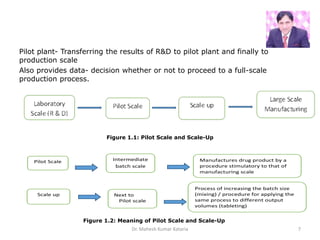
The document discusses pilot plant scale-up techniques in pharmaceutical manufacturing, emphasizing its role in transforming lab-scale formulas into viable products through process validation and production control. It outlines the significance of pilot plants for investigating product and process viability, generating data for full-scale production decisions, and training personnel. Additionally, it highlights the need for optimizing processes, ensuring quality, and complying with regulations in the transition from research and development to commercial production.