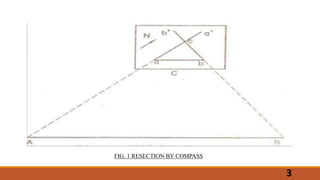
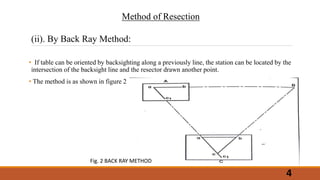
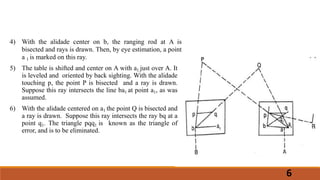
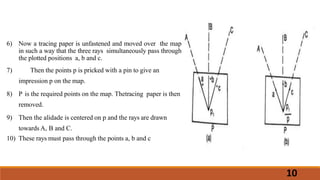
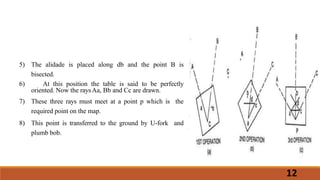
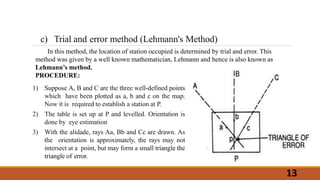
The document describes the methods of resection used in plane table surveying to determine the position of a station. It details four resection methods: by compass, back sighting, two-point problem, and three-point problem, each with specific procedures for accurately locating a new station based on known reference points. The text also covers mechanical, graphical, and trial-and-error techniques for solving the three-point problem, emphasizing the steps necessary for precision in surveying.