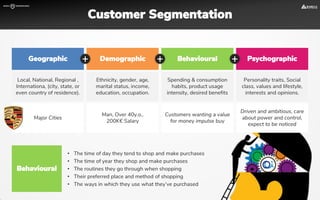
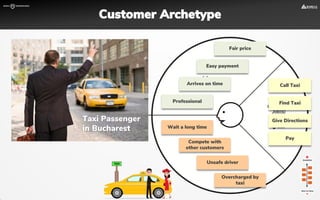
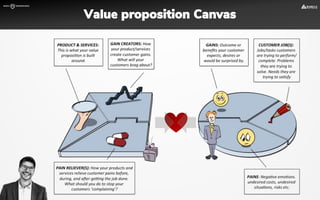
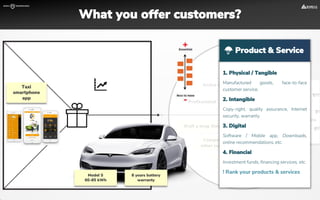
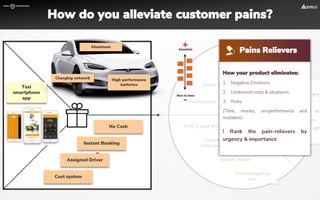
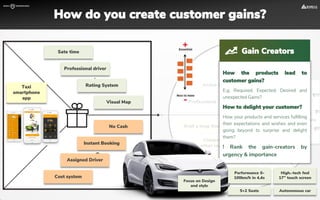
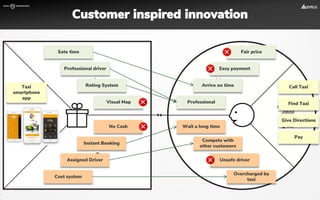
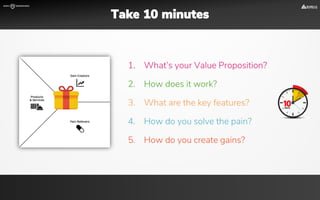
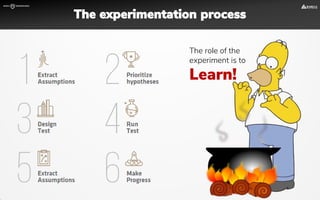
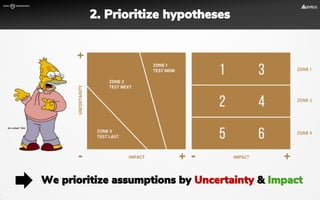
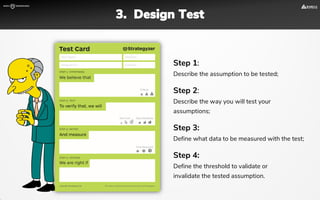
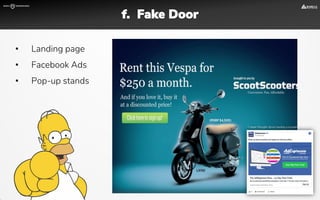
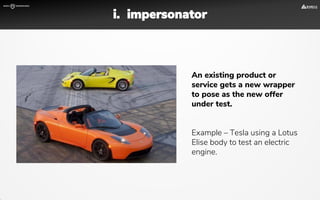
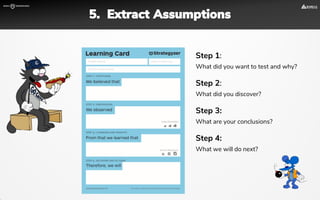
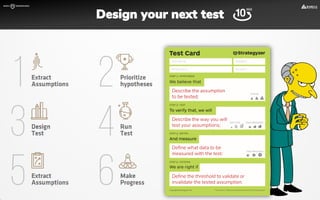
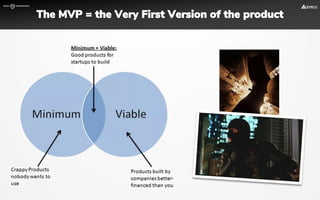
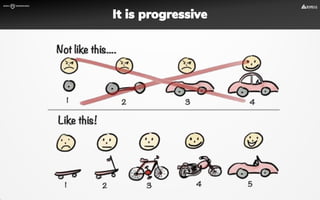
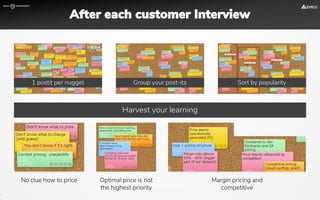
The document focuses on strategies for developing a value proposition in the context of intrapreneurship, emphasizing customer segmentation based on various demographic and behavioral factors. It outlines the importance of understanding customer pains and gains, and provides methodologies for validating business ideas through experiments and feedback. Additionally, it describes best practices for creating a minimum viable product (MVP) that meets customer needs while minimizing complexity and focusing on key functionalities.