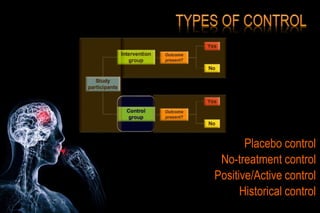
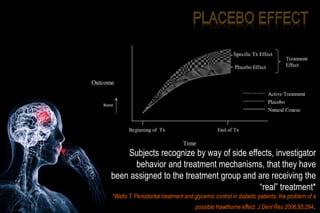
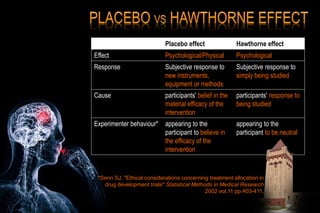
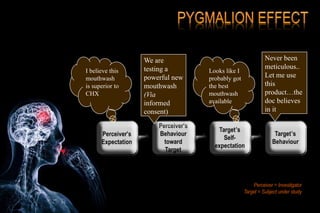
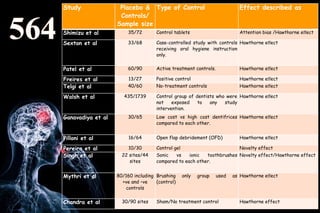
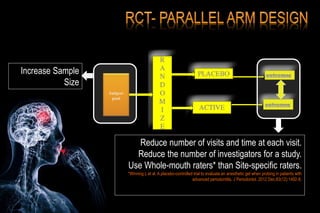
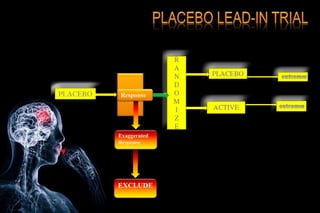
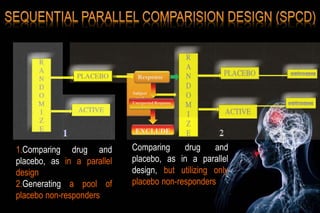
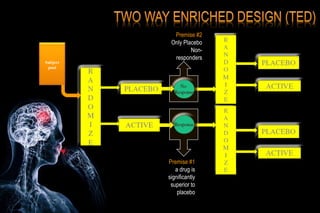
The document discusses the complexities surrounding the use of placebo in clinical trials, particularly focusing on effects like the placebo effect and Hawthorne effect. It reviews various studies that highlight the impact of subjects' perceptions and investigator behavior on treatment outcomes. Additionally, it addresses methodological considerations and the ethical implications of using placebo controls in research, especially in the context of periodontology.