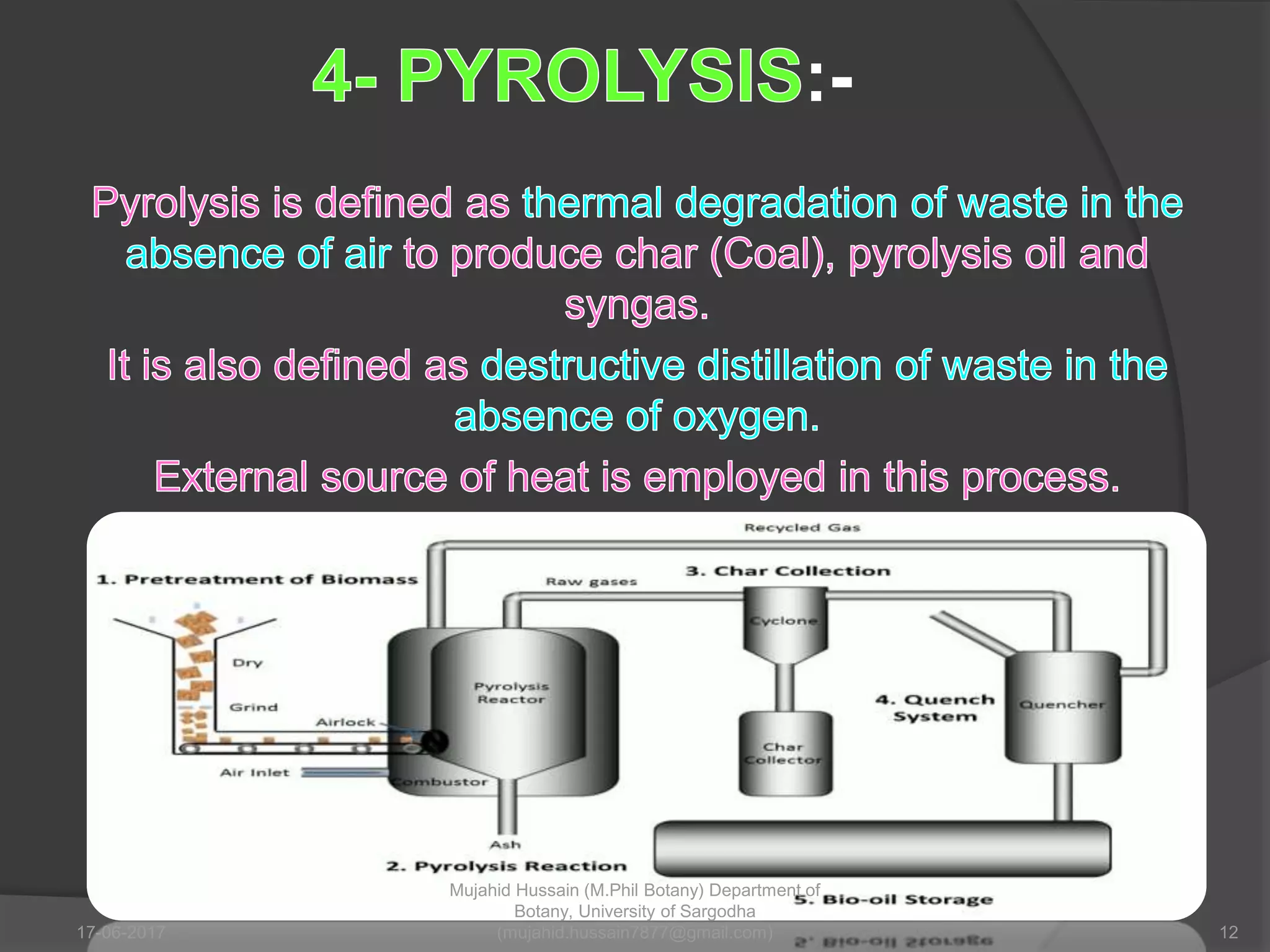
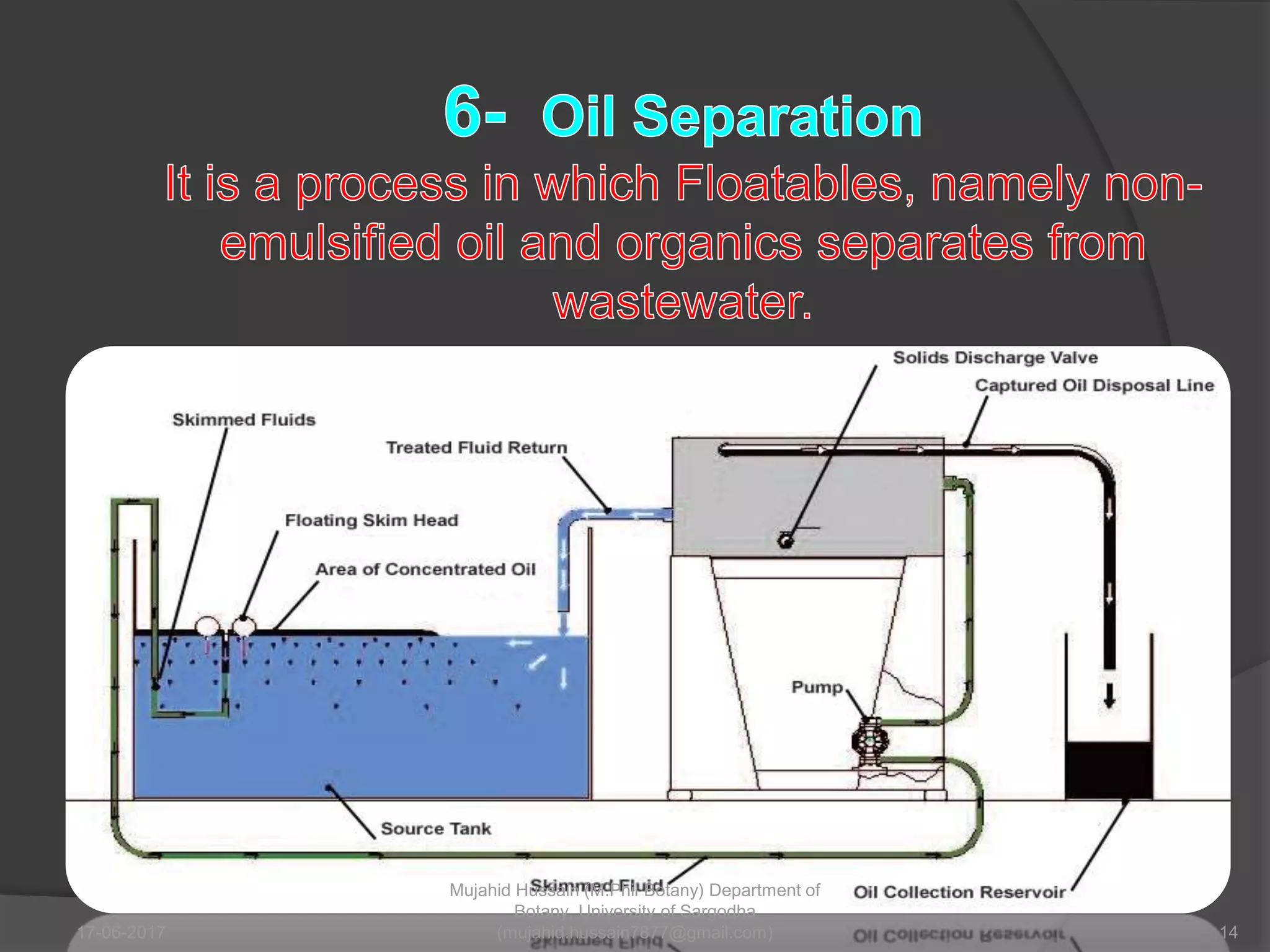
This document discusses various physical methods for waste disposal, including crushing, compaction, recovery, sedimentation, flotation, and landfilling. It notes that physical treatment processes are often simple and low-cost, and the choice of method depends on the physical form and characteristics of the waste. Specific processes like crushing, compaction, and recovery are used to break up, compress, and separate recyclable materials from waste.