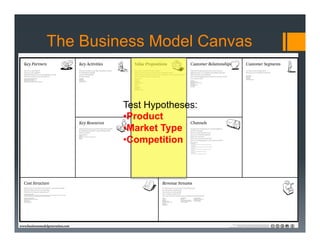
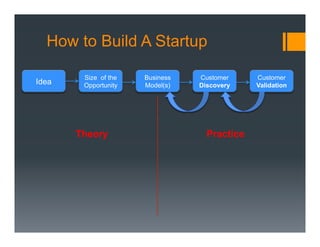
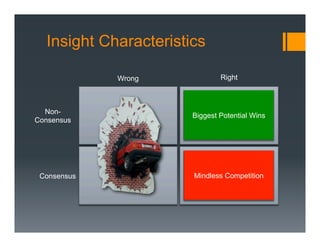
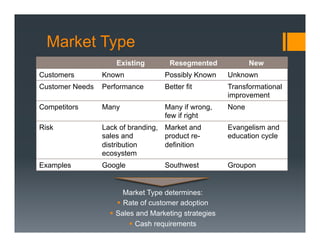
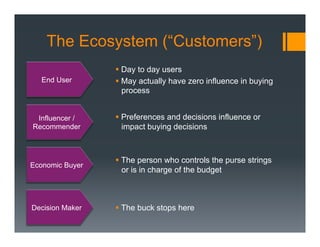
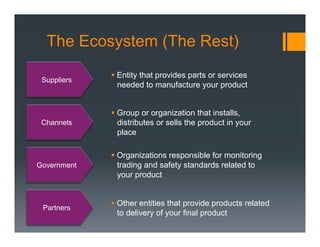
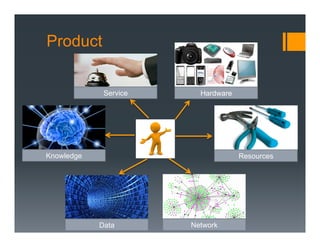
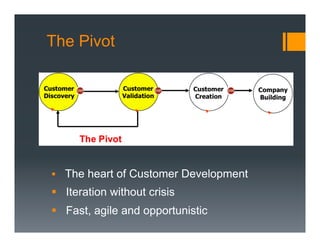
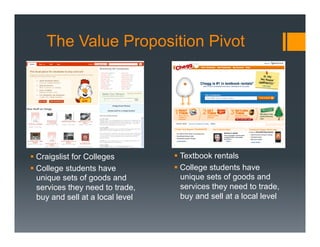
The document outlines a framework for developing a startup's value proposition through the Business Model Canvas, focusing on key questions regarding problem identification, market type, competition, and product offerings. It emphasizes the significance of understanding customer needs, market dynamics, and competitive landscape to validate hypotheses and create a Minimum Viable Product (MVP). Various testing methodologies, customer interactions, and potential pivots are also discussed to refine the business model and ensure product-market fit.