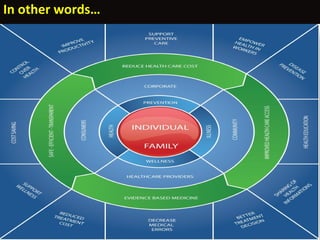
The document summarizes the P.I.E.R. project, which aimed to improve quality, productivity, and value of a mental health service experiencing staffing issues and low performance. The project formed a diverse focus group and developed an interactive, multilingual online health resource to promote early psychosis intervention, informed choice, empowerment, and community engagement. Milestones included reviewing evidence, developing consent forms and narratives/videos, and planning for dissemination. The goal was to improve access, outcomes, and cost efficiency through an inclusive, evidence-based, and collaborative approach.