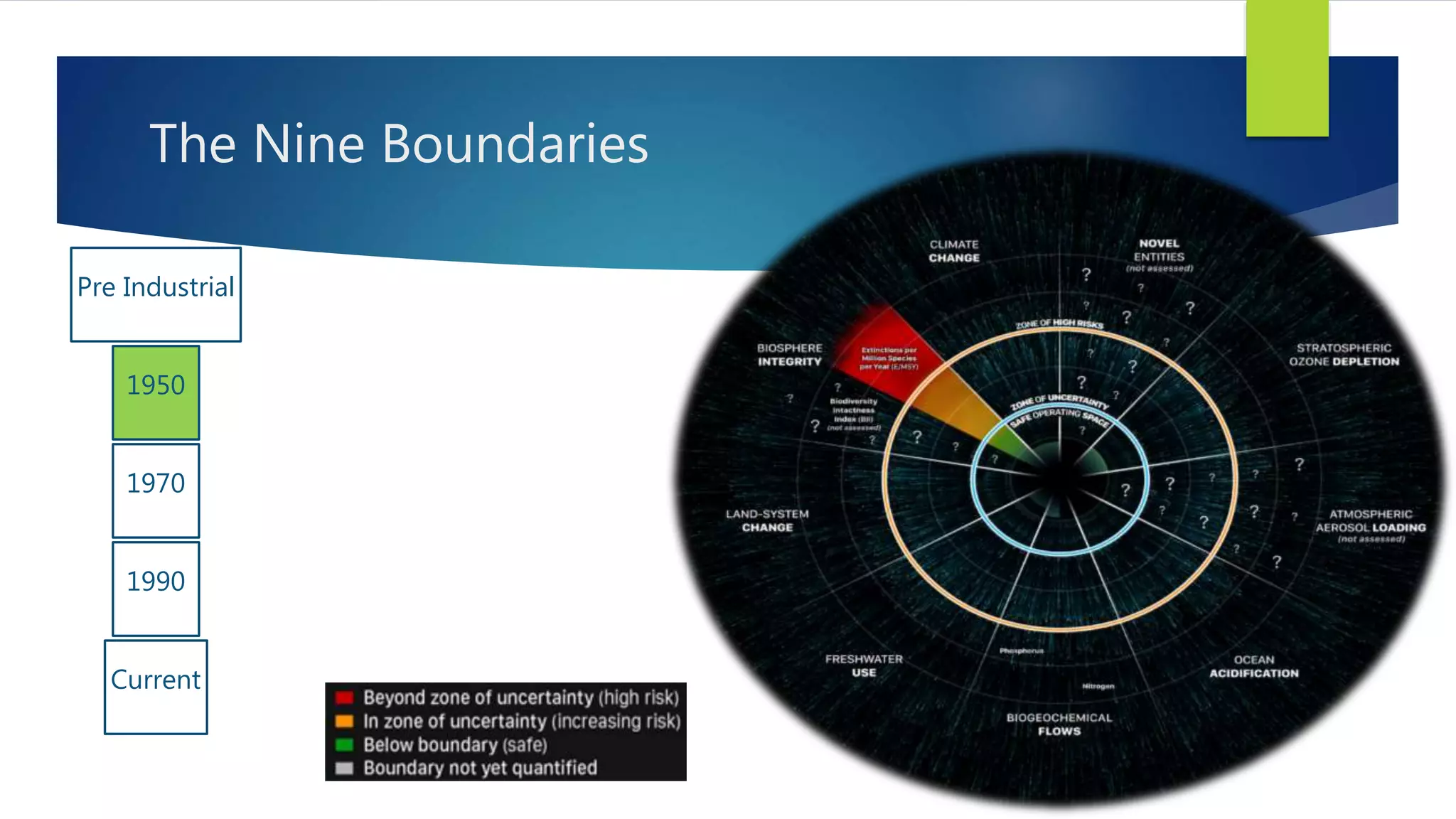
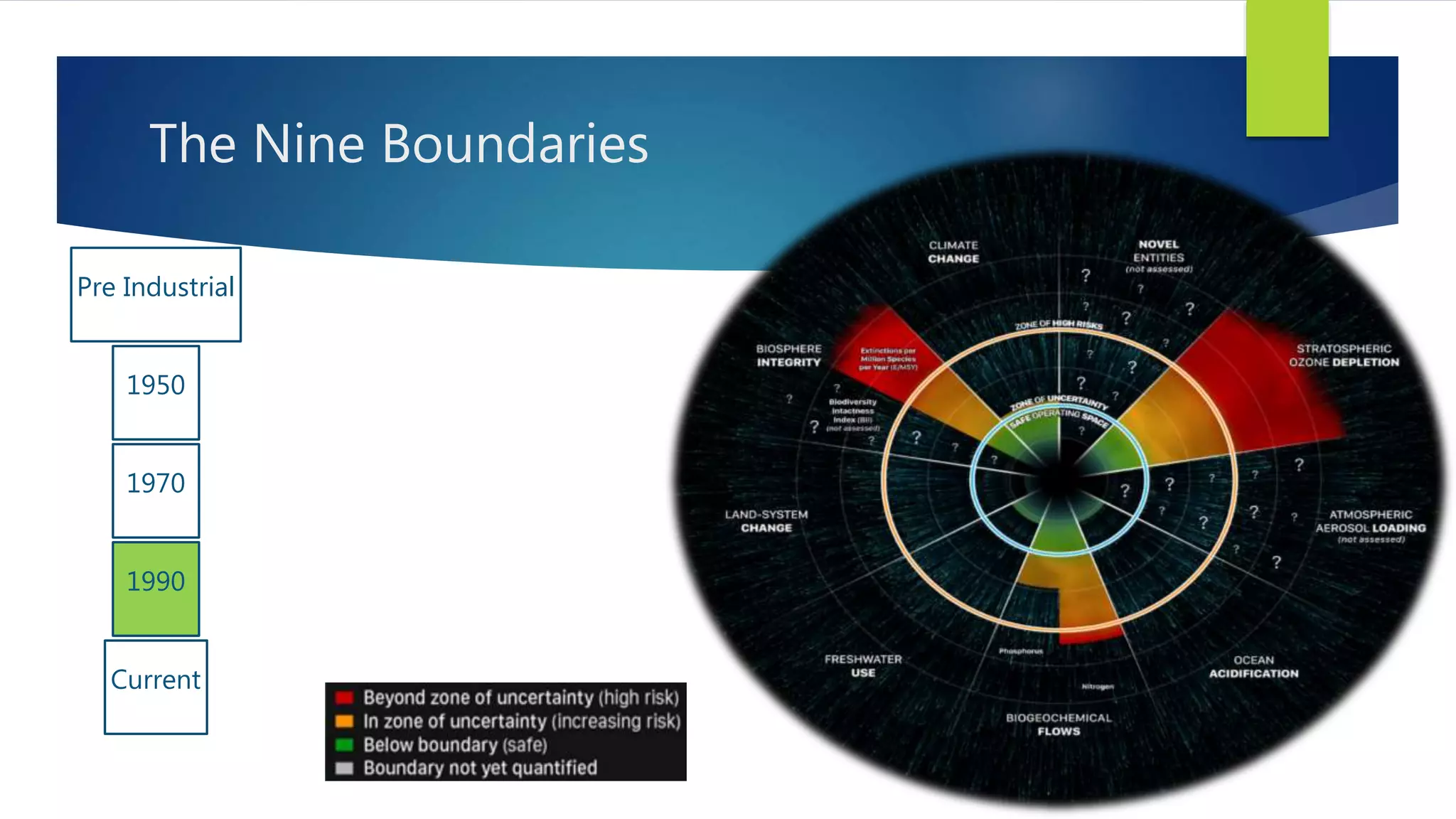
The document discusses planetary boundaries, which are nine Earth system processes identified as being critical for human survival. Exceeding the proposed boundaries for these processes risks severe environmental change. The boundaries discussed include climate change, ocean acidification, biodiversity loss, land use change, freshwater use, and biogeochemical flows of nitrogen and phosphorus. Crossing the proposed quantitative boundaries for some of these processes, like climate change and land use, risks triggering abrupt environmental shifts. The document argues that human activity has become the dominant driver of environmental change and that exceeding planetary boundaries endangers Earth's life support systems.