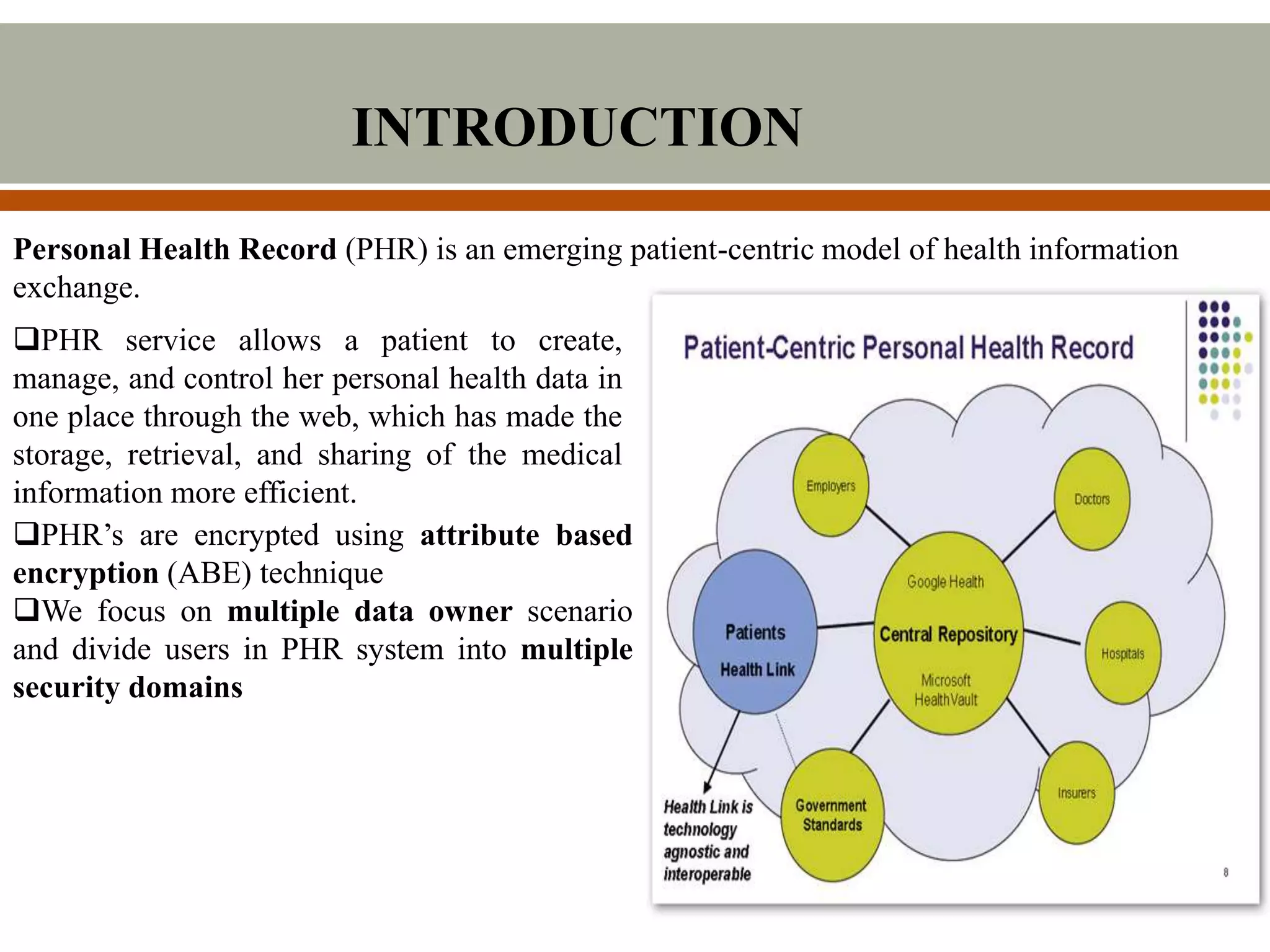
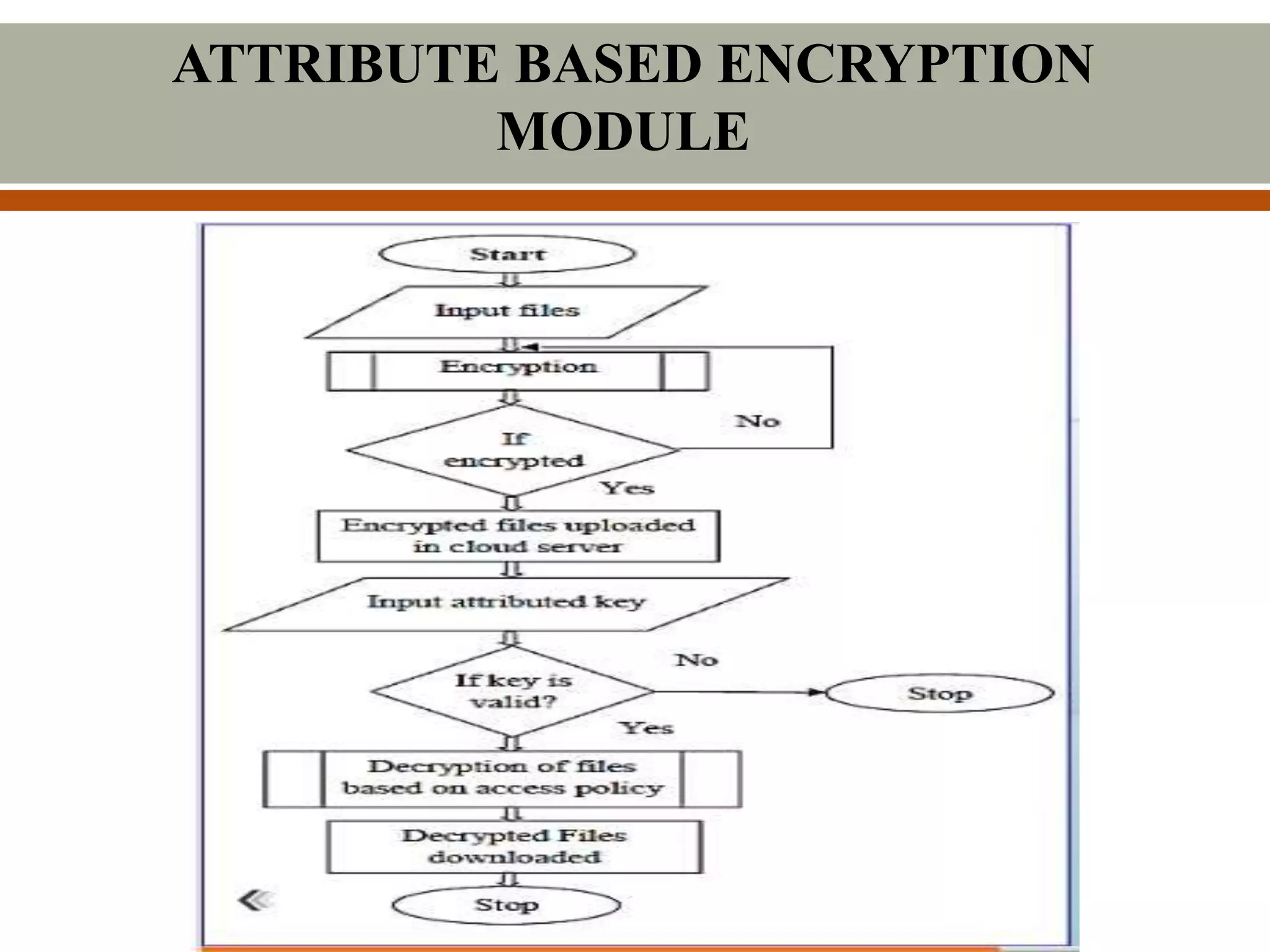
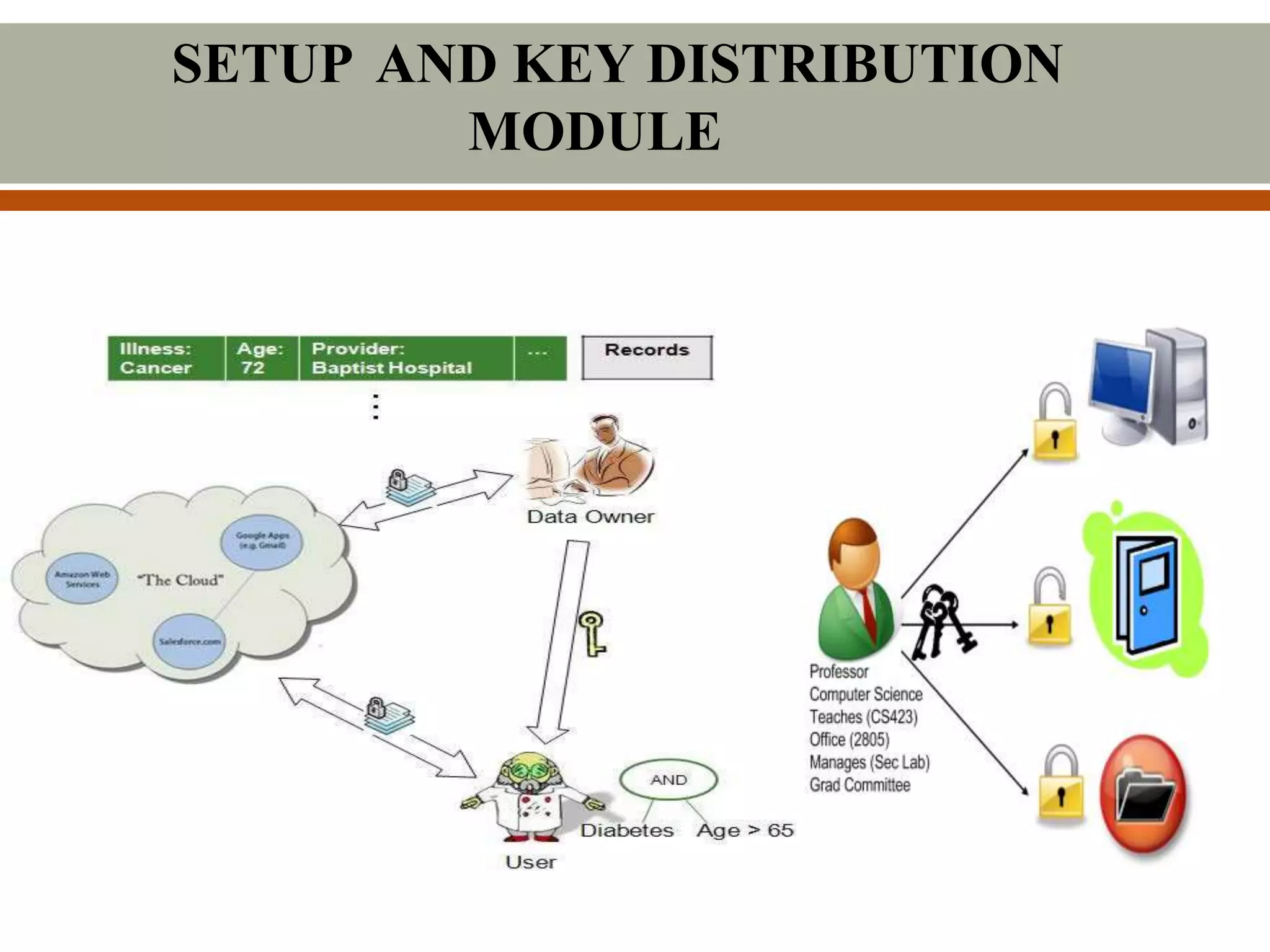
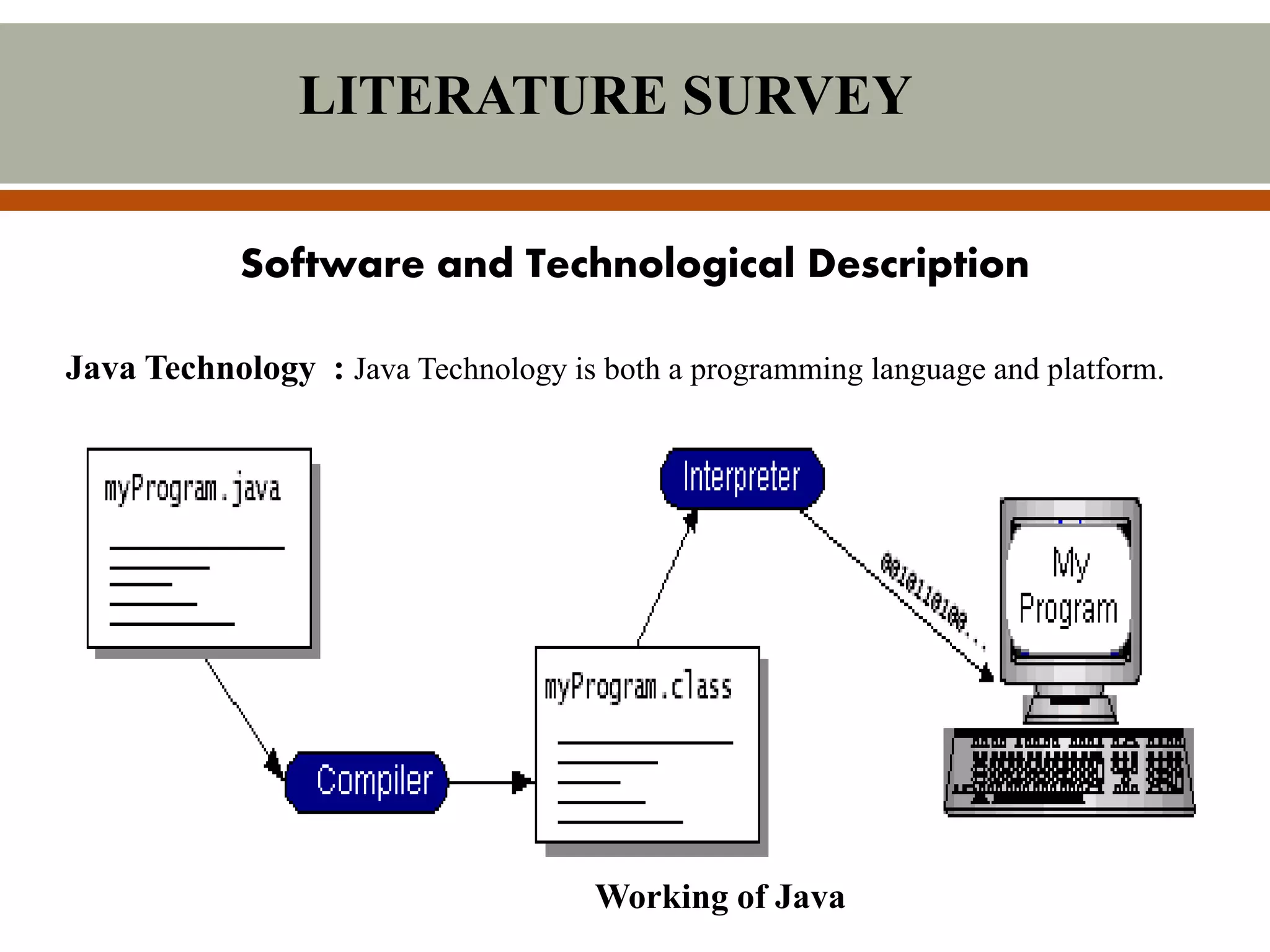
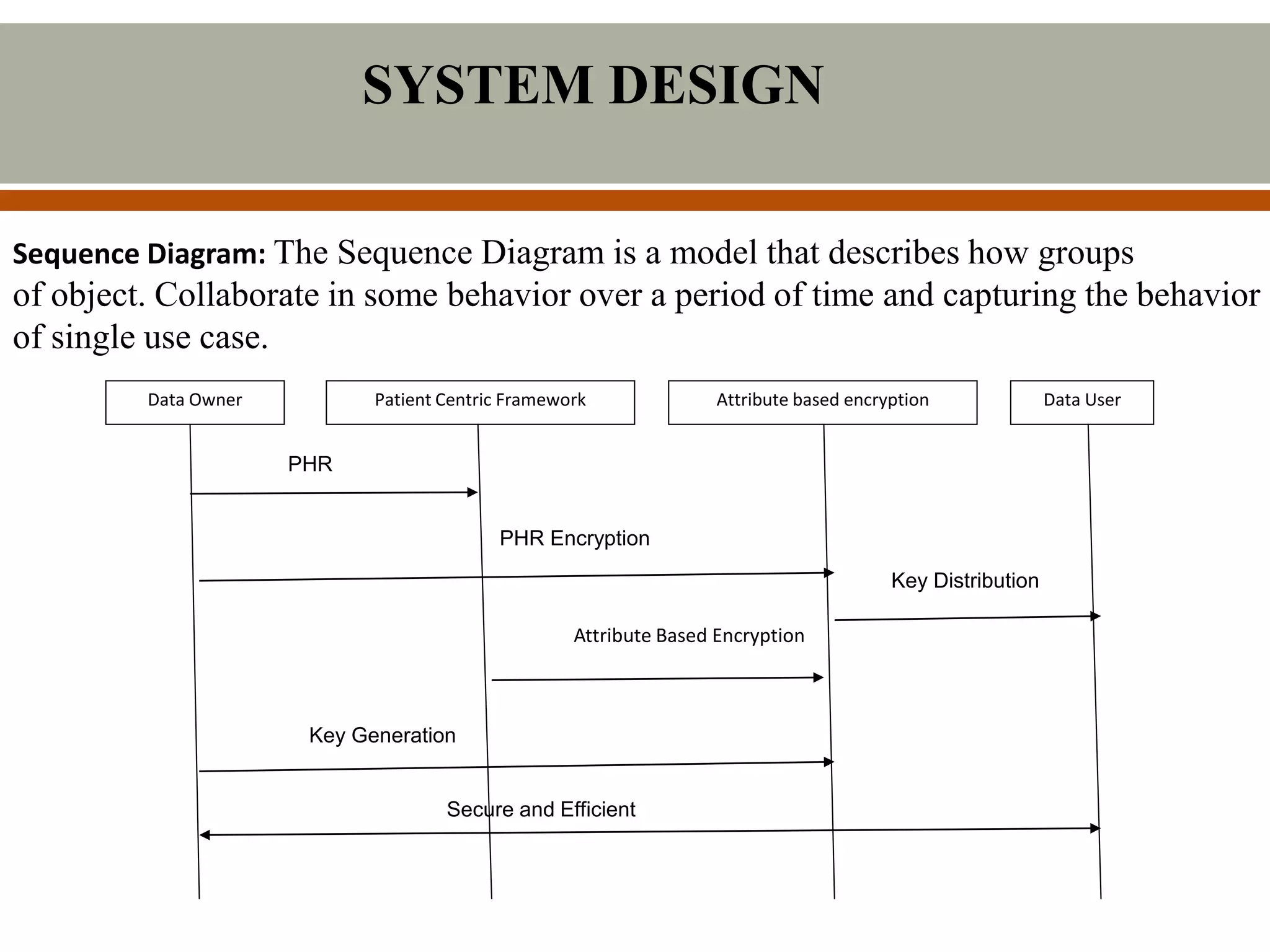
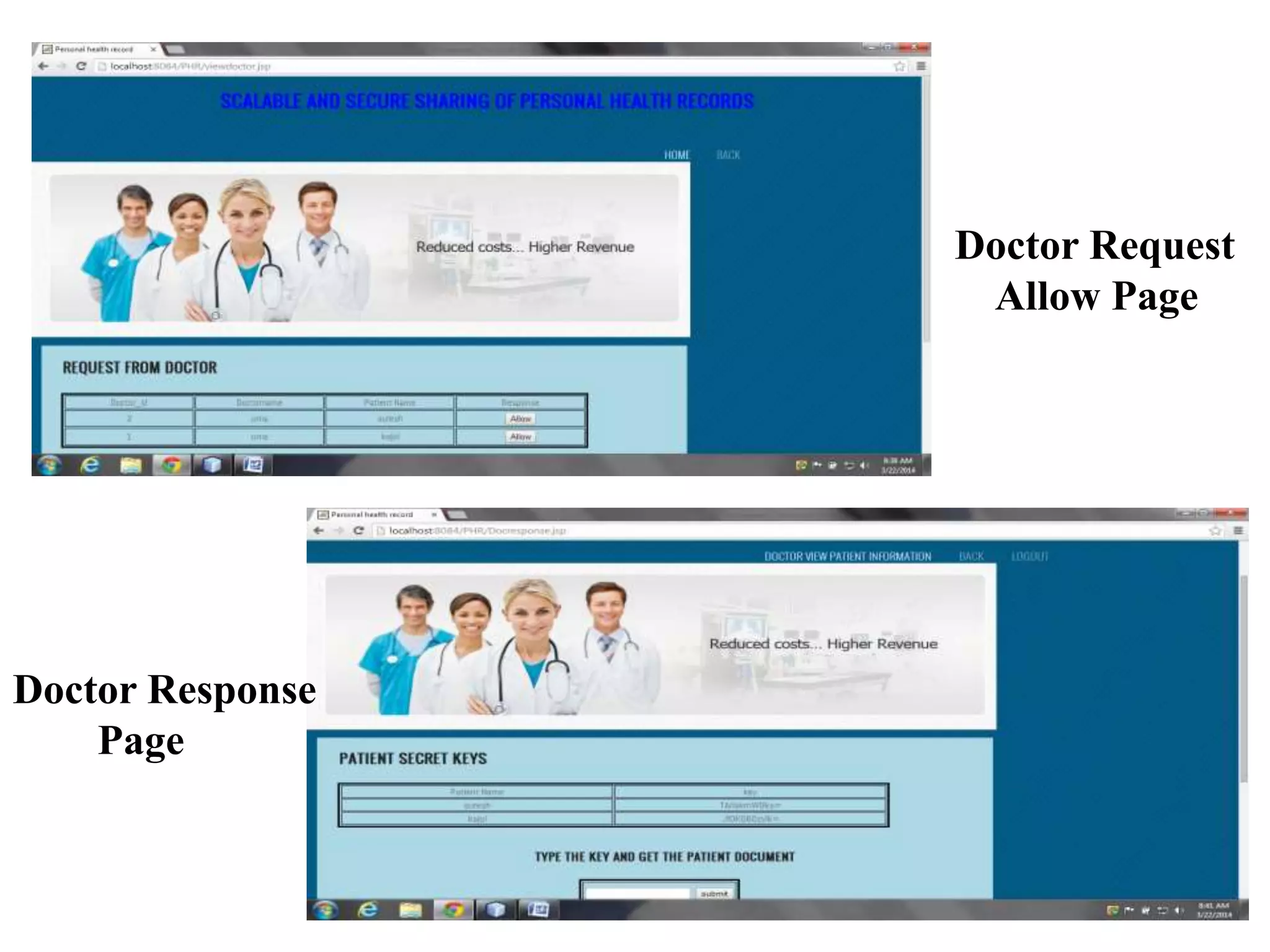
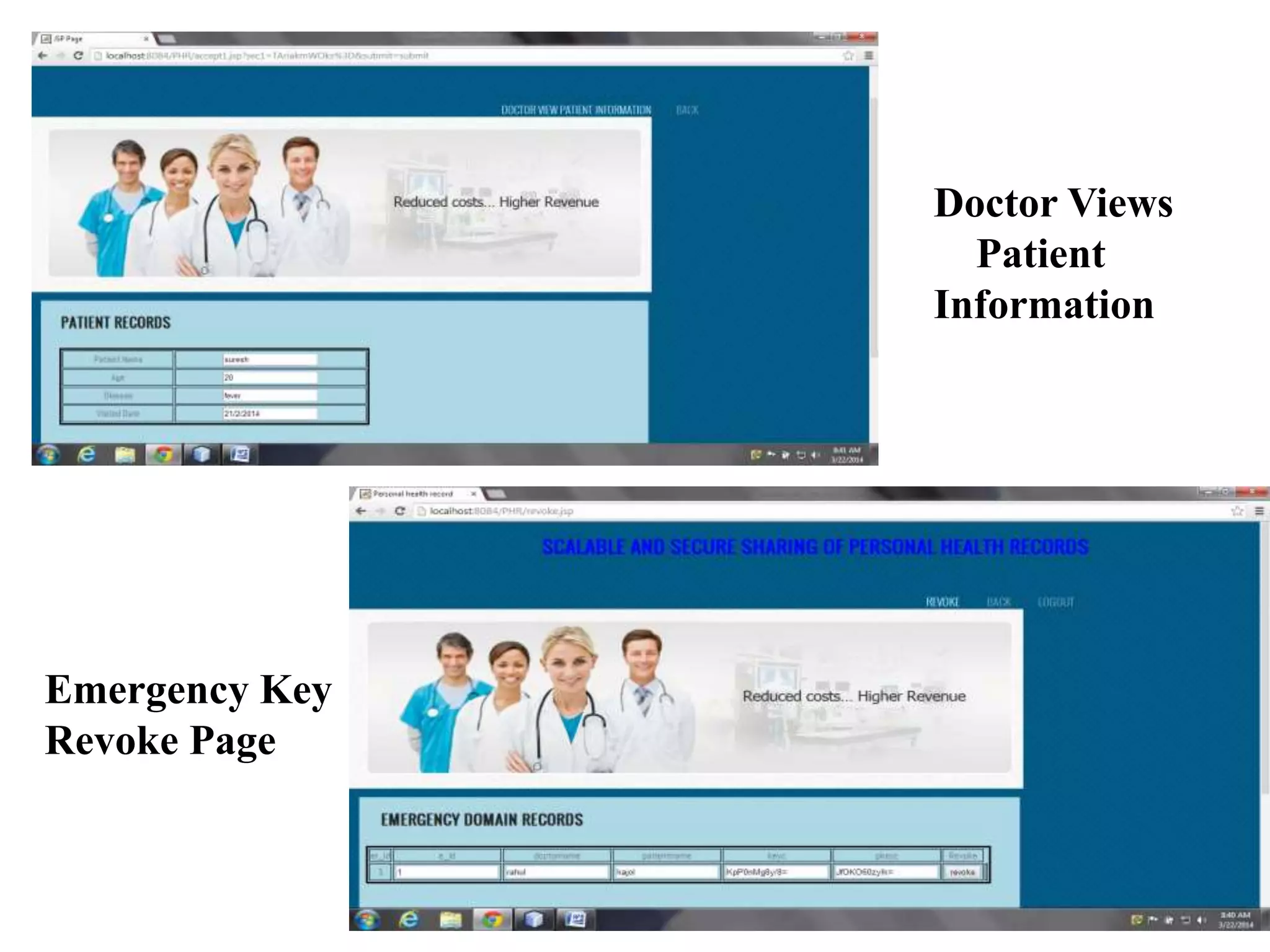
