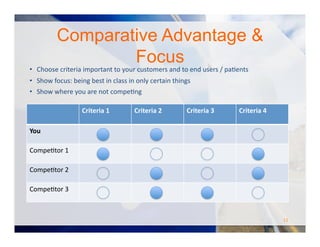
The document outlines guidelines for pitching a business plan, emphasizing the importance of presenting a compelling value proposition, understanding competitive advantages, and defining an effective market strategy. It provides a detailed structure for a pitch deck, including essential slides such as company overview, problem identification, product solution, market analysis, and financial projections. Additionally, it offers practical advice for engaging with investors and common pitfalls to avoid during presentations.