This document describes a proposed system for scalable and secure sharing of personal health records in cloud computing using attribute-based encryption. The system aims to address security issues with existing personal health record systems, such as privacy risks, scalability of key management, access control and user revocation. The proposed system uses attribute-based encryption to encrypt personal health records and a novel patient-centric framework with access control mechanisms. It allows for multiple data owners, dynamic access policies, and on-demand revocation of user access. The system is intended to be scalable, secure and efficient while ensuring patient control over personal health information.

















![REFERENCES
[1] “The health insurance portability and accountability act.” [Online]. Available:
http://www.cms.hhs.gov/HIPAAGenInfo/01 Overview.asp
[2] “Google, Microsoft say hip a a stimulus rule doesn’t apply to them,”
http://www.ihealthbeat.org/Articles/2009/4/8/.
[3] V. Goyal, O. Pandey, A. Sahai, and B. Waters, “Attribute-based encryption for fine-grained access control
of encrypted data,” in CCS ’06, 2006, pp. 89–98.
[4] J. Benaloh, M. Chase, E. Horvitz, and K. Lauter, “Patient controlled encryption: ensuring privacy of
electronic medical records,” in CCSW ’09, 2009, pp. 103–114.
[5] S. Muller, S. Katzenbeisser, and C. Eckert, “Distributed attribute based encryption,” Information Security
and Cryptology–ICISC 2008, pp. 20–36, 2009.
[6] Y. Zheng, “Key-policy attribute-based encryption scheme implementation,”
http://www.cnsr.ictas.vt.edu/resources.html.
[7] WWW.W3SCHOOLS.COM.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/efc75276-c116-464c-be81-de16d6a60f26-160401055031/75/phr-26-2048.jpg)
